Ppt Pythagorean Theorem And Its Converse Powerpoint Presentation
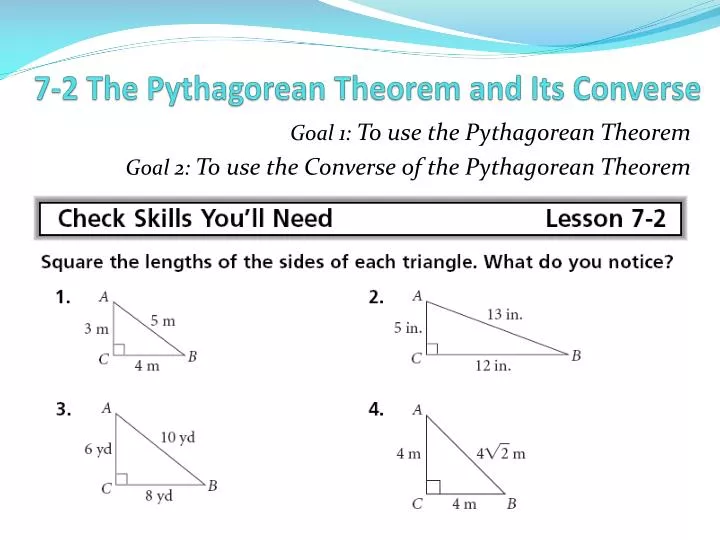
Ppt 7 2 The Pythagorean Theorem And Its Converse Powerpoint Pythagorean theorem and its converse. lesson 11.4 notes. pythagorean theorem. the pythagorean theorem is one of the most converse of the pythagorean thrm. – a free powerpoint ppt presentation (displayed as an html5 slide show) on powershow id: 33f24 ngnjm. Pythagorean theorem and its converse. section 8 1. pythagorean theorem. in a right triangle the sum of the squares of the measures of the legs equals the square of the measure of the hypotenuse. a 2 b 2 = c 2. c. hypotenuse. a. leg. b. leg. example 1.
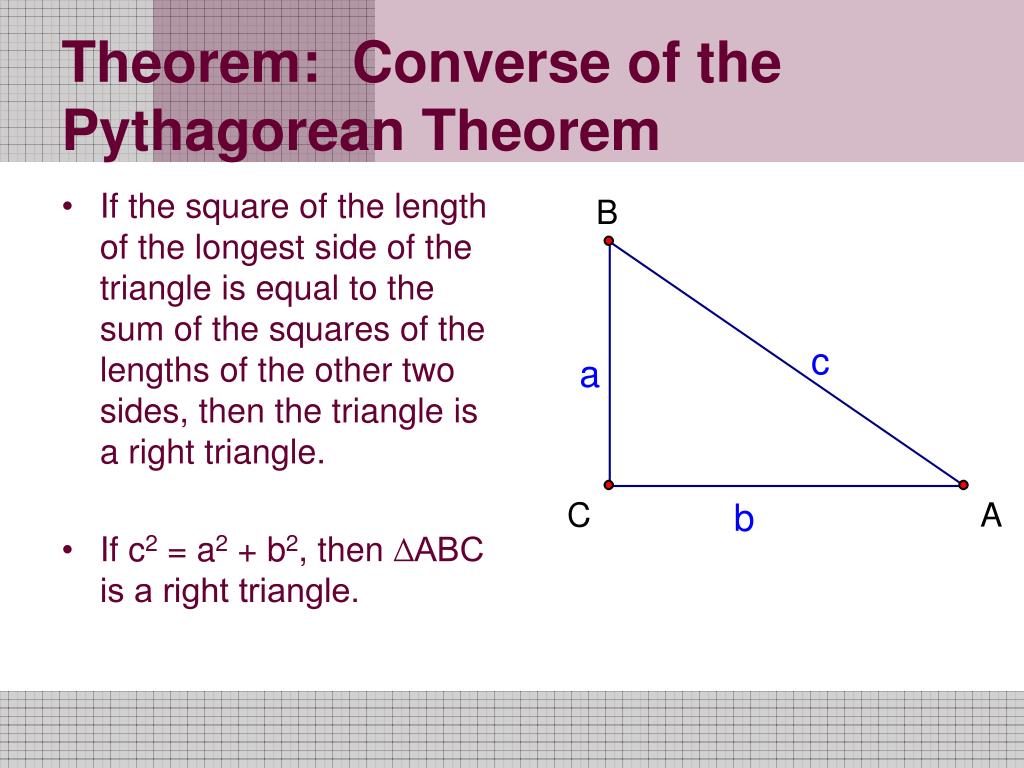
Ppt The Converse Of The Pythagorean Theorem Powerpoint Presentation Step 1: write the formula. step 3: simplify the side without the “c” by squaring the two numbers and adding them together. we are not done yet…. step 2: substitute or “plug in” the lengths of the legs into the pythagorean theorem for the “a” and “b” variables. step 4: solve for c by using the square root. Presentation on theme: "pythagorean theorem and its converse"— presentation transcript: 1 pythagorean theorem and its converse objective to use the pythagorean theorem and its converse essential understanding: if you know the lengths of any two sides of a right triangle, you can find the length of the third side by using the pythagorean theorem. The pythagorean theorem and its converse lesson 8 1 additional examples pythagorean triples a2 b2 = c2use the pythagorean theorem. 162 302 = c2substitute 16 for a and 30 for b. 256 900 = c2simplify. 1156 = c2 34 = ctake the square root. the length of the hypotenuse is 34. the lengths of the sides, 16, 30, and 34, form a pythagorean triple. Ai enhanced description. l. lmrogers03. this document discusses the pythagorean theorem and its converse. it explains that if the square of one side of a triangle is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides, then the triangle is a right triangle. it provides examples of determining if triangles are acute, right, or obtuse by.

Comments are closed.