Ppt Pharmacodynamics Mechanism Of Drug Action Receptor Pharmacology
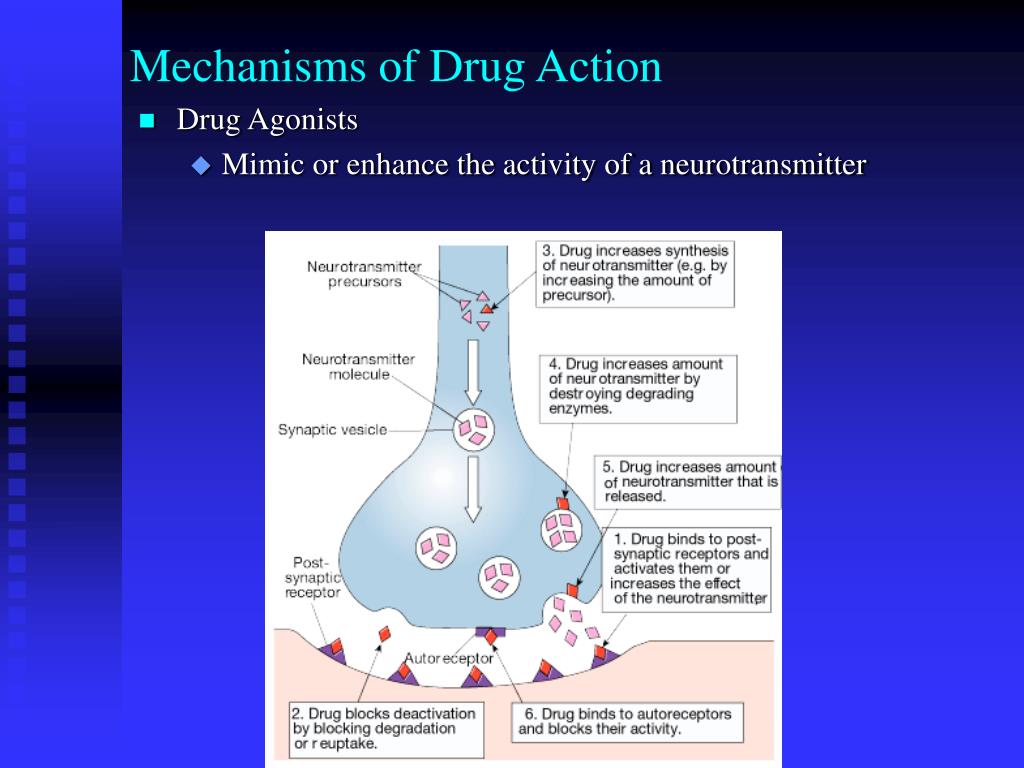
Ppt Mechanisms Of Drug Action Powerpoint Presentation Free Download 8. some common terms • agonist: an agent which activates a receptor to produce an effect similar to a that of the physiological signal molecule, e.g. muscarine and nicotine • antagonist: an agent which prevents the action of an agonist on a receptor or the subsequent response, but does not have an effect of its own, e.g. atropine and muscarine • inverse agonist: an agent which activates. Pharmacodynamics, mechanism of drug action. nov 17, 2019 • download as pptx, pdf •. 15 likes • 1,627 views. a. asma aslam. follow. complete information on receptors and their mechanism of actions briefly discussed about pharmacodynamics and up regulation and desensitization of receptors, read more. 1 of 69.

Ppt Pharmacodynamics Mechanism Of Drug Action Receptor Pharmacology Mechanism of drug action. 1. drugs can interact with receptors, ion channels, enzymes, and carrier molecules in cells. 2. receptor mediated mechanisms involve drugs binding to receptors, forming drug receptor complexes that trigger biological responses. non receptor mechanisms do not involve receptors. 3. Antagonism: when one drug decreases or abolishes the action of another, they are said to be antagonistic • effect of drugs a b < effect of drug a effect of drug b • usually in an antagonistic pair one drug is inactive as such but decreases the effect of the other • depending on the mechanism involved, antagonism may be • physical. Presentation transcript. introduction pharmacodynamics: study of the biochemical and physiologic effects of drugs and their mechanisms of action. drug action • the main ways by which drugs act are via interaction with cell proteins, namely receptors, ion channels, enzymes and transport carrier proteins. Pharmacodynamics phl 315 (423 2020) reference: basic & clinical pharmacology bertram g. katzung, md, phd 14th edition. slide 3 . pharmacodynamics pharmacodynamics describes the actions of a drug the actions of a drug on the body and the influence of drug concentrations on the magnitude of the response. types of drug action: stimulation 2.

Mechanism Of Drug Action Pharmacodynamics Youtube Presentation transcript. introduction pharmacodynamics: study of the biochemical and physiologic effects of drugs and their mechanisms of action. drug action • the main ways by which drugs act are via interaction with cell proteins, namely receptors, ion channels, enzymes and transport carrier proteins. Pharmacodynamics phl 315 (423 2020) reference: basic & clinical pharmacology bertram g. katzung, md, phd 14th edition. slide 3 . pharmacodynamics pharmacodynamics describes the actions of a drug the actions of a drug on the body and the influence of drug concentrations on the magnitude of the response. types of drug action: stimulation 2. 2. introduction to drug receptor interactions and pharmacodynamics receptors: protein molecules including enzymes, transporters and ion channels where a ligand (specific endogenous neurotransmitter hormone or an external pharmacological agent (drug)) binds to, resulting in a cellular response. unique exception: orphan receptors are receptors. Overview of pharmacodynamics clinical pharmacology.

Mechanisms Of Drug Action And Pharmacodynamics Pharmacology An 2. introduction to drug receptor interactions and pharmacodynamics receptors: protein molecules including enzymes, transporters and ion channels where a ligand (specific endogenous neurotransmitter hormone or an external pharmacological agent (drug)) binds to, resulting in a cellular response. unique exception: orphan receptors are receptors. Overview of pharmacodynamics clinical pharmacology.

Comments are closed.