Ppt Chapter 21 Transition Metals And Coordination Chemistry

Ppt Chapter 21 Transition Metals And Coordination Chemistry 16 chapter 21(b) transition metals and coordination chemistry (cont’d) 17 figure 21.4: the structures of the chromium(vi) anions: (a) cr 2 o 7 2 , which exists in acidic solution, and (b) cro 4 2 , which exists in basic solution. Chapter 21: transition metals and coordination chemistry. chapter 21: transition metals and coordination chemistry. review of transition metal properties coordination compounds isomerism crystal field theory this is covered in textbook sections: 21.1 (first half) 21.3 (skip nomenclature) 21.4 21.5 21.6. figure 21.5. 447 views • 12 slides.
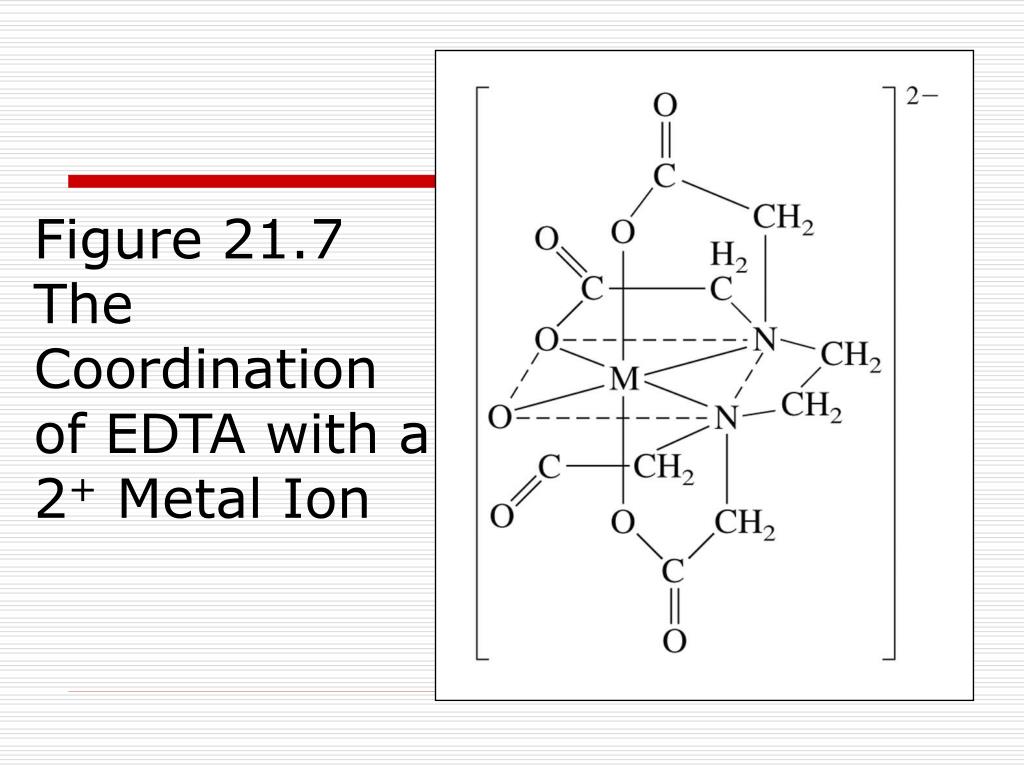
Ppt Chapter 21 Transition Metals And Coordination Chemistry 1 coordination chemistry. ligands bonding to metals. 2 donor acceptor complexes. 3 definitions lewis acid = acceptor = usually a transition metal cation. lewis base = donor = ligand = usually something with a lone electron pair coordination number = # of metal ligand attachments (from the metal’s point of view) denticity = # of attachments a. Chapter 21: transition metals and coordination chemistry • review of transition metal properties • coordination compounds • isomerism • crystal field theory this is covered in textbook sections: 21.1 (first half) 21.3 (skip nomenclature) 21.4 21.5 21.6. figure 21.5. figure 21.6 bidentate and monodentate ligands. table21.13 common ligands. Presentation transcript. transition metals and coordination chemistry chapter 23. transition metals • similarities within a given period • and within a given group. • last electrons added are inner electrons (d’s, f’s). multiple oxidation states. metallic behavior reducing strength • lower oxidation state = more metallic. Faculty. steven dessens. notes and practice problems. chem 1412 general chemistry ii (with lab) chem 1412 previous textbook powerpoints. chem 1412 chang powerpoints. chapter 22 transition metal chemistry and coordination compounds.

Ppt Transition Metals And Coordination Chemistry Powerpoint Presentation transcript. transition metals and coordination chemistry chapter 23. transition metals • similarities within a given period • and within a given group. • last electrons added are inner electrons (d’s, f’s). multiple oxidation states. metallic behavior reducing strength • lower oxidation state = more metallic. Faculty. steven dessens. notes and practice problems. chem 1412 general chemistry ii (with lab) chem 1412 previous textbook powerpoints. chem 1412 chang powerpoints. chapter 22 transition metal chemistry and coordination compounds. Most often, this involves a donor atom with a lone pair of electrons that can form a coordinate bond to the metal. figure 19.2.2 19.2. 2: (a) covalent bonds involve the sharing of electrons, and ionic bonds involve the transferring of electrons associated with each bonding atom, as indicated by the colored electrons. Transition metal ions are often coloured they. absorb em radiation because of loss of degeneracy. of d orbitals those which absorb in the visible. region will appear the complementary colour. 21. the 5 d orbitals in an isolated atom are. degenerate. ligands cause the d orbitals to become. non degenerate.

Comments are closed.