Positioning Lateral Supine

Supine Position Definition Explanation Pros And Cons Lateral position helps relieve pressure on the sacrum and heels, especially for people who sit or are confined to bed rest in supine or fowler’s position. body weight distribution. in this position, most of the body weight is distributed to the lateral aspect of the lower scapula , the lateral aspect of the ilium, and the greater trochanter of the femur . These positions include supine, prone, dorsal recumbent, lithotomy, lateral, sims, fowlers, trendelenburg, and lithotomy. this review will guide you through the different patient positioning terms, what the position can be used for, and complications that can arise from the position.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/supine_position-5bb0ec5146e0fb002693dccc.jpg)
Anatomical Position Definitions And Illustrations Supine position. this is the most common position for surgery with a patient lying on his or her back with head, neck, and spine in neutral positioning and arms either adducted alongside the patient or abducted to less than 90 degrees. arm abduction maintained under 90 degrees prevents undue pressure of the humerus on the axilla, thereby. Procedure steps: position the bed flat. raise the bed height. raise the side rail on the side of the bed the resident will be facing after repositioning for safety. move to the working side of the bed, which is opposite the side rail that was raised. explain to the resident that you will move them closer to you before turning on the count of three. The four main anatomical positions are supine, prone, right lateral recumbent, and left lateral recumbent. each position is used in different medical circumstances. these positions are often discussed in tandem with anatomical directional terms, which are used to locate structures relative to parts of the human body. they are particularly. Table 3.6 patient positions in bed; position. description. supine position: patient lies flat on back. additional supportive devices may be added for comfort. supine position: prone position: patient lies on stomach with head turned to the side. prone position: lateral position: patient lies on the side of the body with the top leg over the.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/positions-5bb0f1d74cedfd002615d0ca.png)
Anatomical Position Definitions And Illustrations The four main anatomical positions are supine, prone, right lateral recumbent, and left lateral recumbent. each position is used in different medical circumstances. these positions are often discussed in tandem with anatomical directional terms, which are used to locate structures relative to parts of the human body. they are particularly. Table 3.6 patient positions in bed; position. description. supine position: patient lies flat on back. additional supportive devices may be added for comfort. supine position: prone position: patient lies on stomach with head turned to the side. prone position: lateral position: patient lies on the side of the body with the top leg over the. 1. supine position. what the supine position looks like: in the supine position, a patient lies flat on their back. nurses can use different variations of this position. for example, depending on your patient’s condition, you might place your legs out straight, extended, or slightly bent. your arms may be up or down. when the supine position. Supine position vs. semi supine position. semi supine position refers to positions where the patient is lying on the surgical table but with additional articulations. these are commonly referred to as: 5. lawn chair position: a variation where the hips and knees are slightly flexed and above the level of the heart.
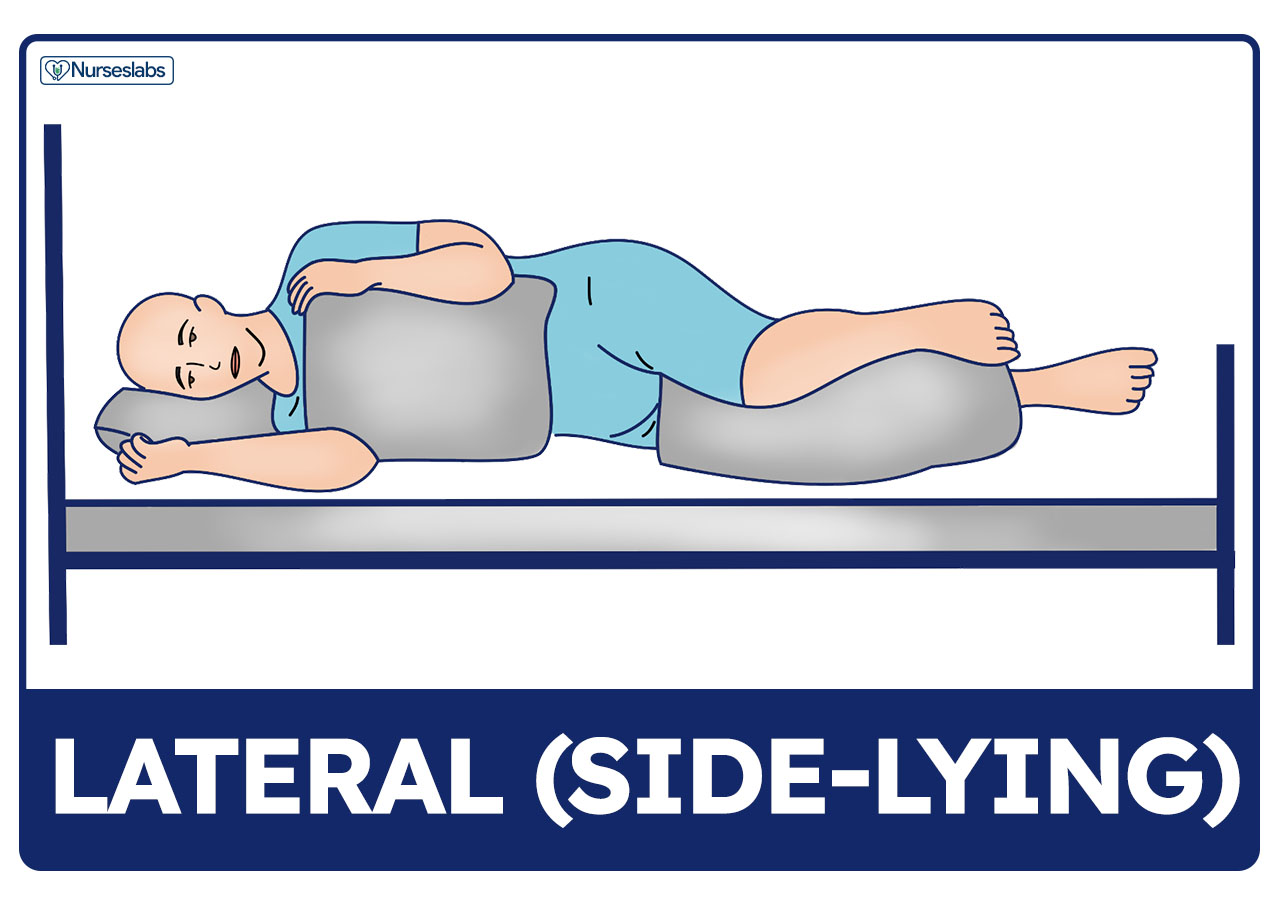
Patient Positioning Complete Guide And Cheat Sheet For Nurses 1. supine position. what the supine position looks like: in the supine position, a patient lies flat on their back. nurses can use different variations of this position. for example, depending on your patient’s condition, you might place your legs out straight, extended, or slightly bent. your arms may be up or down. when the supine position. Supine position vs. semi supine position. semi supine position refers to positions where the patient is lying on the surgical table but with additional articulations. these are commonly referred to as: 5. lawn chair position: a variation where the hips and knees are slightly flexed and above the level of the heart.
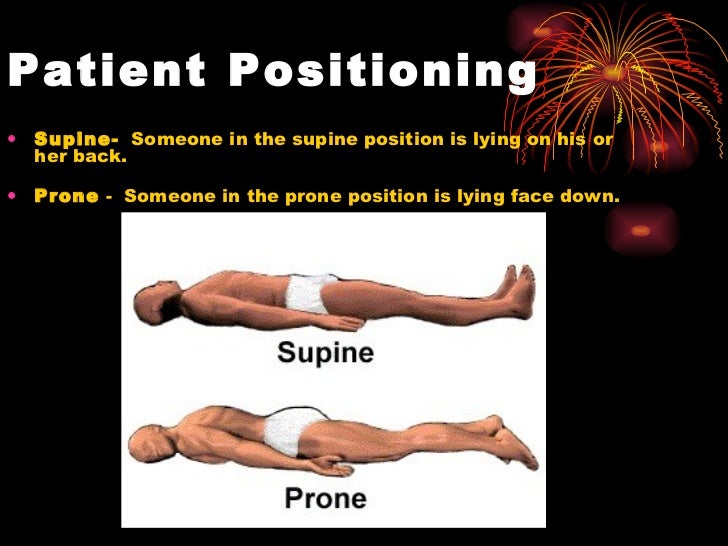
Patient Positioning

Comments are closed.