Pneumonia Etiology Clinical Features Diagnosis Treatment Harrison

Pneumonia Etiology Clinical Features Diagnosis Treatment Definition. pneumonia is an infection of the pulmonary parenchyma. despite being the cause of significant morbidity and mortality, it is often misdiagnosed, mistreated, and underestimated. pneumonia historically was typically classified as community acquired (cap), hospital acquired (hap), or ventilator associated (vap). Hi guys! welcome to pulmonology series on the channel. in this lecture, we will deal with pneumonia, its etiology, clinical features, diagnosis, algorithm al.

Pneumonia Bronchiectasis And Lung Abscess Pulmonology Harrisons Metlay jp, waterer gw, long ac, et al. diagnosis and treatment of adults with community acquired pneumonia. an official clinical practice guideline of the american thoracic society and infectious diseases society of america. am j respir crit care med 2019; 200:e45. fine mj, auble te, yealy dm, et al. Harrison’s textbook of internal medicine defines pneumonia as an infection of the pulmonary parenchyma caused by various organisms. it states that pneumonia is not a single disease but a group of specific infections, each with a different epidemiology, pathogenesis, presentation and clinical course [11]. Diagnosis of pneumonia in adults presenting with signs of lower respiratory tract infection is important because it requires specific treatment and follow up. pneumonia is usually diagnosed by a combination of clinical history, physical examination and or laboratory tests. Pneumonia is a respiratory infection characterized by inflammation of the alveolar space and or the interstitial tissue of the lungs. in industrialized nations, it is the leading infectious cause of death. pneumonia is most commonly transmitted via aspiration of airborne pathogens (primarily bacteria, but also viruses and fungi) but may also.

Types Of Pneumonia And Symptoms Patienteducationmd Diagnosis of pneumonia in adults presenting with signs of lower respiratory tract infection is important because it requires specific treatment and follow up. pneumonia is usually diagnosed by a combination of clinical history, physical examination and or laboratory tests. Pneumonia is a respiratory infection characterized by inflammation of the alveolar space and or the interstitial tissue of the lungs. in industrialized nations, it is the leading infectious cause of death. pneumonia is most commonly transmitted via aspiration of airborne pathogens (primarily bacteria, but also viruses and fungi) but may also. Community acquired pneumonia (cap) is one of the most commonly diagnosed illnesses worldwide. the clinical presentation of cap varies, ranging from mild disease characterized by limited shortness of breath and productive cough to severe disease characterized by fever, respiratory distress, and sepsis. because of the wide spectrum of associated. Pneumonia and your lungs enlarge image. pneumonia is an infection that inflames the air sacs in one or both lungs. the air sacs may fill with fluid or pus (purulent material), causing cough with phlegm or pus, fever, chills, and difficulty breathing. a variety of organisms, including bacteria, viruses and fungi, can cause pneumonia.
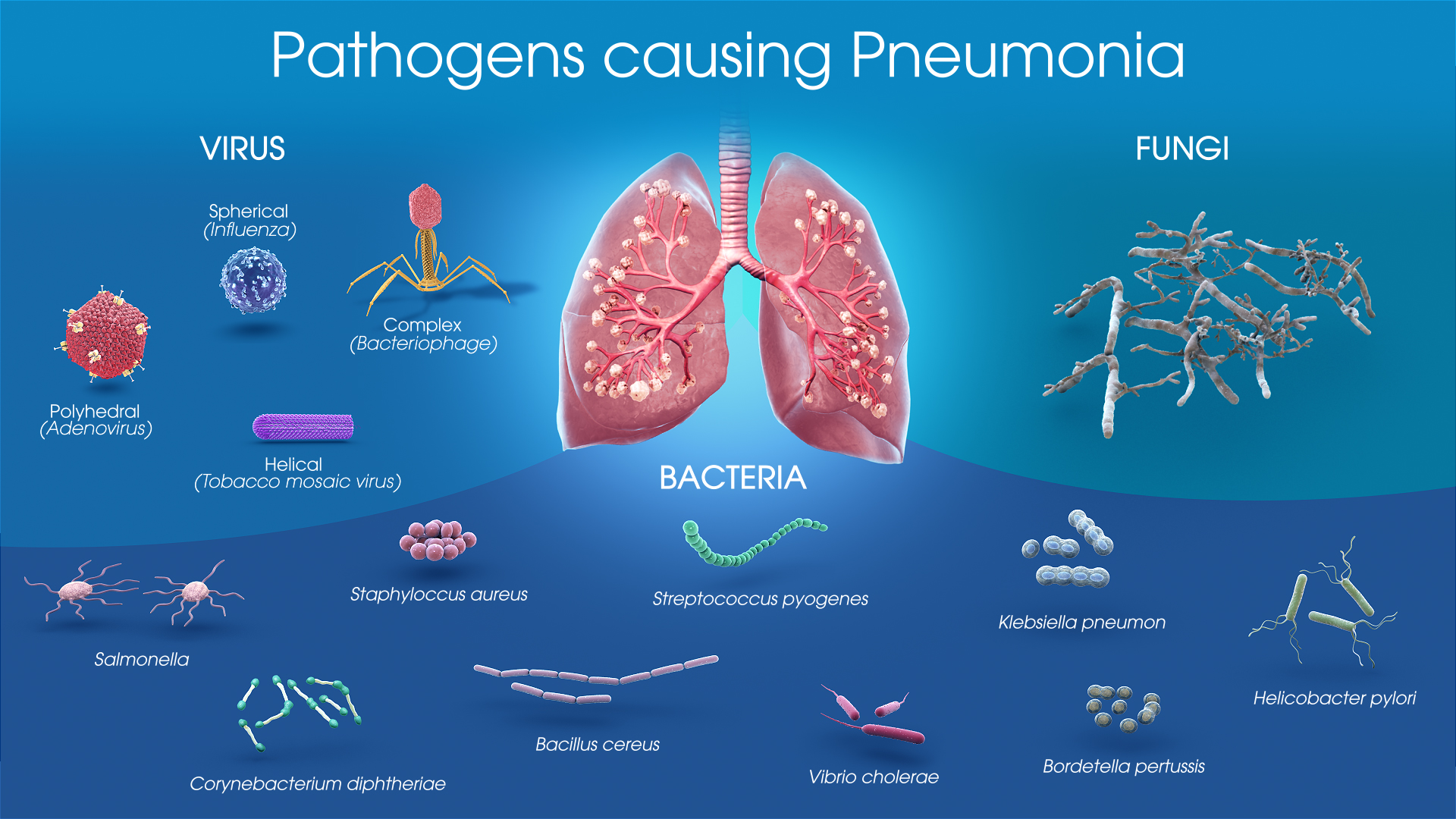
Neumonía On Emaze Community acquired pneumonia (cap) is one of the most commonly diagnosed illnesses worldwide. the clinical presentation of cap varies, ranging from mild disease characterized by limited shortness of breath and productive cough to severe disease characterized by fever, respiratory distress, and sepsis. because of the wide spectrum of associated. Pneumonia and your lungs enlarge image. pneumonia is an infection that inflames the air sacs in one or both lungs. the air sacs may fill with fluid or pus (purulent material), causing cough with phlegm or pus, fever, chills, and difficulty breathing. a variety of organisms, including bacteria, viruses and fungi, can cause pneumonia.

Comments are closed.