Preventing Surgical Site Infections By D Morrow Openpediatrics

Preventing Surgical Site Infections By D Morrow Openpediatrics Youtube Learn about strategies to prevent surgical site infections, and risk factors for surgical site infections in pediatric cardiac patients.direct links to chapt. Guideline for the prevention of surgical site infection (1999) organ transplantation. sources print share. national center for emerging and zoonotic infectious diseases (ncezid) occupationally acquired infections and healthcare workers. updated recommendations on chlorhexidine impregnated (c i) dressings.
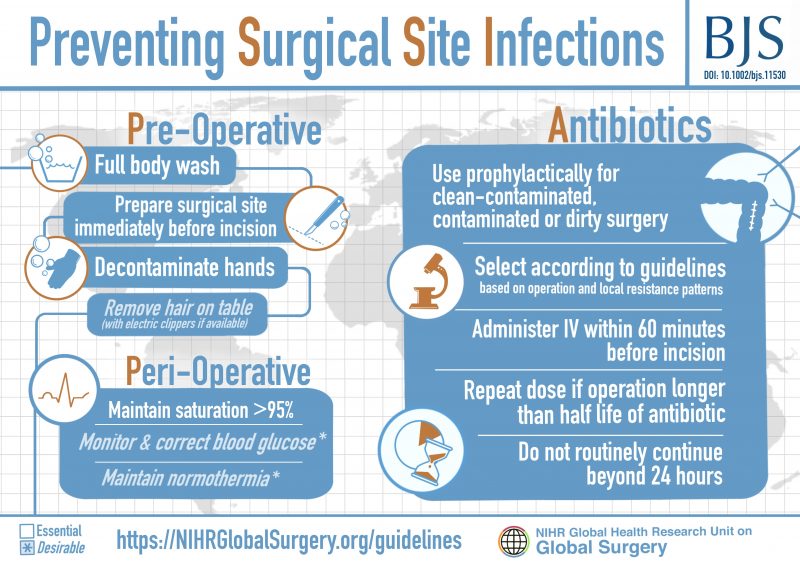
Global Guidelines For Prevention Of Surgical Site Infection Published This guideline covers preventing and treating surgical site infections in adults, young people and children who are having a surgical procedure involving a cut through the skin. it focuses on methods used before, during and after surgery to minimise the risk of infection. Surgical site infections (ssis) are infections of the incision or organ or space that occur after surgery. 1 surgical patients initially seen with more complex comorbidities 2 and the emergence of antimicrobial resistant pathogens increase the cost and challenge of treating ssis. 3 5 the prevention of ssi is increasingly important as the number. The first ever global guidelines for the prevention of surgical site infection (ssi) were published on 3 november 2016, then updated in some parts and published in a new edition in december 2018. they include a list of 29 concrete recommendations on 23 topics for the prevention of ssi in the pre , intra and postoperative periods, which are based on 28 systematic reviews of the evidence. 58570. laparoscopy, surgical, with total hysterectomy, for uterus 250 g or less. note: scope is reported based on the primary incision site. if an open and scope code is assigned to procedures in the same nhsn procedure category, then the procedure should be reported to nhsn as scope = no.

Text Preventing Surgical Site Infections Healthclips Online The first ever global guidelines for the prevention of surgical site infection (ssi) were published on 3 november 2016, then updated in some parts and published in a new edition in december 2018. they include a list of 29 concrete recommendations on 23 topics for the prevention of ssi in the pre , intra and postoperative periods, which are based on 28 systematic reviews of the evidence. 58570. laparoscopy, surgical, with total hysterectomy, for uterus 250 g or less. note: scope is reported based on the primary incision site. if an open and scope code is assigned to procedures in the same nhsn procedure category, then the procedure should be reported to nhsn as scope = no. The cdc defines an ssi as an infection related to a surgical procedure that occurs near the surgical site within 30 days following surgery (or up to 90 days following surgery where an implant is involved) [ 5,6 ]. incisional ssis are further divided into those involving only skin and subcutaneous tissues (superficial incisional ssi) and those. Conclusions and relevancesurgical site infections affect approximately 0.5% to 3% of patients undergoing surgery and are associated with longer hospital stays than patients with no surgical site infections. avoiding razors for hair removal, maintaining normothermia, use of chlorhexidine gluconate plus alcohol–based skin preparation agents.

Comments are closed.