Phases Of Plant Growth
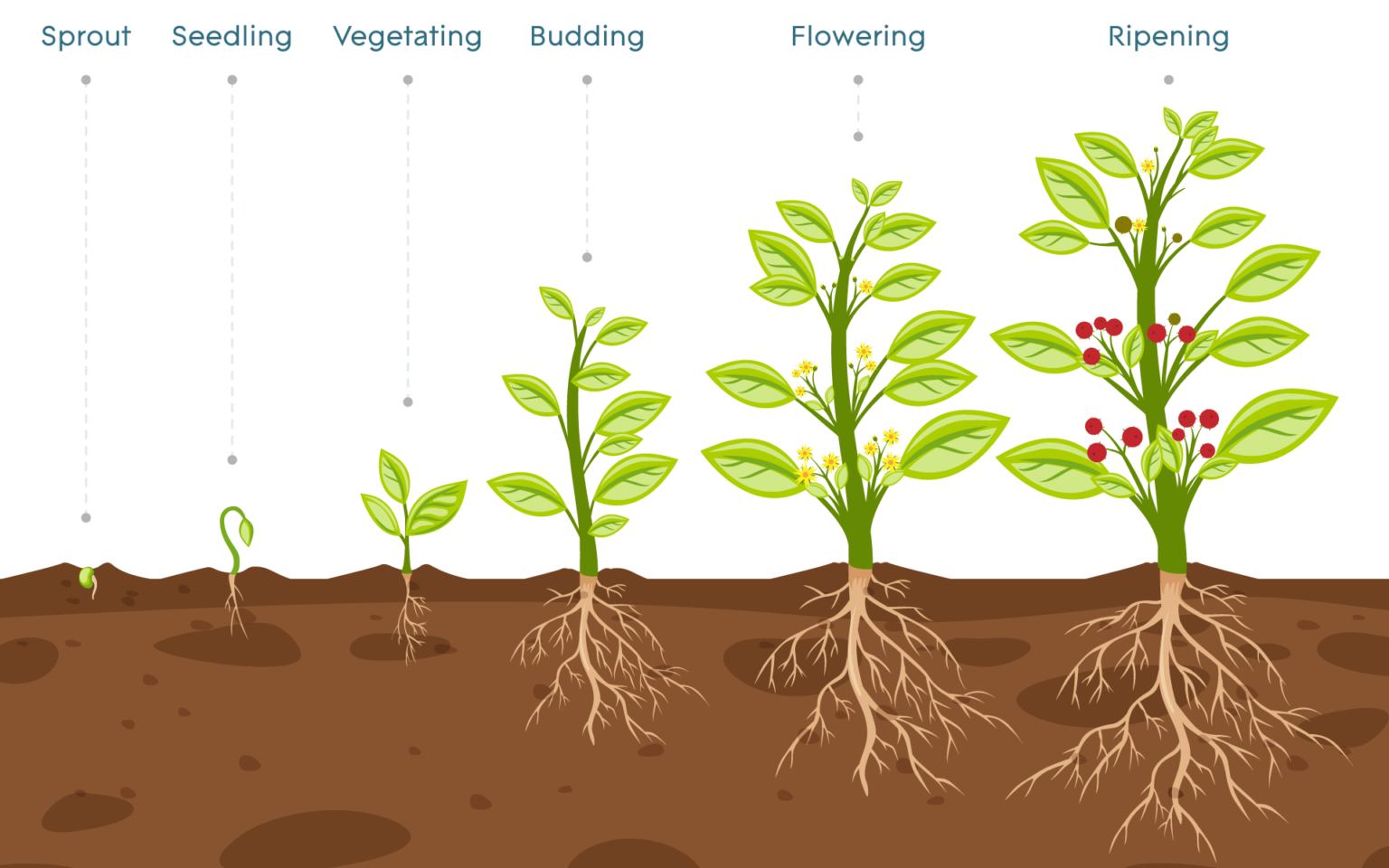
Plant Growth Stages An Overview Agrowtronics Iiot For Growing Key takeaways. – plants go through different stages of growth from seed to seed, which are called the plant life cycle. – the main stages of a plant’s life cycle are seed, germination, seedling, adult plant, pollination, and seed dispersal. – different types of plants have different life cycles, depending on their shape, size, lifespan. 1. sprout. it is the initial stage of plant growth. during this period, the seeds germinate, forming leaves that are different from the true leaves of a plant. the seeds contain all the nutrients required for germination. depending on the type of seed, sprouting can take several weeks. 2.

Phases Of Plant Growth 1406309 Vector Art At Vecteezy 3. vegetative stage: growth and development. next in the stages of plant growth is the vegetative stage. plants invest energy in root development to maintain and expand their root system. as the roots grow and branch out, they explore a larger soil volume, seeking essential elements for healthy growth. 5. ripening. after pollination, the plant’s flowers start to produce fruit. the fruits contain the plant’s seeds. this is the final stage in the plant’s life cycle and marks the beginning of a new generation of plants. in the vegetable and fruit gardens, this is the most productive of all the plant growth stages. One of the most useful things i ever learned about plants is how to observe the stages of plant growth. all plants follow the same basic patterns of growth on their way to maturity and this gives us a better way to identify and understand those plants more deeply. the simplest way to describe plant growth is with 4 stages:. Phases of growth in plants. there are three phases of growth – meristematic, elongation and maturation. we can understand this better by looking at a seed. we already know that the tips of roots and shoots exhibit continuous growth and hence are meristematic. the cells in this region are rich in protoplasm and have large nuclei.

Comments are closed.