Peripheral Artery Disease Amputation Vascular Peripheral Vasc

Peripheral Arterial Disease Prevention Sanara Medtech Amputation remains a frequent and feared outcome in patients with peripheral artery disease (pad). although typically characterized as major or minor on the extent of tissue loss, the etiologies and outcomes after amputation by extent are not well understood. in addition, emerging data suggest that the drivers and outcomes of amputation in patients with pad may differ in those with and without. Background. lower extremity peripheral artery disease (le pad) is a prevalent condition in the us, affecting approximately 8 million americans. 1, 2 although about 50% of patients with pad are asymptomatic (rutherford classification 0; table 1), they are at an increased risk of mortality, myocardial infarction (mi), and stroke. 3 – 6 the most frequent clinical manifestation of pad is.

Peripheral Artery Disease вђ A Common And Costly Vascular Issue It is estimated that >2 million patients are living with an amputation in the united states. peripheral artery disease (pad) and diabetes mellitus account for the majority of nontraumatic amputations. the standard measurement to diagnose pad is the ankle brachial index, which integrates all occlusive disease in the limb to create a summary value of limb artery occlusive disease. despite its. Lower extremity peripheral artery disease (pad) affects 12% to 20% of americans 60 years and older. the most significant risk factors for pad are hyperlipidemia, hypertension, diabetes mellitus. Peripheral artery disease (pad) is the development of chronic arterial occlusive disease of the lower extremities due to atherosclerosis. 1 pad is associated with atherosclerosis of other vascular beds, and the presence of diabetes mellitus is known to both increase the incidence of pad, as well as accelerate disease progression and worsen disease severity. 2 given this, patients with. Peripheral artery disease (pad) stems from atherosclerosis of lower extremity arteries with resultant arterial narrowing or occlusion. the most severe form of pad is termed chronic limb threatening ischemia and carries a significant risk of limb loss and cardiovascular mortality. diabetes mellitus i ….
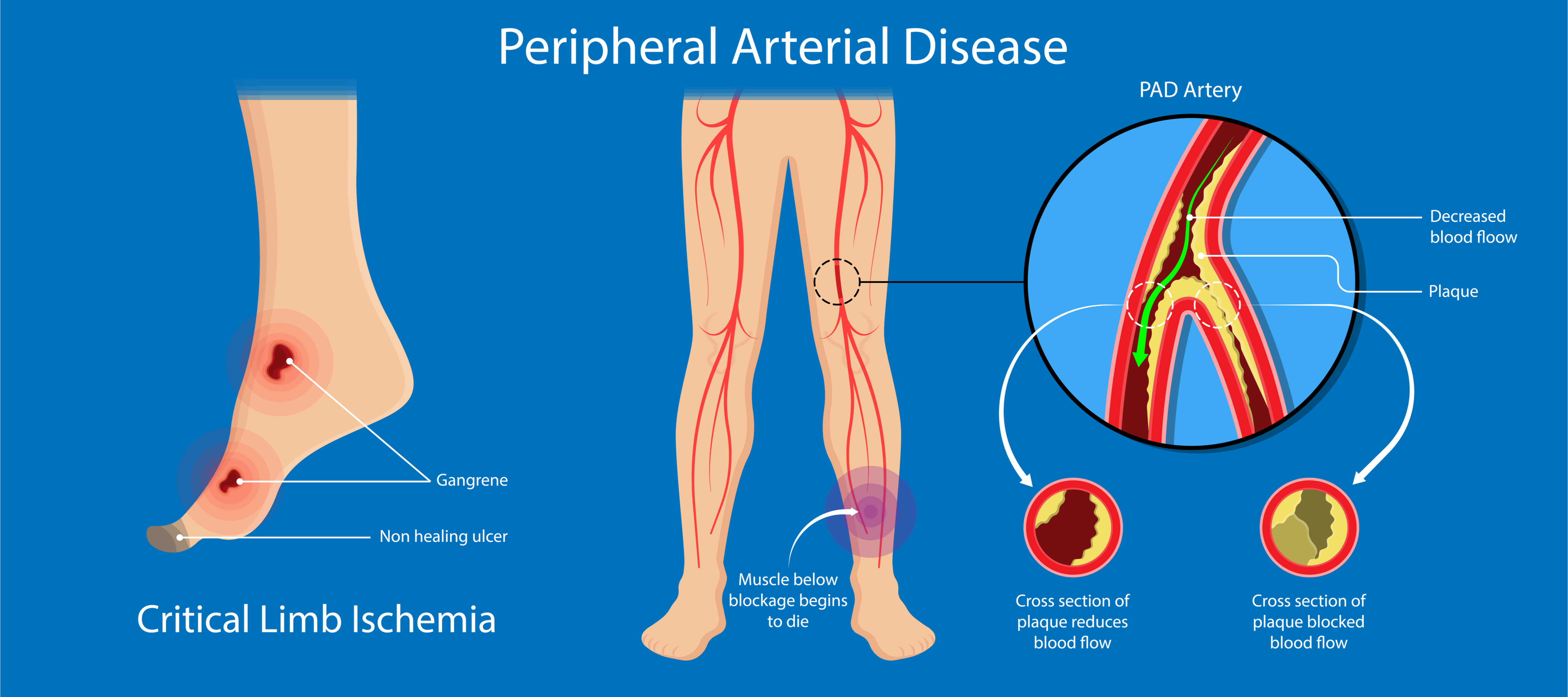
Peripheral Artery Disease вђ Wockhardthospitals Peripheral artery disease (pad) is the development of chronic arterial occlusive disease of the lower extremities due to atherosclerosis. 1 pad is associated with atherosclerosis of other vascular beds, and the presence of diabetes mellitus is known to both increase the incidence of pad, as well as accelerate disease progression and worsen disease severity. 2 given this, patients with. Peripheral artery disease (pad) stems from atherosclerosis of lower extremity arteries with resultant arterial narrowing or occlusion. the most severe form of pad is termed chronic limb threatening ischemia and carries a significant risk of limb loss and cardiovascular mortality. diabetes mellitus i …. Microvascular disease (mvd) potentiates risk of amputation in peripheral artery disease (pad). pad and mvd arise from a collection of shared risk factors through mechanisms that remain unknown. both pad and mvd are associated with an increased risk of amputation. together, the risk of amputation is potentiated suggesting a synergistic adverse. Introduction. between 51–93% of all lower limb major amputations are due to peripheral artery disease (pad), 1 although there is a considerable variation in the incidence of lower limb amputation across the world. 2 nevertheless, the global prevalence of pad as well as that of diabetes mellitus, a major contributing factor, is rising.
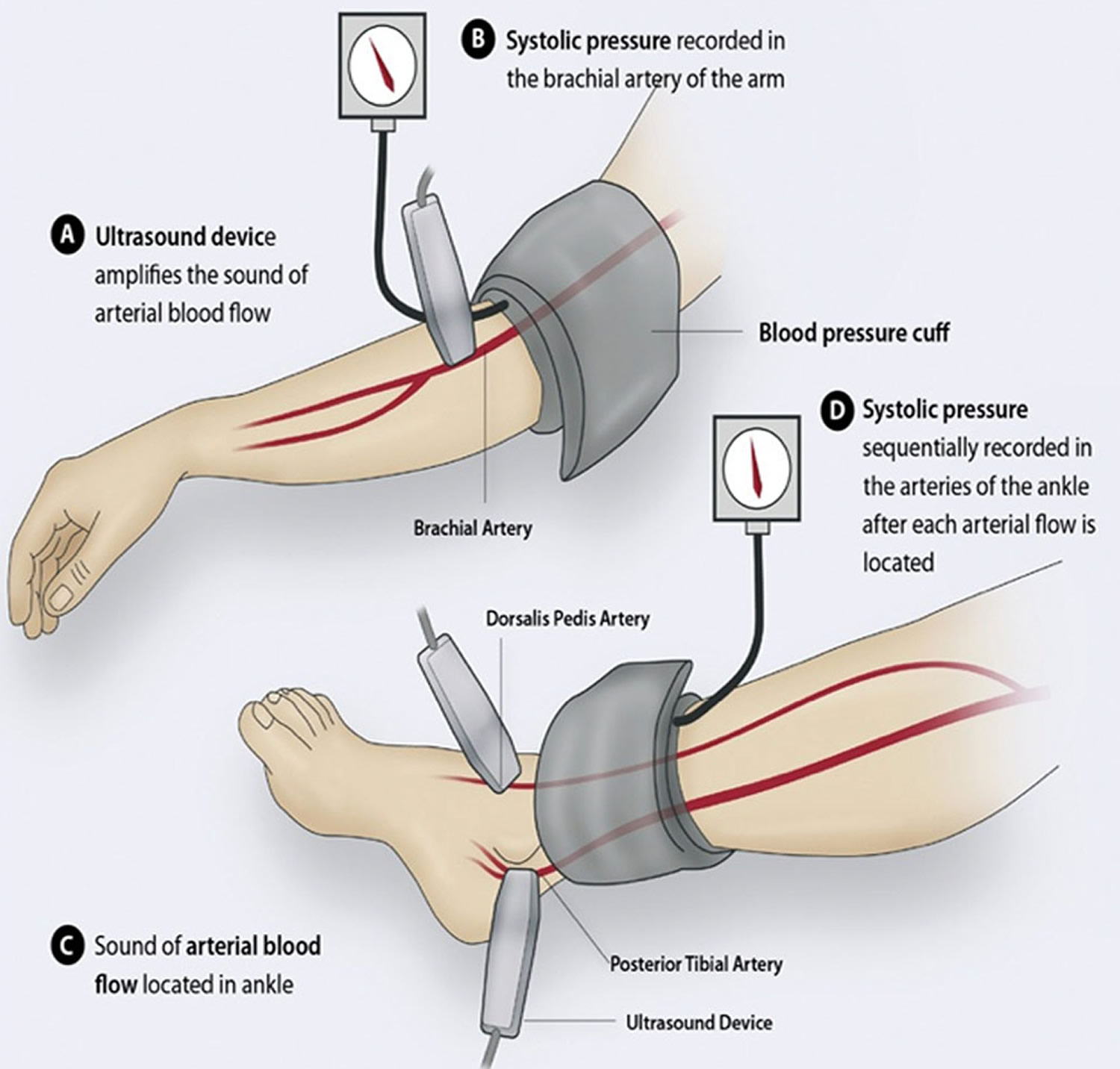
Peripheral Artery Disease Causes Symptoms Treatment Microvascular disease (mvd) potentiates risk of amputation in peripheral artery disease (pad). pad and mvd arise from a collection of shared risk factors through mechanisms that remain unknown. both pad and mvd are associated with an increased risk of amputation. together, the risk of amputation is potentiated suggesting a synergistic adverse. Introduction. between 51–93% of all lower limb major amputations are due to peripheral artery disease (pad), 1 although there is a considerable variation in the incidence of lower limb amputation across the world. 2 nevertheless, the global prevalence of pad as well as that of diabetes mellitus, a major contributing factor, is rising.

Comments are closed.