Polymerase Chain Reaction Pcr Definition Steps Principle Application
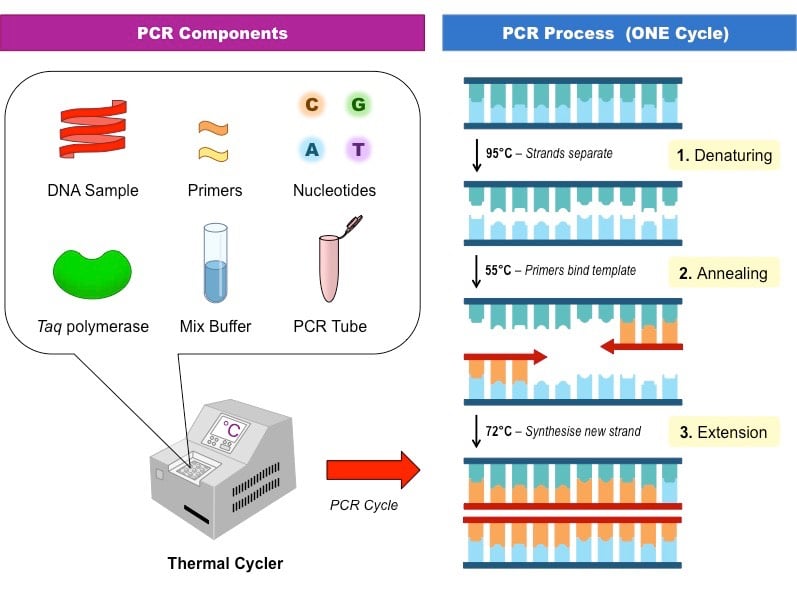
Polymerase Chain Reaction Pcr Principle Steps Applications Pcr is an enzymatic process in which a specific region of dna is replicated over and over again to yield many copies of a particular sequence. the most widely used target nucleic acid amplification method is the polymerase chain reaction (pcr). this method combines the principles of complementary nucleic acid hybridization with those of nucleic. Polymerase chain reaction ( pcr), a technique used to make numerous copies of a specific segment of dna quickly and accurately. the polymerase chain reaction enables investigators to obtain the large quantities of dna that are required for various experiments and procedures in molecular biology, forensic analysis, evolutionary biology, and.
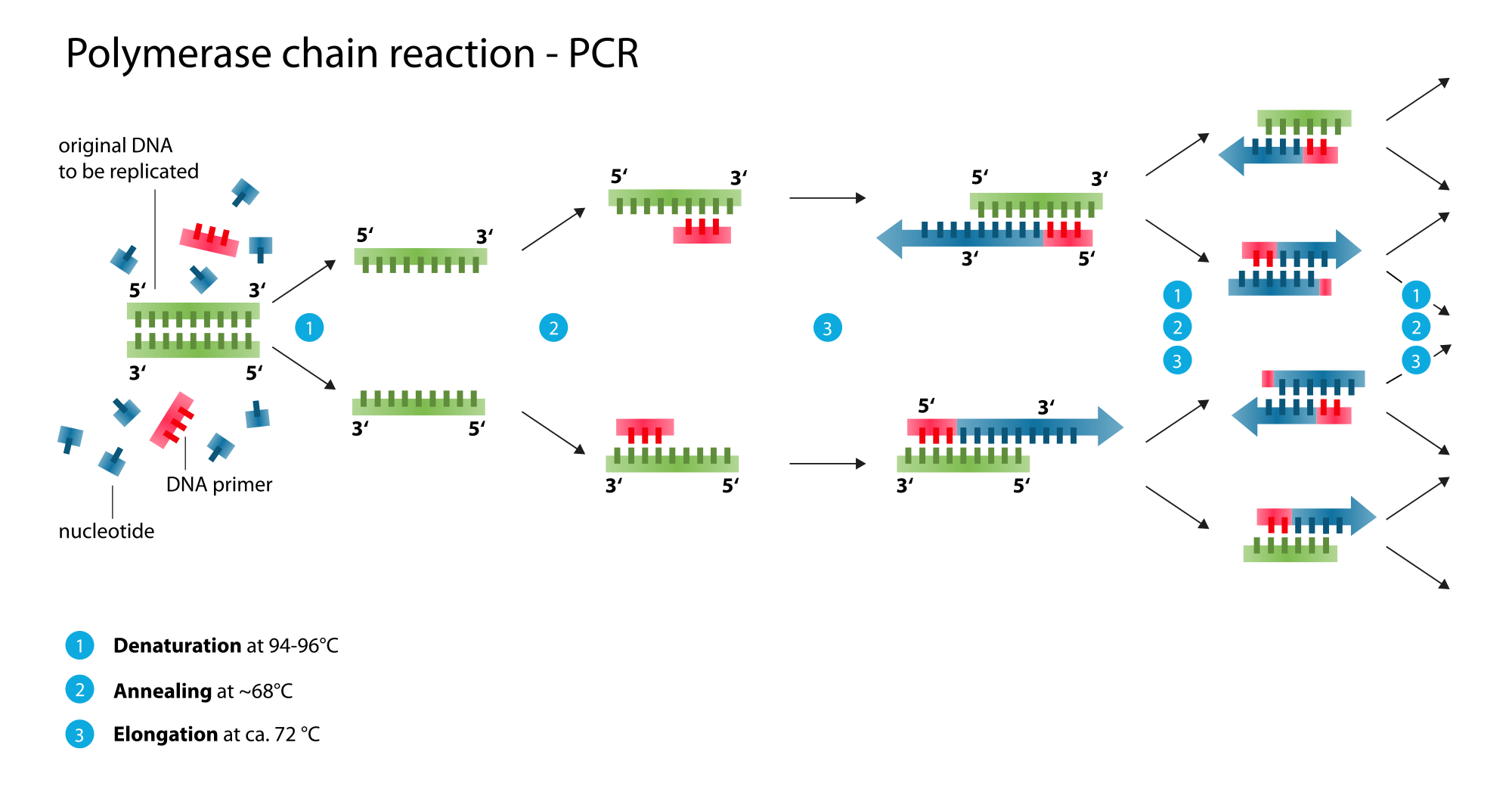
Polymerase Chain Reaction Pcr Steps Types And Applications Principle of pcr. the pcr technique is based on the enzymatic replication of dna. in pcr, a short segment of dna is amplified using primer mediated enzymes. dna polymerase synthesises new strands of dna complementary to the template dna. the dna polymerase can add a nucleotide to the pre existing 3’ oh group only. How does it work. the three basic steps of pcr are: denaturation: the double stranded dna is heated to almost 95°c to split the hydrogen bonds between the base pairs so that the dna strand is opened up (turned into a single strand). annealing: the temperature is lowered to almost 55°c, which helps the primers to bind to their corresponding. Polymerase chain reaction (pcr) has three major steps. steps of polymerase chain reactions (pcr) annealing (primer binding): the temperature is lowered (45 60 °c) so the primers can attach themselves to the single stranded dna strands. extension (synthesis of new dna): it starts at the annealed primer and works its way along the dna strand (72. The polymerase chain reaction (pcr) is a laboratory nucleic acid amplification technique used to denature and renature short segments of deoxyribonucleic acid (dna) or ribonucleic acid (rna) sequences using dna polymerase i enzyme, an isolate from thermus aquaticus, known as taq dna.[1][2] in 1985, pcr was introduced by mullis and colleagues for which they received a nobel prize.[3] it is a.

Comments are closed.