Ppt Transition Metals And Coordination Compounds Powerpoint
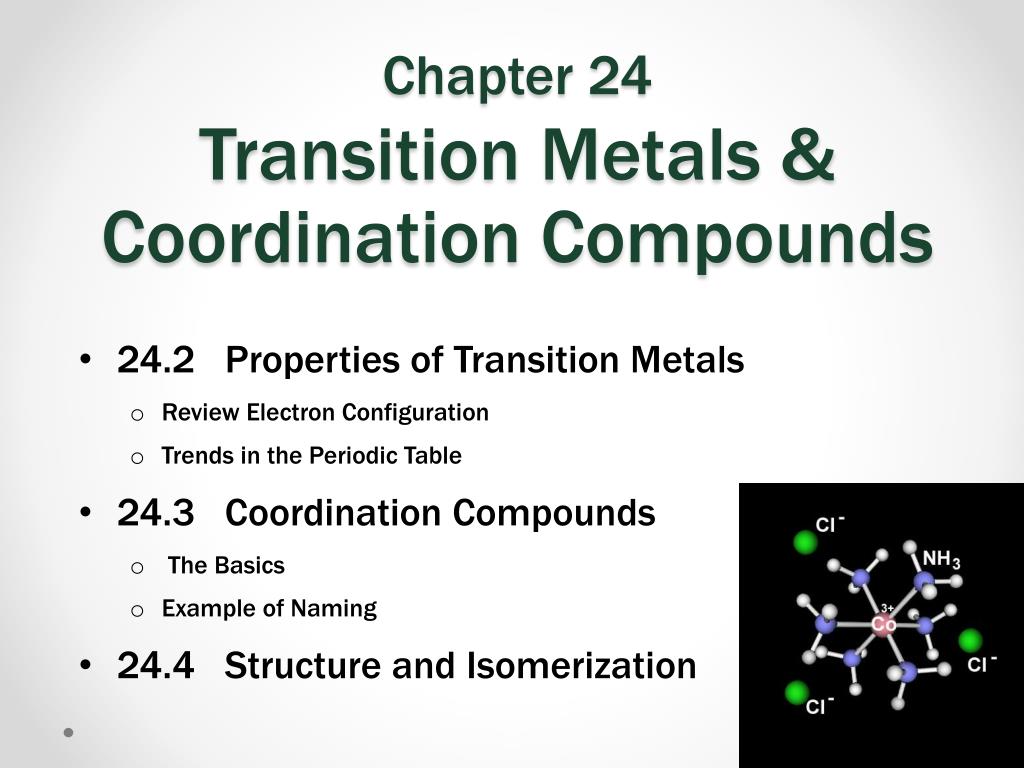
Ppt Chapter 24 Transition Metals Coordination Compounds Powerpointо Faculty. steven dessens. notes and practice problems. chem 1412 general chemistry ii (with lab) chem 1412 previous textbook powerpoints. chem 1412 chang powerpoints. chapter 22 transition metal chemistry and coordination compounds. Transition metals. this document provides information about transition metals and their coordination compounds. it discusses the key characteristics of transition metals, including having multiple oxidation states and forming colored compounds. transition metals form coordination complexes by acting as lewis acids and coordinating with ligands.
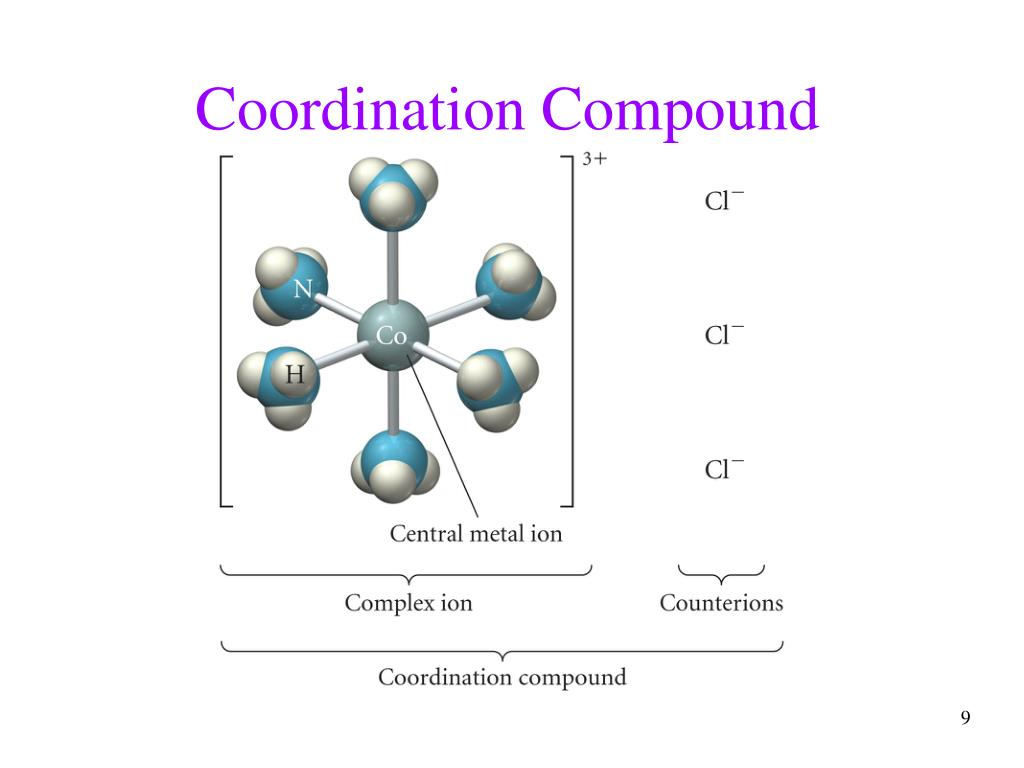
Ppt Transition Metals And Coordination Compounds Powerpoint Exception to the trend: there is an increase in electronegativity from the 3d (1st row transition metals) to the 4d (2nd row transition metals). oxidation states in general, stability is found in full or half full shells, and in a configuration that looks like a noble gas. geometries anne marie helmenstine, ph.d., about guide. chapter 24. 13. properties of the transition metals all transition metals are metals, whereas main group elements in each period change from metal to nonmetal many transition metal compounds are colored and paramagnetic, whereas most main group ionic compounds are colorless and diamagnetic the properties of transition metal compounds are related to the electron configuration of the metal ion . The complex ion co (nh3)63 . ionic compounds with transition metals • most compounds are colored because the transition metal ion in the complex ion can absorb visible light of specific wavelengths. • many compounds are paramagnetic. electron configurations • example • v: [ar]4s23d3 • fe: [ar]4s23d6 • exceptions: cr and cu • cr. Coordination compounds • alfred werner in the 1890’s • transition metals have two types of valence (combining abilities) • primary valence – ability to form ionic bonds with oppositely charged ions • secondary valence – ability to to bind to lewis bases (ligands) to form complex ions.
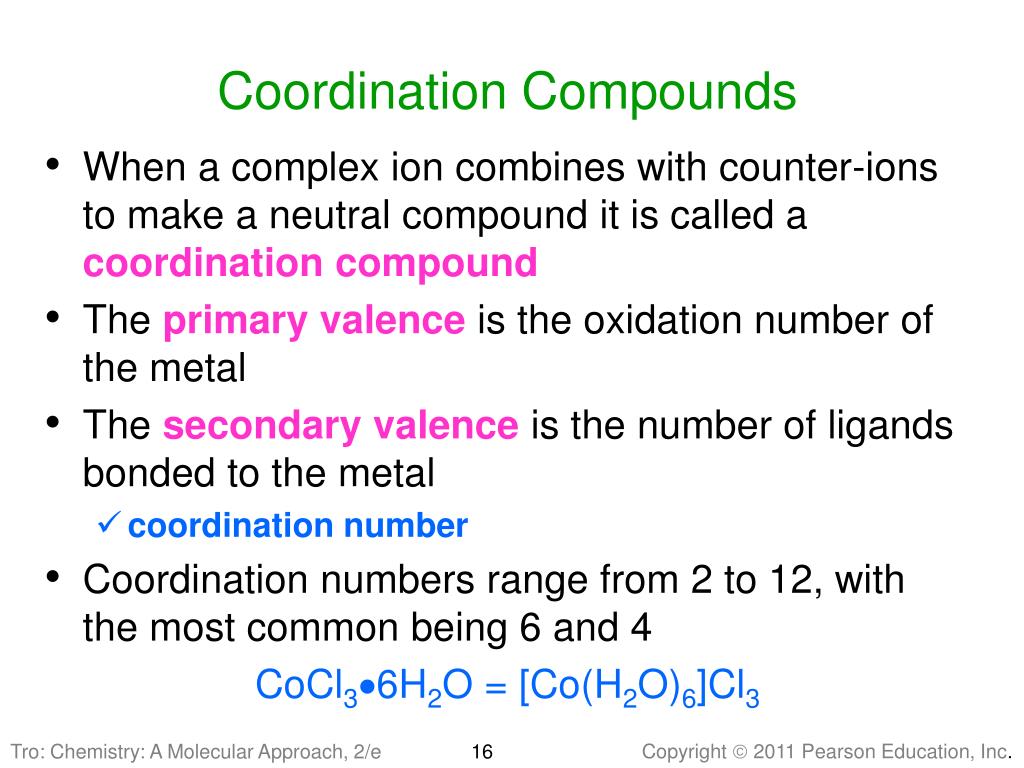
Ppt Chapter 24 Transition Metals And Coordination Compounds The complex ion co (nh3)63 . ionic compounds with transition metals • most compounds are colored because the transition metal ion in the complex ion can absorb visible light of specific wavelengths. • many compounds are paramagnetic. electron configurations • example • v: [ar]4s23d3 • fe: [ar]4s23d6 • exceptions: cr and cu • cr. Coordination compounds • alfred werner in the 1890’s • transition metals have two types of valence (combining abilities) • primary valence – ability to form ionic bonds with oppositely charged ions • secondary valence – ability to to bind to lewis bases (ligands) to form complex ions. It begins by introducing coordination compounds and providing examples like chlorophyll and hemoglobin. it then summarizes werner's theory of coordination compounds from 1898, which proposed that metals form primary ionic bonds and secondary non ionic bonds of fixed coordination number with ligands in coordination spheres. the document defines. Title: transition metals and coordination chemistry 1 chapter 20. transition metals and coordination chemistry; 2 chapter 20 transition metals and coordination chemistry. 20.1 the transition metals a survey 20.2 the first row transition metals 20.3 coordination compounds 20.4 isomerism 20.5 bonding in complex ions the localized electron model 20.6.

Ppt Chapter 24 Transition Metals Coordination Compounds Powerpointо It begins by introducing coordination compounds and providing examples like chlorophyll and hemoglobin. it then summarizes werner's theory of coordination compounds from 1898, which proposed that metals form primary ionic bonds and secondary non ionic bonds of fixed coordination number with ligands in coordination spheres. the document defines. Title: transition metals and coordination chemistry 1 chapter 20. transition metals and coordination chemistry; 2 chapter 20 transition metals and coordination chemistry. 20.1 the transition metals a survey 20.2 the first row transition metals 20.3 coordination compounds 20.4 isomerism 20.5 bonding in complex ions the localized electron model 20.6.

Ppt Transition Metal Chemistry And Coordination Compounds Powerpoin

Comments are closed.