Perfect Competition And Supply And Demand
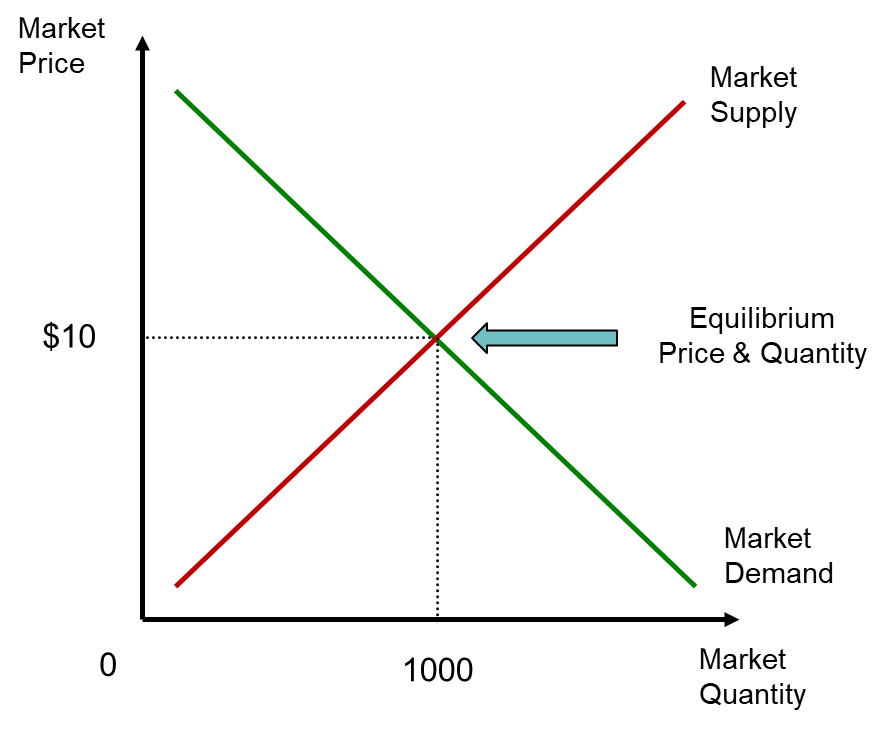
Perfect Competition And Supply And Demand Vrogue Co In a market characterized by perfect competition, price is determined through the mechanisms of supply and demand. prices are influenced both by the supply of products from sellers and by the demand for products by buyers. to illustrate this concept, let’s create a supply and demand schedule for one particular good sold at one point in time. Perfect competition is a market structure in which the following five criteria are met: 1) all firms sell an identical product; 2) all firms are price takers they cannot control the market price.
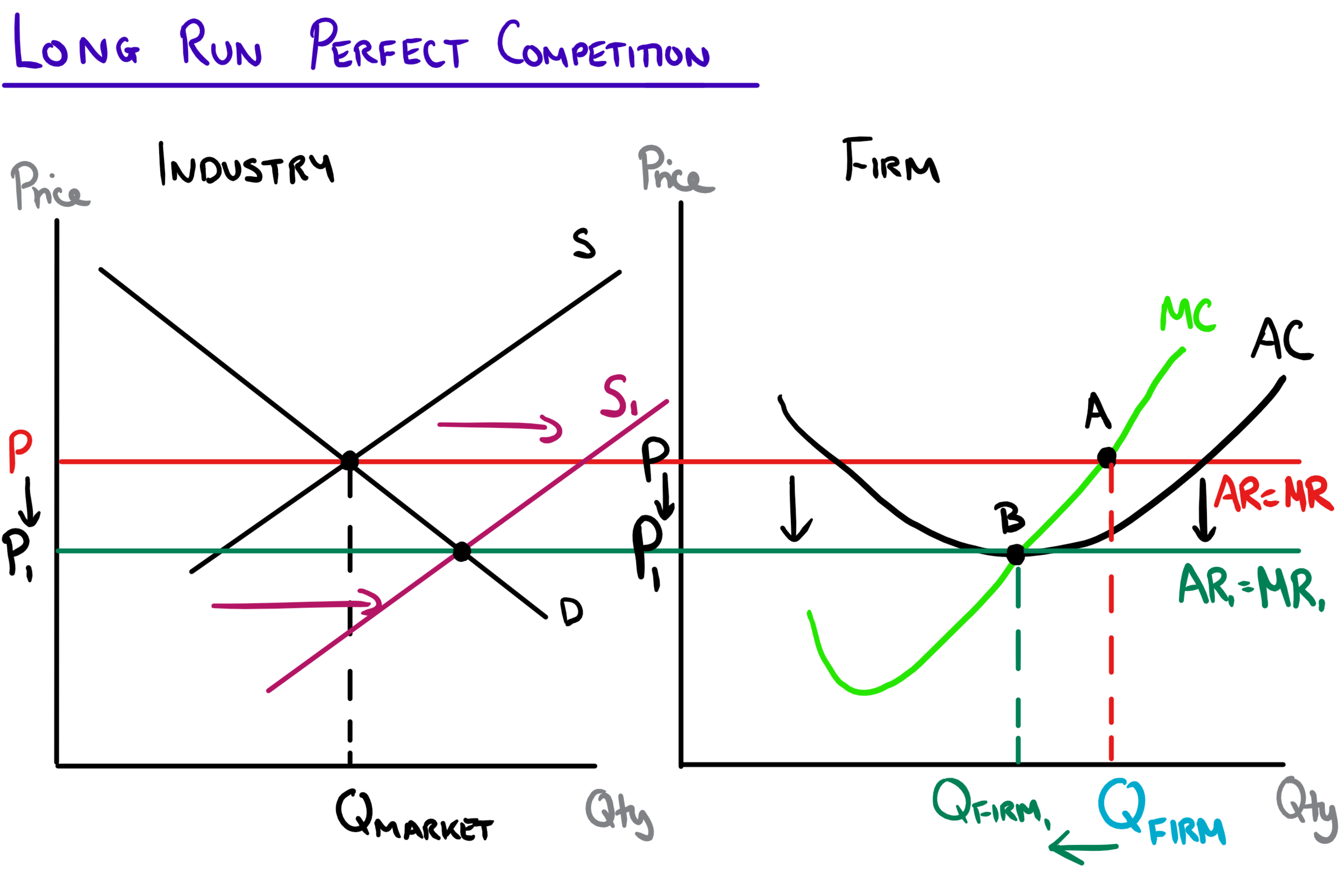
Perfect Competition The Theory And Why It Matters Outlier Perfect competition in the long run: in the long run, economic profit cannot be sustained. the arrival of new firms in the market causes the demand curve of each individual firm to shift downward, bringing down the price, the average revenue and marginal revenue curve. in the long run, the firm will make zero economic profit. The central characteristic of the model of perfect competition is the fact that price is determined by the interaction of demand and supply; buyers and sellers are price takers. the model assumes: a large number of firms producing identical (homogeneous) goods or services, a large number of buyers and sellers, easy entry and exit in the. The four main takeaways of the model are the following: 1. in perfect competition, equilibrium occurs at the intersection of supply and demand. equilibrium, in economics, refers to the outcome that quantities in the model gravitate towards. in perfect competition, equilibrium occurs at the point where supply equals demand. Key points. a perfectly competitive firm is a price taker, which means that it must accept the equilibrium price at which it sells goods. if a perfectly competitive firm attempts to charge even a tiny amount more than the market price, it will be unable to make any sales. perfect competition occurs when there are many sellers, there is easy.
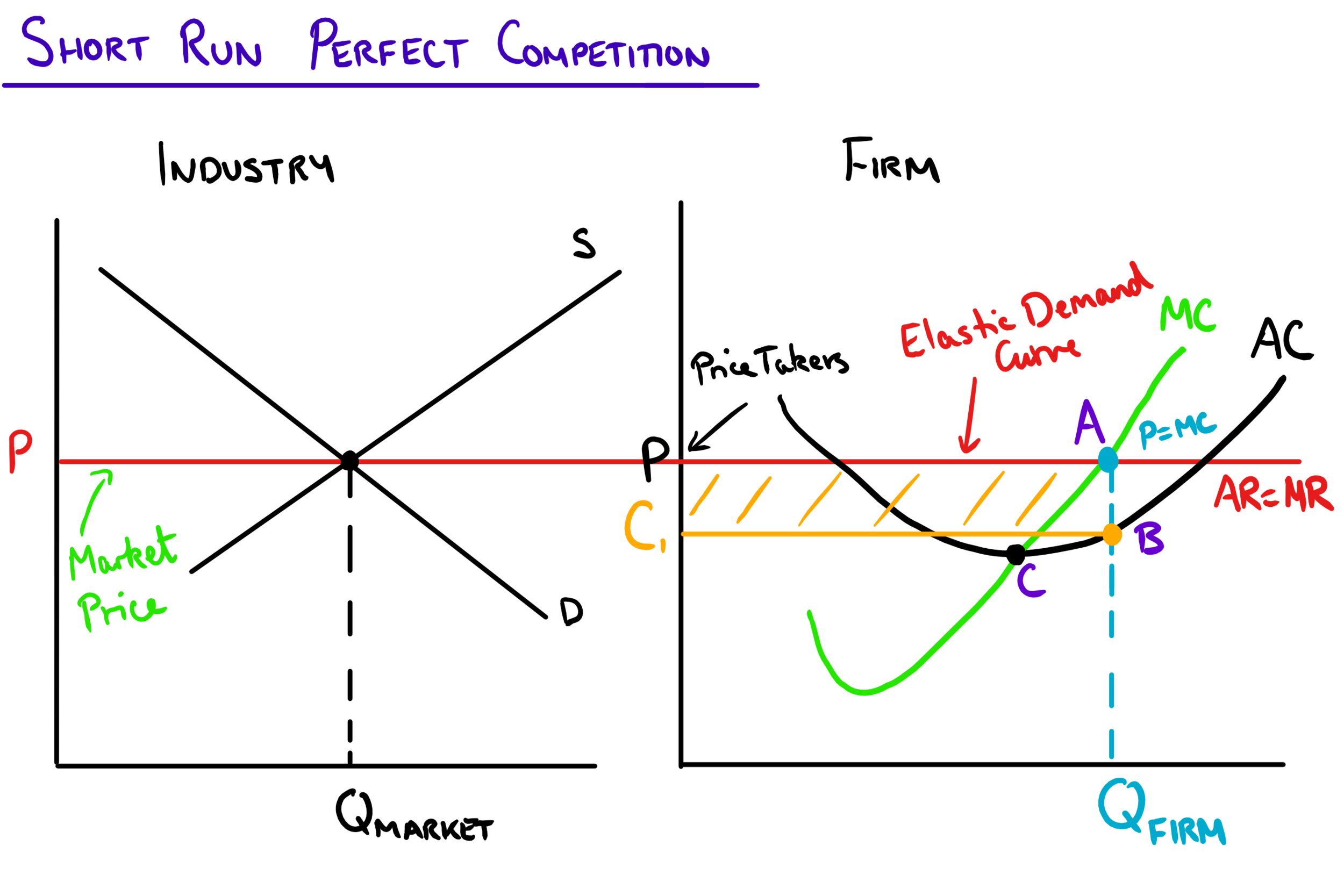
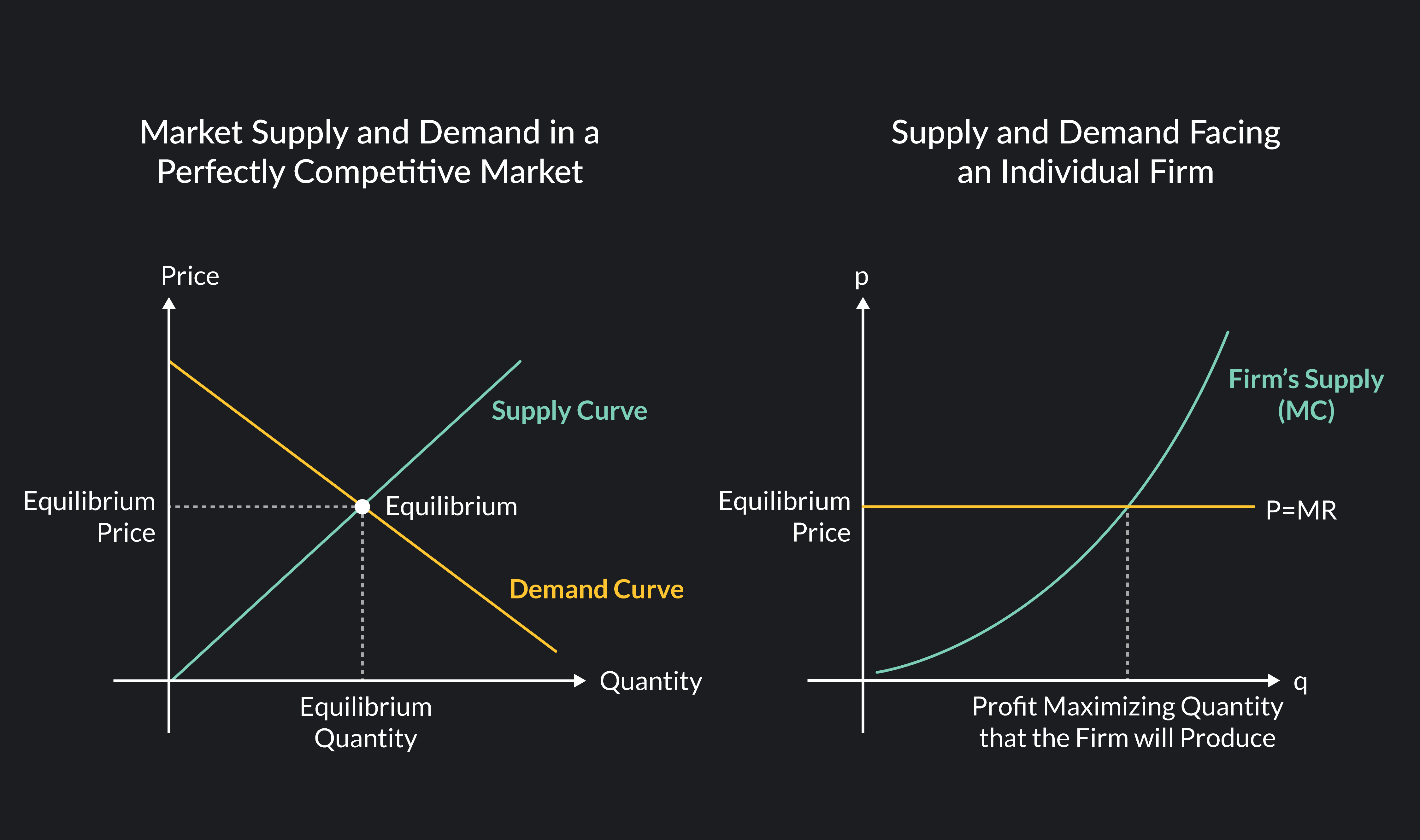
Perfect Competition And Supply And Demand Vrogue Co The four main takeaways of the model are the following: 1. in perfect competition, equilibrium occurs at the intersection of supply and demand. equilibrium, in economics, refers to the outcome that quantities in the model gravitate towards. in perfect competition, equilibrium occurs at the point where supply equals demand. Key points. a perfectly competitive firm is a price taker, which means that it must accept the equilibrium price at which it sells goods. if a perfectly competitive firm attempts to charge even a tiny amount more than the market price, it will be unable to make any sales. perfect competition occurs when there are many sellers, there is easy. All firms are price takers, therefore the firm’s demand curve is perfectly elastic. there is perfect information and knowledge. diagram for perfect competition. the industry price is determined by the interaction of supply and demand, leading to a price of pe. the individual firm will maximise output where mr = mc at q1. V. t. e. in economics, specifically general equilibrium theory, a perfect market, also known as an atomistic market, is defined by several idealizing conditions, collectively called perfect competition, or atomistic competition. in theoretical models where conditions of perfect competition hold, it has been demonstrated that a market will reach.
Graph Of Perfect Competition All firms are price takers, therefore the firm’s demand curve is perfectly elastic. there is perfect information and knowledge. diagram for perfect competition. the industry price is determined by the interaction of supply and demand, leading to a price of pe. the individual firm will maximise output where mr = mc at q1. V. t. e. in economics, specifically general equilibrium theory, a perfect market, also known as an atomistic market, is defined by several idealizing conditions, collectively called perfect competition, or atomistic competition. in theoretical models where conditions of perfect competition hold, it has been demonstrated that a market will reach.

Perfect Competition Definition And Characteristics вђ Tutor S Tips

Comments are closed.