Posterior Wall Acetabulum Fracture Surgery Unstable Hip Fracture

Posterior Wall Acetabulum Fracture Surgery Unstable Hip Fracture Oct. 06, 2017. fractures of the acetabulum are challenging orthopedic injuries to repair, at times leaving multiple small fragments of fractured bone and cartilage. compounded by the location in a region challenging in which to work and fraught with risk, these "puzzle pieces" must be brought back together to restore hip function and mobility. Images. acetabulum fractures are pelvis fractures that involve the articular surface of the hip joint and may involve one or two columns, one or two walls, or the roof within the pelvis. diagnosis can be made radiographically with dedicated pelvis radiographs (including judet views) but frequently require ct pelvis for surgical planning.
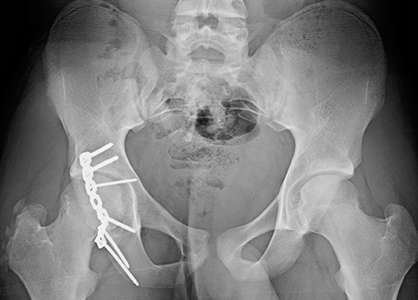
Posterior Wall Acetabular Fracture Broken Hip Socket Orthopaedic The socket is part of your pelvis and is called the acetabulum. both the ball and socket have a smooth layer called cartilage between them, which helps them move easily. a posterior wall break is when the back (posterior) part of your hip socket breaks. this part is important because it helps keep the ball in the socket. Posterior wall fractures are the most common type of acetabular fractures. treatment can be conservative or surgical. operative treatment is indicated for acetabular fractures that result in hip joint instability and or incongruity, as well injuries with incarceration of fragments of bone or soft tissue within the hip joint. Orthopaedic surgeons have identified a number of different acetabular fracture patterns. these fracture patterns are based on: location — such as a break in the anterior (front) or posterior (back) column of the bone or the area around the bony rim (wall) of the acetabulum. orientation — such as a break that is straight across the bone. An acetabular fracture is a break in your acetabulum. your acetabulum is the socket part of the hip joint. acetabular fracture types are classified by pattern and severity. acetabular fractures are painful injuries that usually require surgery. complications such as hip arthritis can arise due to the cartilage that surrounds your hip socket.
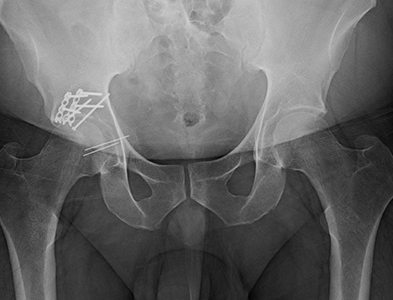
Posterior Wall Acetabular Fracture Broken Hip Socket Orthopaedic Orthopaedic surgeons have identified a number of different acetabular fracture patterns. these fracture patterns are based on: location — such as a break in the anterior (front) or posterior (back) column of the bone or the area around the bony rim (wall) of the acetabulum. orientation — such as a break that is straight across the bone. An acetabular fracture is a break in your acetabulum. your acetabulum is the socket part of the hip joint. acetabular fracture types are classified by pattern and severity. acetabular fractures are painful injuries that usually require surgery. complications such as hip arthritis can arise due to the cartilage that surrounds your hip socket. Criteria for hip stability after fracture of the posterior acetabular wall have been described by several authors. 7–10 previously, it was generally accepted that fractures involving more than 50% of the posterior wall are unstable and require open reduction and fixation, whereas those involving less than 20% are stable and can be managed nonoperatively. 7–10 more recently, it has been. Epend on fragment location, size, and displacement, directs management. although important in the assessment of posterior wall fractures, ct is unreliable when used to determine stability. the dynamic fluoroscopic examination under anesthesia (eua) is the benchmark in assessment of hip stability, and fractures deemed stable by eua have good radiographic and functional outcomes. in fractures.

Comments are closed.