Ppt Sequences And Mathematical Induction Powerpoint Presentation
Ppt Sequences And Mathematical Induction Powerpoint Presentation Chapter 4: sequences and mathematical induction 4.1 sequences . 4.2 , 4.3 mathematical induction 4.4 strong mathematical induction and wop instructor: hayk melikya [email protected]. a sequence (informally) is a collection of elements (objects or numbers usually infinite number of) indexed by integers. sequences examples each individual. Recursive algorithms are often shorter, more elegant, and easier to understand than their iterative counterparts. however, iterative algorithms are usually more efficient in their use of space and time. chapter 3 sequences mathematical induction recursion sequences sequences sequences represent ordered lists of elements.
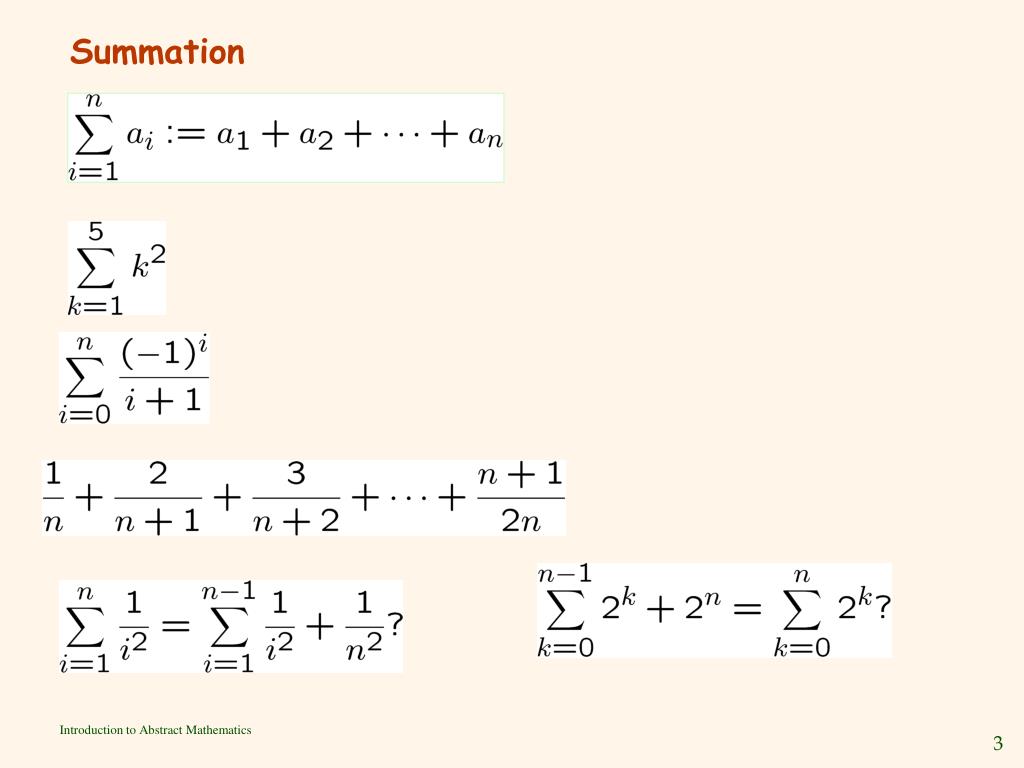
Ppt Chapter 4 Sequences And Mathematical Induction Powerpoint 4.1 sequences . 4.2 , 4.3 mathematical induction 4.4 strong mathematical induction and wop instructor: hayk melikya [email protected] * * but if m0, n0 had common – a free powerpoint ppt presentation (displayed as an html5 slide show) on powershow id: 4a66ee njnmz. Sequence and series | ppt. Mathematical induction is a powerful method to prove properties for natural numbers, playing a crucial role in discrete mathematics and computer science. it is closely linked to recursion and well ordering principles, essential in analyzing sequences and recursive algorithms. this summary introduces the definitions of sequences, terms, and explicit formulas, emphasizing the importance of. A sequence can be finite or infinite. the sequence has a last term or final term. (such as seq. 1) the sequence continues without stopping. (such as seq. 2) both sequences have a general rule: an = 2n where n is the term # and an is the nth term. the general rule can also be written in function notation: f (n) = 2n.

Comments are closed.