Piaget S Stages Of Cognitive Development Child Development Theories
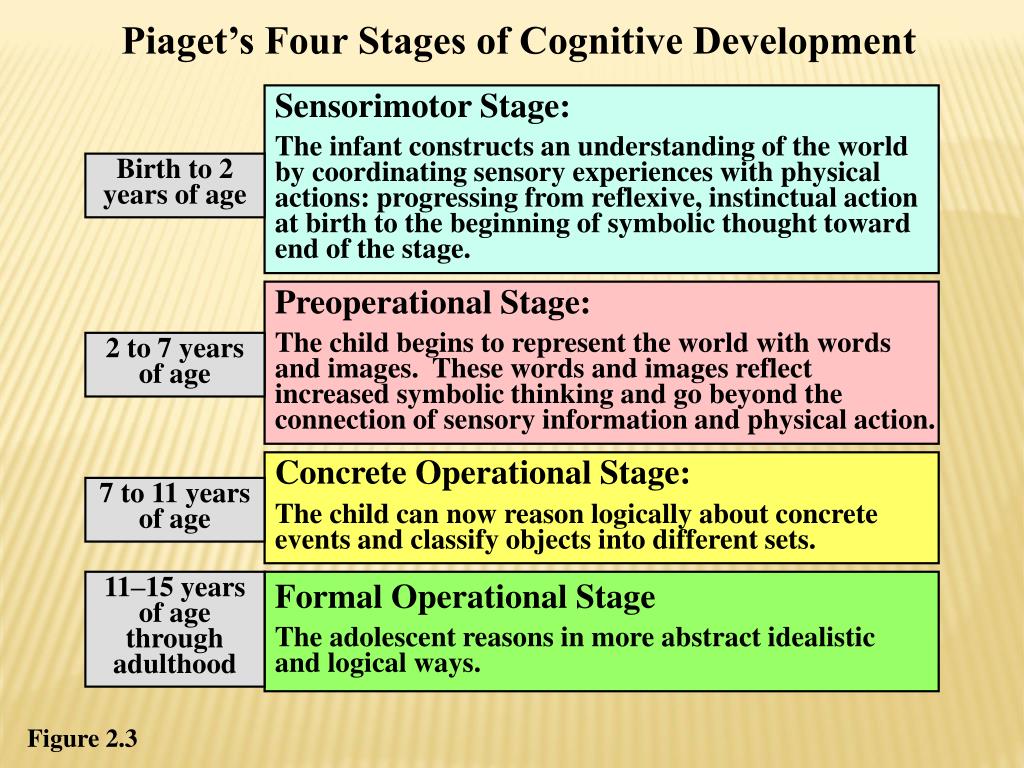
Ppt Child Development Theories Powerpoint Presentation Id 174952 Jean piaget's theory of cognitive development suggests that children move through four different stages of learning. his theory focuses not only on understanding how children acquire knowledge, but also on understanding the nature of intelligence. piaget's stages are: sensorimotor stage: birth to 2 years. preoperational stage: ages 2 to 7. Piaget divided children’s cognitive development into four stages; each of the stages represents a new way of thinking and understanding the world. he called them (1) sensorimotor intelligence, (2) preoperational thinking, (3) concrete operational thinking, and (4) formal operational thinking. each stage is correlated with an age period of.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/2795457-article-piagets-stages-of-cognitive-development-5a95c43aa9d4f900370bf112.png)
Piaget S 4 Stages Of Cognitive Development Explained Initiative versus guilt (3–6 years) industry versus inferiority (6 years–puberty) identity versus identity confusion (puberty–young adulthood) not all of the developmental stages in erikson’s theory correspond to the cognitive stages proposed by piaget. for example, piaget’s preoperational stages overlap with the second and third. Summary. piaget’s stages of development describe how children learn as they grow up. there are four distinct stages: sensorimotor, preoperational, concrete operational, and formal operational. Piaget's theory of cognitive development is based on the belief that a child gains thinking skills in four stages: sensorimotor, preoperational, concrete operational, and formal operational. these stages roughly correspond to specific ages, from birth to adulthood. children progress through these stages at different paces, but according to. Development. jean piaget’s theory of cognitive development suggests that children progress through a series of stages of mental development. the theory outlines four distinct stages from birth through adolescence, focusing on how children acquire knowledge, reasoning, language, morals, and memory. piaget’s stages of development are: stage.

Jean Piagets Theory Of Cognitive Development Piaget's theory of cognitive development is based on the belief that a child gains thinking skills in four stages: sensorimotor, preoperational, concrete operational, and formal operational. these stages roughly correspond to specific ages, from birth to adulthood. children progress through these stages at different paces, but according to. Development. jean piaget’s theory of cognitive development suggests that children progress through a series of stages of mental development. the theory outlines four distinct stages from birth through adolescence, focusing on how children acquire knowledge, reasoning, language, morals, and memory. piaget’s stages of development are: stage. Preoperational. concrete operational. formal operational. the goals of each stage are understanding: object permanence. symbolic thought. operational thought. grasping abstract concepts. piaget. Jean piaget in ann arbor. piaget's theory of cognitive development, or his genetic epistemology, is a comprehensive theory about the nature and development of human intelligence. it was originated by the swiss developmental psychologist jean piaget (1896–1980). the theory deals with the nature of knowledge itself and how humans gradually come.
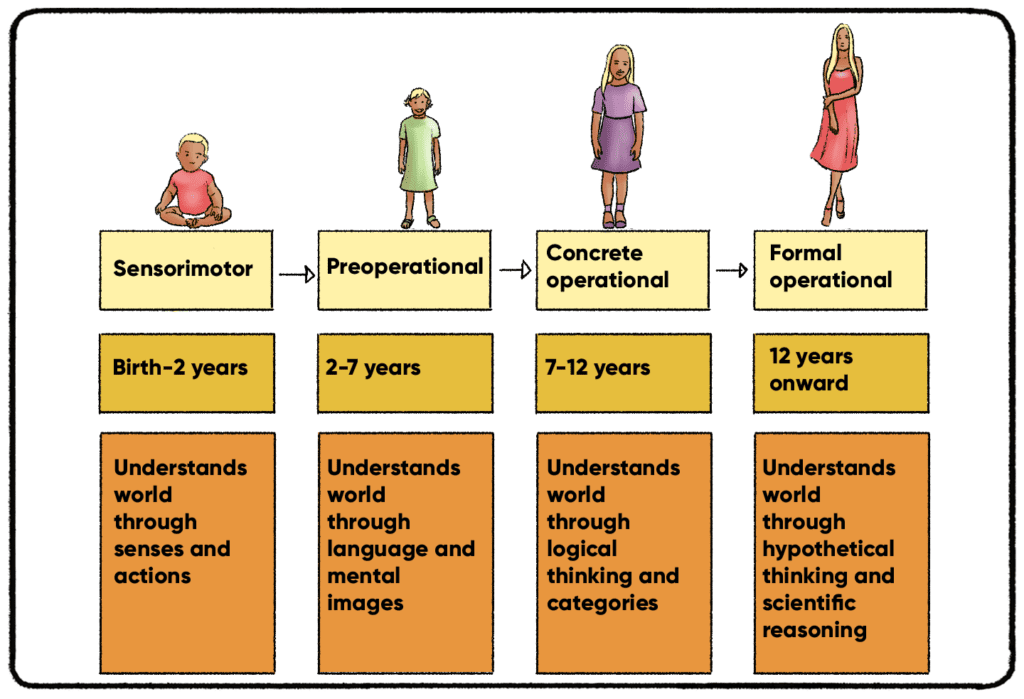
Jean юааpiagetтащsюаб юааtheoryюаб юааof Cognitiveюаб юааdevelopmentюаб Practical Psychology Preoperational. concrete operational. formal operational. the goals of each stage are understanding: object permanence. symbolic thought. operational thought. grasping abstract concepts. piaget. Jean piaget in ann arbor. piaget's theory of cognitive development, or his genetic epistemology, is a comprehensive theory about the nature and development of human intelligence. it was originated by the swiss developmental psychologist jean piaget (1896–1980). the theory deals with the nature of knowledge itself and how humans gradually come.
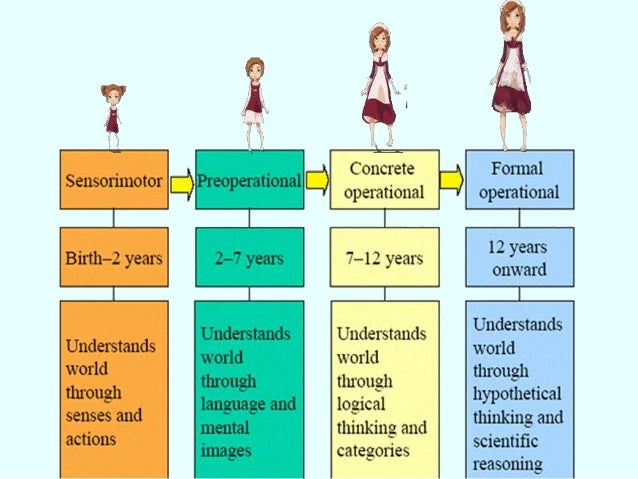
Piaget S Stages Of Cognitive Development

Comments are closed.