Ppt Muscle Contraction And The Sliding Filament Theory Powerpoint
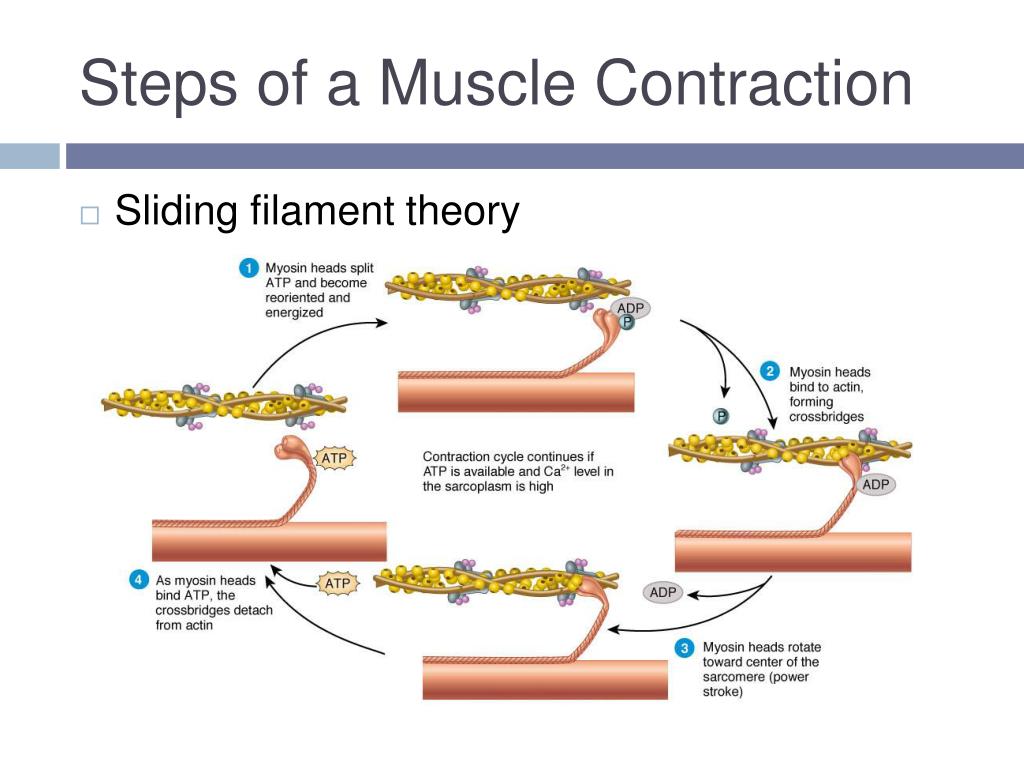
Ppt Muscular Contractions Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id The sliding filament theory of muscle contraction occurs in 5 phases: 1) a nervous impulse causes acetylcholine release at the neuromuscular junction, depolarizing the motor end plate and triggering calcium release from the sarcoplasmic reticulum. 2) calcium binds to troponin, displacing tropomyosin and exposing actin binding sites for myosin. The sliding filament theory of muscle contraction occurs in 5 phases: 1) a nervous impulse causes acetylcholine release at the neuromuscular junction, depolarizing the motor end plate and triggering calcium release from the sarcoplasmic reticulum. 2) calcium binds to troponin, displacing tropomyosin and exposing actin binding sites for myosin.

Ppt The Sliding Filament Mechanism Powerpoint Presentation Id 2208766 Sliding filament theory. the document describes the sliding filament theory of muscle contraction. it explains that muscle shortening occurs when the actin filament slides over the myosin filament, reducing the distance between z lines in the sarcomere. it further describes the roles of calcium ions, tropomyosin, troponin, actin, myosin and atp. This process comprised of several steps is called the sliding filament theory. it is also called the walk along theoryor the ratchet theory. after the atp has bound to the myosin head, the binding of myosin to actin molecule takes place: once the actin active sites are uncovered, the myosin binds to it: power stroke. Sliding filament theory in its most basic form: • muscle contraction occurs when the myosin and actin filaments slide across each other. • what actually occurs is myosin pulls the actin in. • this shortens the muscle and is a muscle contraction. sarcomere and muscle contraction • during muscle contraction in the sarcomere: • the z. Presentation transcript. the sliding filament theory. microstructure of skeletal muscle (recap) actin myosin orientation: • myosin filament (thick). • have long rod shaped tails with 2 globular heads. • the heads form cross bridges. microstructure of skeletal muscle (recap) • actin filament (thin). • tropomyosin is a rigid, rod shaped.
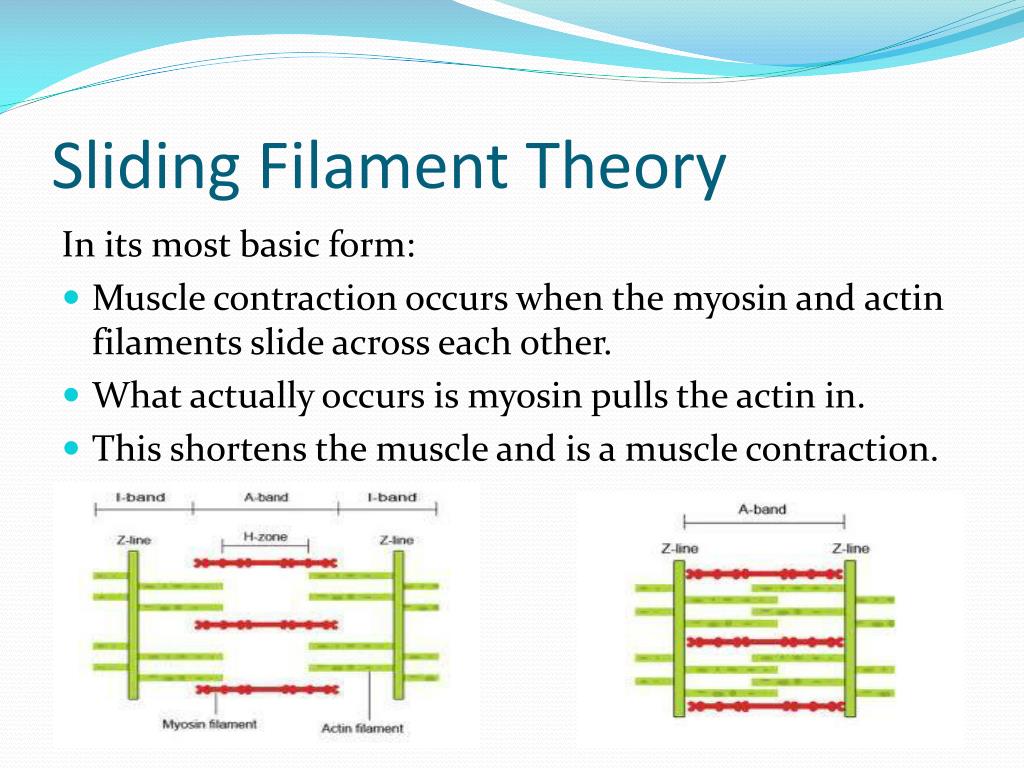
Ppt Muscle Contraction And The Sliding Filament Theory Powerpoint Sliding filament theory in its most basic form: • muscle contraction occurs when the myosin and actin filaments slide across each other. • what actually occurs is myosin pulls the actin in. • this shortens the muscle and is a muscle contraction. sarcomere and muscle contraction • during muscle contraction in the sarcomere: • the z. Presentation transcript. the sliding filament theory. microstructure of skeletal muscle (recap) actin myosin orientation: • myosin filament (thick). • have long rod shaped tails with 2 globular heads. • the heads form cross bridges. microstructure of skeletal muscle (recap) • actin filament (thin). • tropomyosin is a rigid, rod shaped. The document discusses the sliding filament theory of muscle contraction. it explains that [1] muscle fibers contain myofibrils with interlacing actin and myosin filaments, [2] when muscles contract, the filaments slide past each other in a process called the sliding filament theory, and [3] contraction occurs as myosin heads pull actin filaments inward through atp hydrolysis, shortening the. Powerpoint presentation. anatomy and physiology i. muscle structure and contraction. instructor: mary holman. muscle functions produce body movements stabilize body position regulate organ volume move fluids and solid food and wastes in the body produce heat properties of muscle tissue electrical excitability contractility extensibility.

Comments are closed.