Periodic Table Of Elements Transition Metals
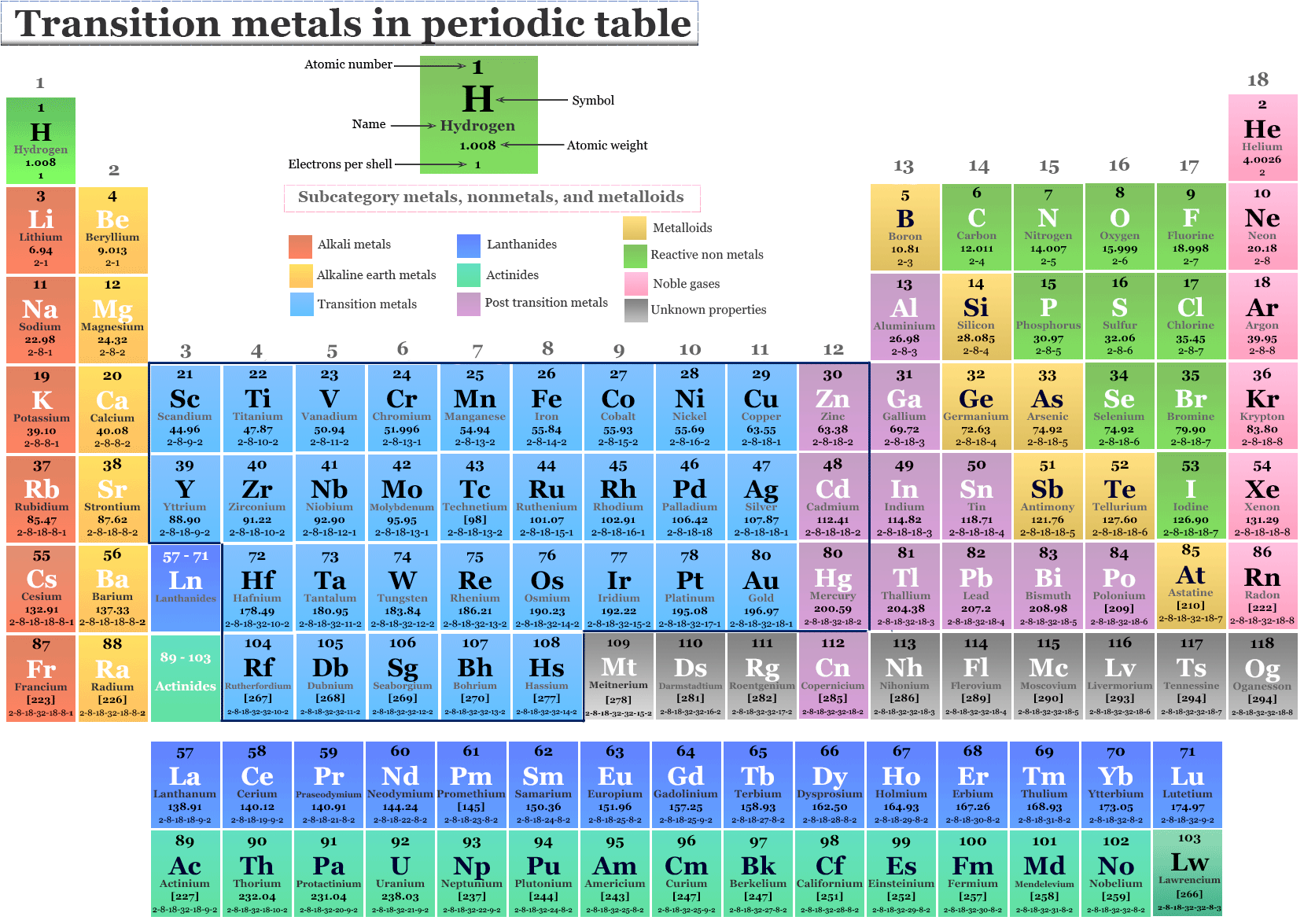
Transition Metals Elements Definition List Properties Most transition metals are grayish or white (like iron or silver), but gold and copper have colors not seen in any other element on the periodic table. the transition metals, as a group, have high melting points. the exception is mercury, which is a liquid at room temperature. by extension, these elements also have high boiling points. Transition metal, any of various chemical elements that have valence electrons—i.e., electrons that can participate in the formation of chemical bonds—in two shells instead of only one. they occupy the middle portions of the long periods of the periodic table of the elements.

Transition Metal Definition Properties Elements Facts Britannica The transition metals are the largest group of elements on the periodic table. they got their name because english chemist charles bury described a transition series of elements in 1921. bury examined the transition from an inner electron layer with 8 electrons to a layer with 18 electrons and from a layer of 18 electrons to one with 32. In chemistry, a transition metal (or transition element) is a chemical element in the d block of the periodic table (groups 3 to 12), though the elements of group 12 (and less often group 3) are sometimes excluded. the lanthanide and actinide elements (the f block) are called inner transition metals and are sometimes considered to be transition. Figure \(\pageindex{2}\): the transition metals are located in groups 3–11 of the periodic table. the inner transition metals are in the two rows below the body of the table. the f block elements are the elements ce through lu, which constitute the lanthanide series (or lanthanoid series ), and the elements th through lr, which constitute the actinide series (or actinoid series ). Actinium, ac, is the first member of the fourth transition series, which also includes rf through rg. figure 19.1.2 19.1. 2: the transition metals are located in groups 3–11 of the periodic table. the inner transition metals are in the two rows below the body of the table.

The Transition Metals Youtube Figure \(\pageindex{2}\): the transition metals are located in groups 3–11 of the periodic table. the inner transition metals are in the two rows below the body of the table. the f block elements are the elements ce through lu, which constitute the lanthanide series (or lanthanoid series ), and the elements th through lr, which constitute the actinide series (or actinoid series ). Actinium, ac, is the first member of the fourth transition series, which also includes rf through rg. figure 19.1.2 19.1. 2: the transition metals are located in groups 3–11 of the periodic table. the inner transition metals are in the two rows below the body of the table. According to the iupac, a transition metal is any element with a partially filled d electron sub shell. this describes groups 3 through 12 on the periodic table, although the f block elements (lanthanides and actinides, below the main body of the periodic table) are also transition metals. the d block elements are called transition metals. Transition elements are the elements that are found in groups 3 12 (old groups iia iib) on the periodic table (salmon colored block in the middle of the table). the term refers to the fact that the \(d\) sublevel , which is in the process of being filled, is in a lower principal energy level than the \(s\) sublevel filled before it.

Comments are closed.