Phase Diagrams Introduction

Pdf Phase Diagrams Introduction Giki Dokumen Tips Phase diagram is a graphical representation of the physical states of a substance under different conditions of temperature and pressure. a typical phase diagram has pressure on the y axis and temperature on the x axis. as we cross the lines or curves on the phase diagram, a phase change occurs. in addition, two states of the substance coexist. Introduction. a phase diagram is a representation of different phases of a system consists of a substance or many substances at two different thermodynamic conditions such as temperature and pressure. phase diagram can also be drawn between other thermodynamic conditions such as between temperature and volume or temperature and solubility etc.
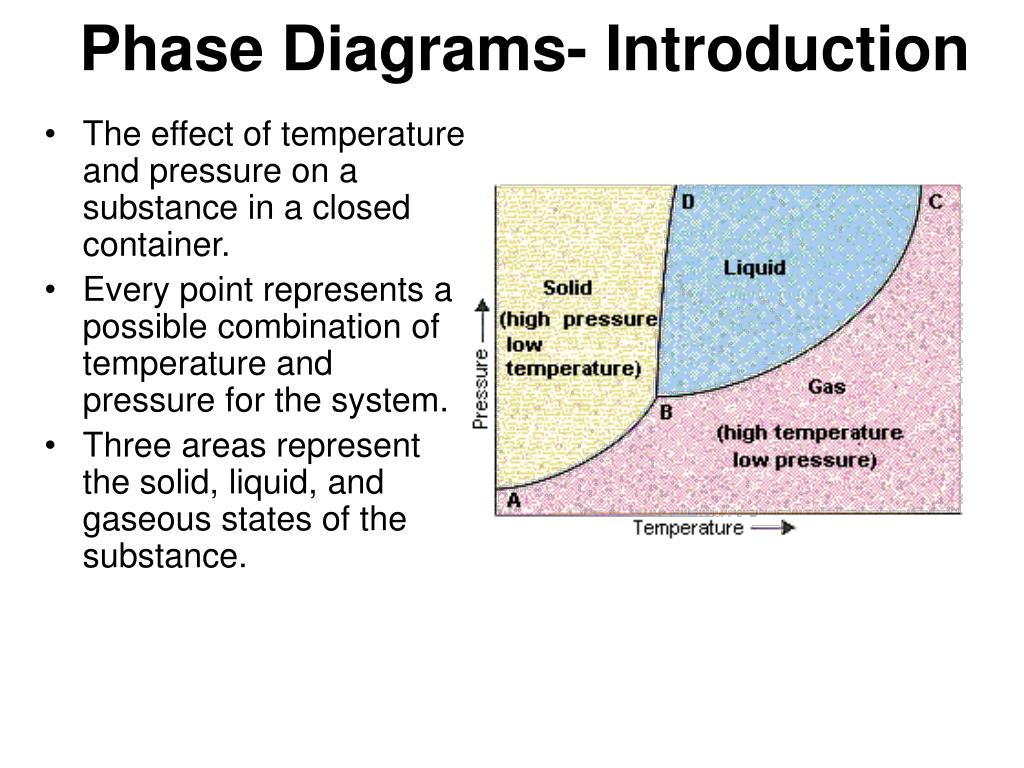
Ppt Phase Diagrams Introduction Powerpoint Presentation Free Mse 2090: introduction to materials science chapter 9, phase diagrams 10 a phase diagrams show what phases exist at equilibrium and what phase transformations we can expect when we change one of the parameters of the system. real materials are almost always mixtures of different elements rather than pure substances: in addition to t and. A typical phase diagram for a pure substance is shown in figure 1. figure 1. the physical state of a substance and its phase transition temperatures are represented graphically in a phase diagram. to illustrate the utility of these plots, consider the phase diagram for water shown in figure 2. figure 2. One component phase diagram. figure 1 illustrates the temperatures and pressures at which water can exist as a solid, liquid or vapor. the curves represent the points at which two of the phases coexist in equilibrium. at the point tt vapor, liquid and solid coexist in equilibrium. in the fields of the diagram (phase fields) only one phase exists. The phase diagram of carbon dioxide. in contrast to the phase diagram of water, the phase diagram of co 2 (figure 16.4.3 16.4. 3) has a more typical melting curve, sloping up and to the right. the triple point is −56.6°c and 5.11 atm, which means that liquid co 2 cannot exist at pressures lower than 5.11 atm.

Ppt Phase Diagrams Introduction 2 Dokumen Tips One component phase diagram. figure 1 illustrates the temperatures and pressures at which water can exist as a solid, liquid or vapor. the curves represent the points at which two of the phases coexist in equilibrium. at the point tt vapor, liquid and solid coexist in equilibrium. in the fields of the diagram (phase fields) only one phase exists. The phase diagram of carbon dioxide. in contrast to the phase diagram of water, the phase diagram of co 2 (figure 16.4.3 16.4. 3) has a more typical melting curve, sloping up and to the right. the triple point is −56.6°c and 5.11 atm, which means that liquid co 2 cannot exist at pressures lower than 5.11 atm. Phase diagram and “degrees of freedom”. phase diagrams is a type of graph used to show the equilibrium conditions between the thermodynamically distinct phases; or to show what phases are present in the material system at various t, p, and compositions. “equilibrium” is important: phase diagrams are determined by using slow cooling. Outline. •part 1 –introduction and basics. •part 2 –fundamental concepts. •part 3 –using phase diagrams. 2. william meier november 2, 2018. a phase diagram is a map. •regions on a phase diagram indicate the stable phases for a set of parameters. 3.

Comments are closed.