Ppt Atomic Structure And Chemical Bonding Powerpoint Presentation 7f5

Ppt Atomic Structure And Chemical Bonding Powerpoint Presentation 7f5 Ionic bonding: summary. an ionic bond is the electrostatic attraction formed between ( ) cations and ( ) anions. the cations and anions are formed when a non metal (high en) steals an electron from a metal (low ie). this transfer of electrons gives each atom a filled valence shell (stable octet) of electrons. Follow. 1) the presentation summarizes atomic structure and chemical bonding models including fundamental particles, rutherford and bohr atomic models, quantum numbers, and types of chemical bonds. 2) it discusses limitations of earlier atomic models and introduces concepts like electron energy levels, photon energy, and spectral lines.
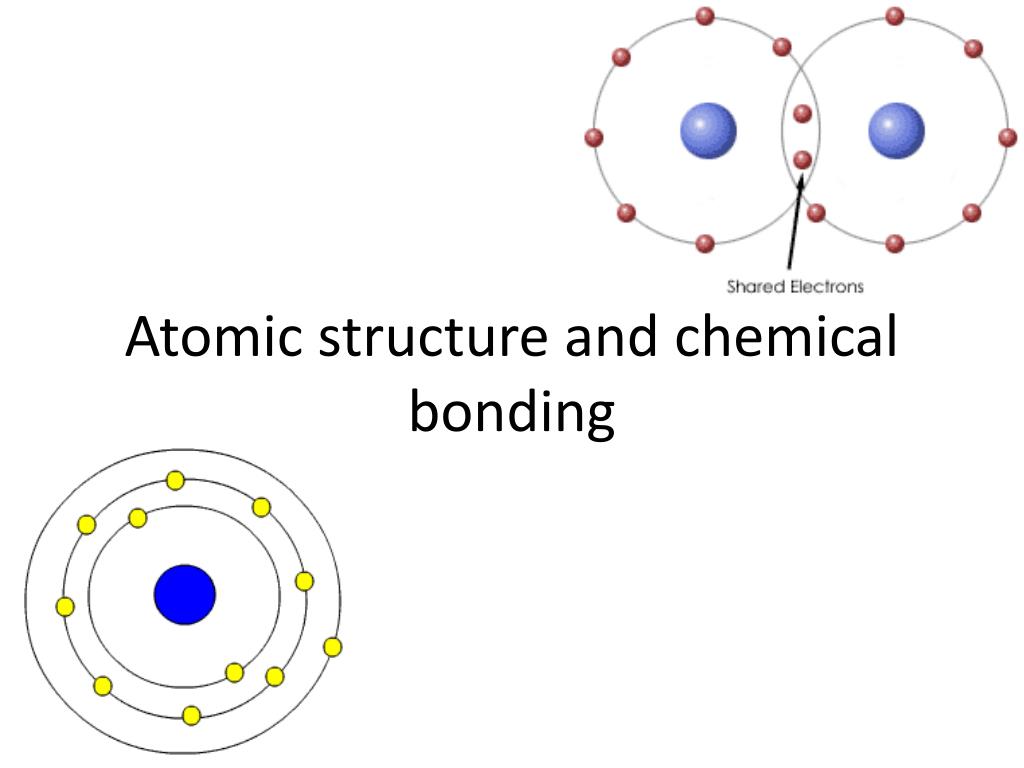
Ppt Atomic Structure And Chemical Bonding Powerpoint Presentation 7f5 Atoms tend to gain, lose, or share electrons in order to get a full set of valence electrons. “octet” – most atoms need 8 valence electrons for a full set. gaining or losing → ions = ionic bonding. sharing = covalent bonding. “dogs teaching chemistry”. Atomic structure and bonding. atomic structure and bonding. unit 2. major subatomic particles. atoms are measured in picometers , 10 12 meters hydrogen atom, 32 pm radius nucleus tiny compared to atom if the atom were a stadium, the nucleus would be a marble radius of the nucleus is on the order of 10 15 m. 769 views • 53 slides. Atomic structure. atoms are composed of 2 regions: 1.) nucleus: the center of the atom. that contains the mass of the atom. 2.) electron cloud: region that surrounds. the nucleus that contains most of the. space in the atom. This document discusses the four main types of chemical bonds: ionic bonds, covalent bonds, hydrogen bonds, and metallic bonds. ionic bonds involve the transfer of electrons between atoms. covalent bonds involve the sharing of electrons between two atoms. hydrogen bonds are electrostatic attractions between hydrogen atoms covalently bonded to.
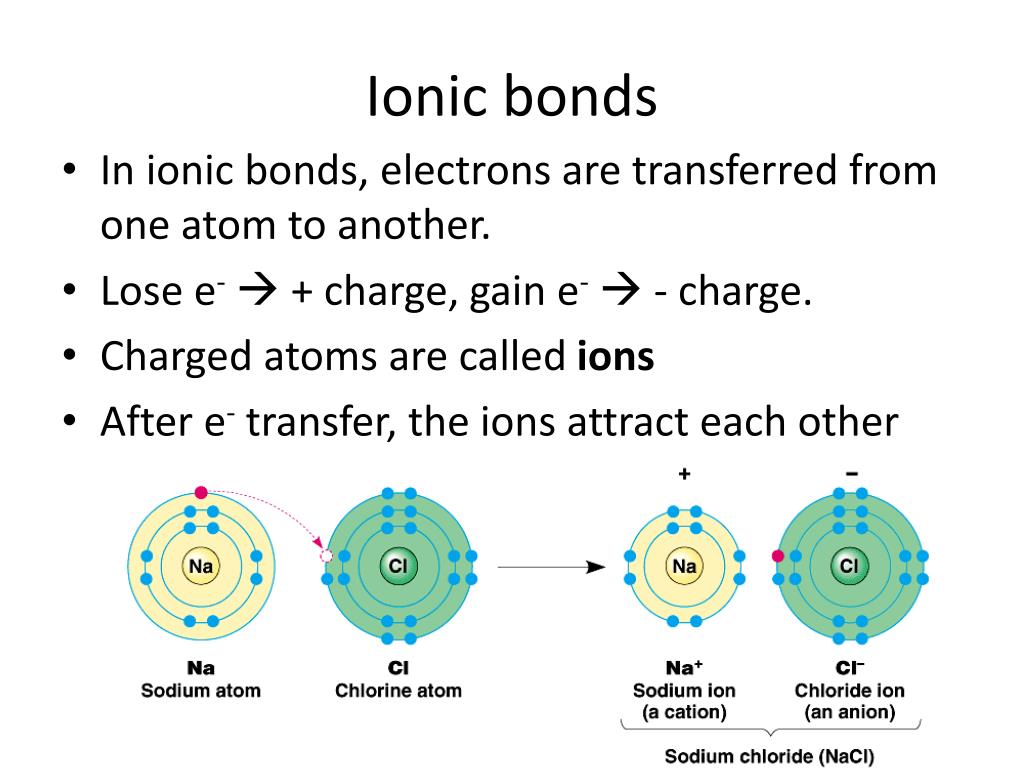
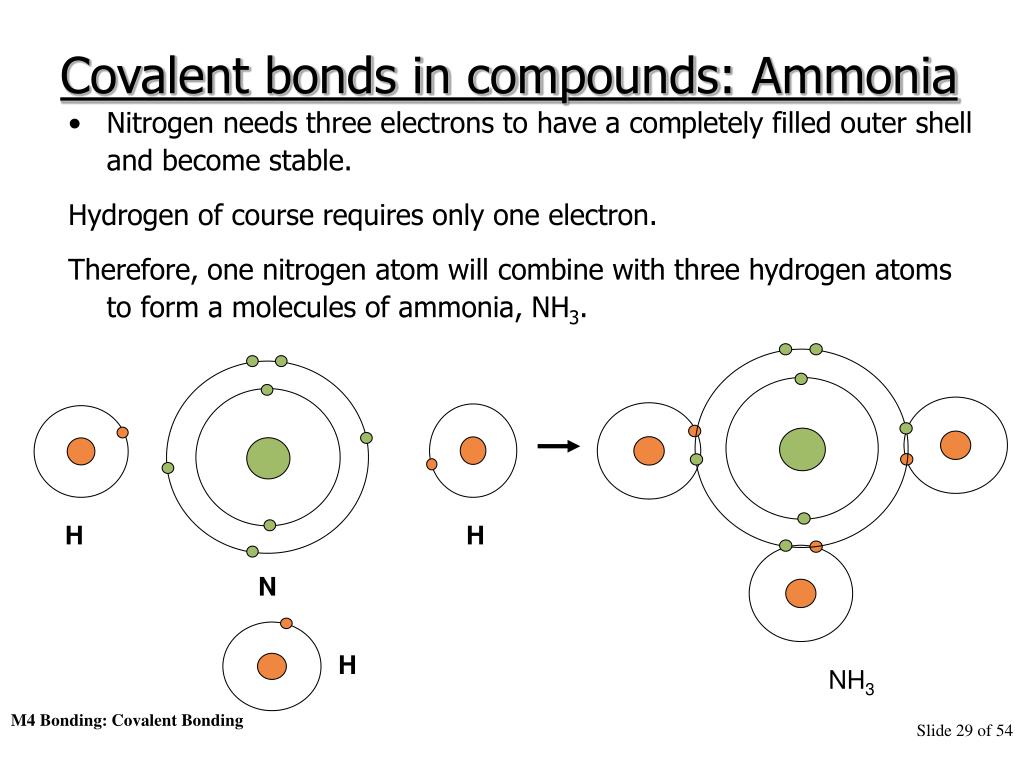
Ppt Atomic Structure And Chemical Bonding Powerpoint Presentation 7f5 Atomic structure. atoms are composed of 2 regions: 1.) nucleus: the center of the atom. that contains the mass of the atom. 2.) electron cloud: region that surrounds. the nucleus that contains most of the. space in the atom. This document discusses the four main types of chemical bonds: ionic bonds, covalent bonds, hydrogen bonds, and metallic bonds. ionic bonds involve the transfer of electrons between atoms. covalent bonds involve the sharing of electrons between two atoms. hydrogen bonds are electrostatic attractions between hydrogen atoms covalently bonded to. Covalent and ionic bonding • covalent bond • definition: a covalent bond is a chemical link between two atoms in which electrons are shared between them. • examples: there is a covalent bond between the oxygen and each hydrogen in a water molecule (h2o). each of the covalent bonds contains two electrons one from a hydrogen atom and one. Chemical bonding occurs for atoms to achieve stable electron configurations. this document discusses ionic and metallic bonding. it explains that ions are formed when atoms gain or lose electrons to achieve stable noble gas electron configurations. metals form cations by losing electrons while nonmetals form anions by gaining electrons.

Ppt Atomic Structure And Chemical Bonding Powerpoint Presentation 7f5 Covalent and ionic bonding • covalent bond • definition: a covalent bond is a chemical link between two atoms in which electrons are shared between them. • examples: there is a covalent bond between the oxygen and each hydrogen in a water molecule (h2o). each of the covalent bonds contains two electrons one from a hydrogen atom and one. Chemical bonding occurs for atoms to achieve stable electron configurations. this document discusses ionic and metallic bonding. it explains that ions are formed when atoms gain or lose electrons to achieve stable noble gas electron configurations. metals form cations by losing electrons while nonmetals form anions by gaining electrons.
Ppt Atomic Structure And Chemical Bonding Powerpoint Presentation 7f5

Comments are closed.