Physical Quantities Scalars Vectors Distance Displacement Speed
Physical Quantities Scalars Vectors Distance Displacement Speed Some physical quantities, like distance, either have no direction or none is specified. a scalar is any quantity that has a magnitude, but no direction. for example, a 20ºc temperature, the 250 kilocalories (250 calories) of energy in a candy bar, a 90 km h speed limit, a person’s 1.8 m height, and a distance of 2.0 m are all scalars. For example, if a train covers a distance of 100 km in 1.0 h, its speed is 100.0 km 1.0 h = 27.8 m s, where the speed is a derived scalar quantity obtained by dividing distance by time. many physical quantities, however, cannot be described completely by just a single number of physical units.

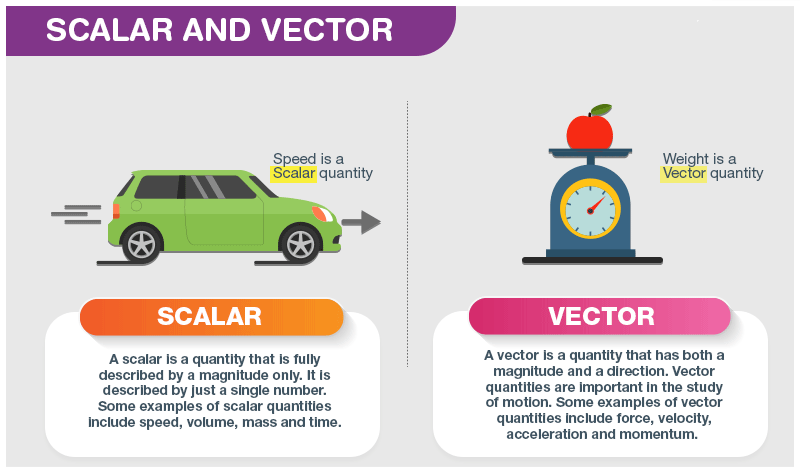
Discover Physiks 03 Distance Vs Displacement Speed Vs Velocity Scalars are quantities that are fully described by a magnitude (or numerical value) alone. vectors are quantities that are fully described by both a magnitude and a direction. the remainder of this lesson will focus on several examples of vector and scalar quantities (distance, displacement, speed, velocity, and acceleration). For example, if a train covers a distance of 100 km in 1.0 h, its speed is 100.0 km 1.0 h = 27.8 m s, where the speed is a derived scalar quantity obtained by dividing distance by time. many physical quantities, however, cannot be described completely by just a single number of physical units. Describe the differences between vectors and scalars using physical quantities as examples. it explains that distance is a vector and direction is important, whereas displacement is a scalar and it has no direction attached to it. For example, a 20ºc 20ºc temperature, the 250 kilocalories (250 calories) of energy in a candy bar, a 90 km h speed limit, a person’s 1.8 m height, and a distance of 2.0 m are all scalars—quantities with no specified direction. note, however, that a scalar can be negative, such as a − 20ºc − 20ºc temperature. in this case, the minus.

1 3 Scalar Vector Quantities Describe the differences between vectors and scalars using physical quantities as examples. it explains that distance is a vector and direction is important, whereas displacement is a scalar and it has no direction attached to it. For example, a 20ºc 20ºc temperature, the 250 kilocalories (250 calories) of energy in a candy bar, a 90 km h speed limit, a person’s 1.8 m height, and a distance of 2.0 m are all scalars—quantities with no specified direction. note, however, that a scalar can be negative, such as a − 20ºc − 20ºc temperature. in this case, the minus. For example, if a train covers a distance of 100 km in 1.0 h, its speed is 100.0 km 1.0 h = 27.8 m s, where the speed is a derived scalar quantity obtained by dividing distance by time. many physical quantities, however, cannot be described completely by just a single number of physical units. A scalar is any quantity that has a magnitude, but no direction. for example, a 20ºc temperature, the 250 kilocalories (250 calories) of energy in a candy bar, a 90 km h speed limit, a person’s 1.8 m height, and a distance of 2.0 m are all scalars—quantities with no specified direction.

Scalar And Vector Quantities Learn Physics Physics Notes Physics For example, if a train covers a distance of 100 km in 1.0 h, its speed is 100.0 km 1.0 h = 27.8 m s, where the speed is a derived scalar quantity obtained by dividing distance by time. many physical quantities, however, cannot be described completely by just a single number of physical units. A scalar is any quantity that has a magnitude, but no direction. for example, a 20ºc temperature, the 250 kilocalories (250 calories) of energy in a candy bar, a 90 km h speed limit, a person’s 1.8 m height, and a distance of 2.0 m are all scalars—quantities with no specified direction.

Comments are closed.