Prevention Of Surgical Site Infection By Paul Anderson M D M S

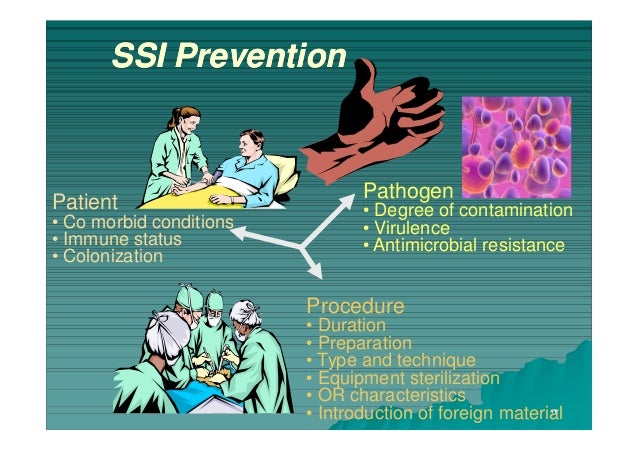
Prevention Of Surgical Site Infection Beyond Scip Anderson 2014 Prevention of surgical site infection was presented by paul anderson, m.d., m.s at the seattle science foundation for the 3rd annual one spine masters course. These infections are typically caused when bacteria from the patient's endogenous flora are inoculated into the surgical site at the time of surgery. development of an infection depends on various factors such as the health of the patient's immune system, presence of foreign material, degree of bacterial wound contamination, and use of.

Ppt Prevention Of Surgical Site Infections Powerpoint Presentation Surgical site infections (ssis) are infections of the incision or organ or space that occur after surgery. 1 surgical patients initially seen with more complex comorbidities 2 and the emergence of antimicrobial resistant pathogens increase the cost and challenge of treating ssis. 3 5 the prevention of ssi is increasingly important as the number. Correspondence: paul a. anderson, md, department of orthopedics and rehabilitation, university of wisconsin, uwmf centennial bldg, 1685 highland ave, 6th floor madison, wi 53705. e mail: [email protected]. A surgical site infection is defined as infection following an operation at an incision site or adjacent to the surgical incision. 1 infections occur in approximately 0.5% to 3% of patients undergoing surgery 2 4 and are among the most prevalent health care–acquired infections. 5 7 surgical site infections are responsible for. A surgical site infection is defined as infection following an. operation at an incision site or adjacent to the surgical. incision. 1. infections occur in approximately 0.5%to 3% of. patients.
Prevention Of Surgical Site Infection Ssi Compatibility Mode A surgical site infection is defined as infection following an operation at an incision site or adjacent to the surgical incision. 1 infections occur in approximately 0.5% to 3% of patients undergoing surgery 2 4 and are among the most prevalent health care–acquired infections. 5 7 surgical site infections are responsible for. A surgical site infection is defined as infection following an. operation at an incision site or adjacent to the surgical. incision. 1. infections occur in approximately 0.5%to 3% of. patients. The united states centers for disease control and prevention has developed criteria that define surgical site infection (ssi) as infection related to an operative procedure that occurs at or near the surgical incision (incisional or organ space) within 30 days of the procedure or within 90 days if prosthetic material is implanted at surgery [ 8 ]. Surgical site infection (ssi) occurs in up to 5% of patients following an inpatient surgical procedure, increasing average hospital length of stay by 9.7 days, risk of mortality by 2 to 11 fold, and costs of hospitalization by more than $20 000 per admission. 1 ssis are defined as either superficial (confined to the skin or subcutaneous tissue), deep (involving the muscle or fascia layers.

Ppt Prevention Of Surgical Site Infections Powerpoint Presentation The united states centers for disease control and prevention has developed criteria that define surgical site infection (ssi) as infection related to an operative procedure that occurs at or near the surgical incision (incisional or organ space) within 30 days of the procedure or within 90 days if prosthetic material is implanted at surgery [ 8 ]. Surgical site infection (ssi) occurs in up to 5% of patients following an inpatient surgical procedure, increasing average hospital length of stay by 9.7 days, risk of mortality by 2 to 11 fold, and costs of hospitalization by more than $20 000 per admission. 1 ssis are defined as either superficial (confined to the skin or subcutaneous tissue), deep (involving the muscle or fascia layers.

Prevention Of Surgical Site Infection вђ Orthopaedicprinciples

Comments are closed.