Piaget S Stages Of Cognitive Development Chart
/2795457-article-piagets-stages-of-cognitive-development-5a95c43aa9d4f900370bf112.png)
Piaget S 4 Stages Of Cognitive Development Explained Piaget divided children’s cognitive development into four stages; each of the stages represents a new way of thinking and understanding the world. he called them (1) sensorimotor intelligence, (2) preoperational thinking, (3) concrete operational thinking, and (4) formal operational thinking. each stage is correlated with an age period of. Jean piaget's theory of cognitive development suggests that children move through four different stages of learning. his theory focuses not only on understanding how children acquire knowledge, but also on understanding the nature of intelligence. piaget's stages are: sensorimotor stage: birth to 2 years. preoperational stage: ages 2 to 7.
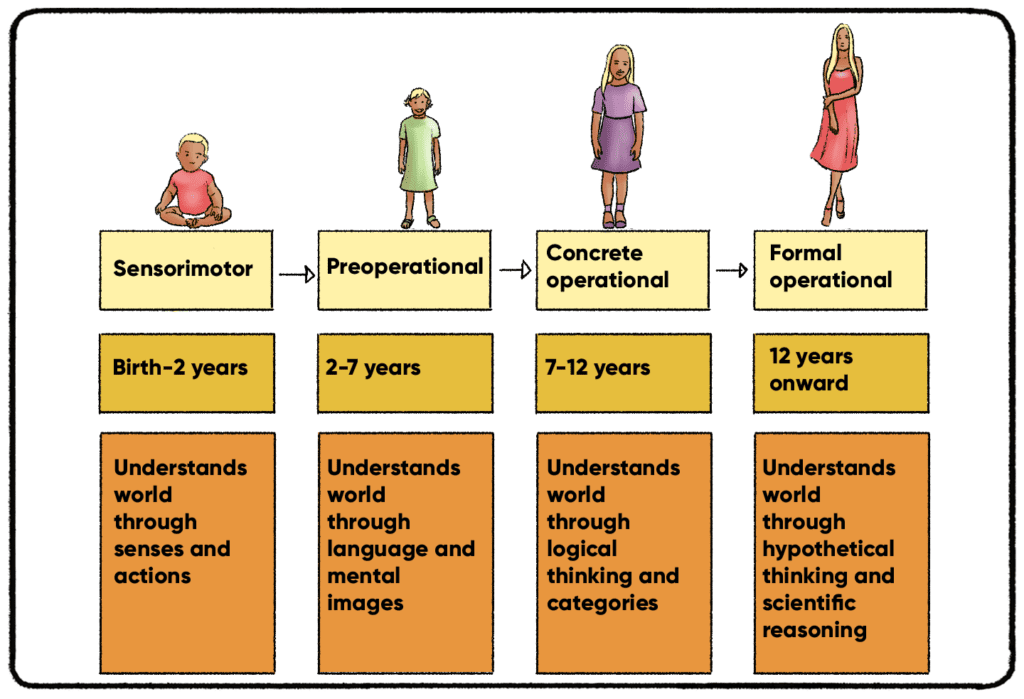
Jean юааpiagetтащsюаб Theory юааof Cognitiveюаб юааdevelopmentюаб Practical Psychology Preoperational. concrete operational. formal operational. the goals of each stage are understanding: object permanence. symbolic thought. operational thought. grasping abstract concepts. piaget. Initiative versus guilt (3–6 years) industry versus inferiority (6 years–puberty) identity versus identity confusion (puberty–young adulthood) not all of the developmental stages in erikson’s theory correspond to the cognitive stages proposed by piaget. for example, piaget’s preoperational stages overlap with the second and third. Summary. piaget’s stages of development describe how children learn as they grow up. there are four distinct stages: sensorimotor, preoperational, concrete operational, and formal operational. There are four piaget stages of cognitive development: sensorimotor stage: birth to 2 years old. preoperational stage: 2 7 years old. concrete operational stage: 7 11 years old. formal operations stage: 11 years old and older. according to jean piaget’s cognitive development theory, children are not capable of performing certain tasks or.

юааpiagetтащsюаб Four юааstagesюаб юааof Cognitiveюаб юааdevelopmentюаб Infographic Child Summary. piaget’s stages of development describe how children learn as they grow up. there are four distinct stages: sensorimotor, preoperational, concrete operational, and formal operational. There are four piaget stages of cognitive development: sensorimotor stage: birth to 2 years old. preoperational stage: 2 7 years old. concrete operational stage: 7 11 years old. formal operations stage: 11 years old and older. according to jean piaget’s cognitive development theory, children are not capable of performing certain tasks or. It focuses on children, from birth through adolescence, and characterizes different stages of development, including: language. morals. memory. reasoning. piaget made several assumptions about. Piaget’s four stages of cognitive development. piaget’s stage 1: sensorimotor. piaget’s sensorimotor stage is the initial developmental stage, typically occurring from birth to around two years of age, during which infants and toddlers primarily learn about the world through their senses and physical actions.

Piaget Developmental Stages Chart Beautiful Stages Of Developmentођ It focuses on children, from birth through adolescence, and characterizes different stages of development, including: language. morals. memory. reasoning. piaget made several assumptions about. Piaget’s four stages of cognitive development. piaget’s stage 1: sensorimotor. piaget’s sensorimotor stage is the initial developmental stage, typically occurring from birth to around two years of age, during which infants and toddlers primarily learn about the world through their senses and physical actions.

Comments are closed.