Proning Position Solusi Tepat Atasi Sesak Nafas Di Masa Pandemi Covid 19
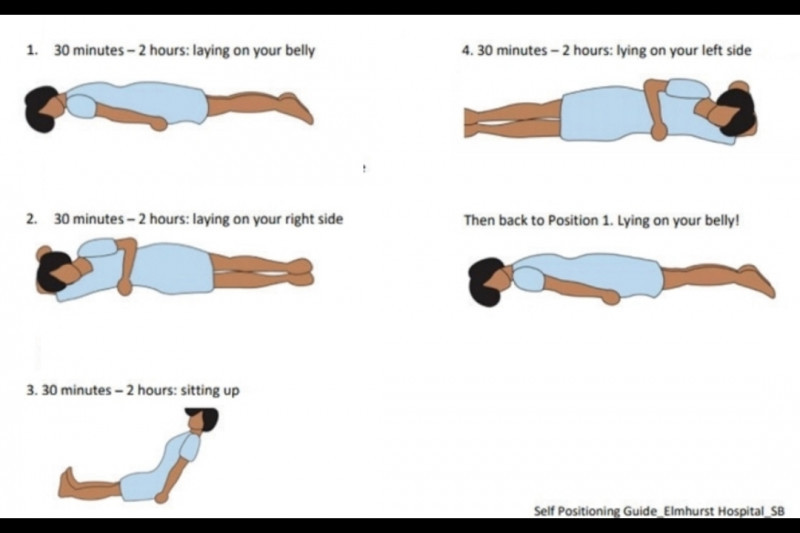
Mengenal Proning Dan Kegunaannya Untuk Pasien Covid 19 Antara News Proning position solusi tepat atasi sesak nafas di masa pandemi covid 19. oleh : sugianto.,skep.ns dari rsup dr.kariadi . sahabat sehat, proning position berasal dari bahasa latin “pronus ‘ yang artinya condong kedepan dan position dari bahas inggris, yang artinya posisi atau sikap badan. When you have covid 19, lying on your belly can help your lungs work better. it can help get more oxygen into your lungs more easily. it can help prevent lung injury. lying on your belly is known as the prone position. you may also hear it called proning. if you’re in the hospital, the healthcare team may position you to help your lungs.

Laman Resmi Republik Indonesia Portal Informasi Indonesia Atasi sesak napas, ini 3 posisi proning position yang bisa dilakukan di rumah. proning position kini dikenal masyarakat, khususnya pasien covid 19. pasien biasanya akan mengalami sesak napas atau gangguan pernapasan. karenanya, tabung oksigen yang sangat dibutuhkan pun menjadi sangat langka dan sulit didapatkan saat ini. Sleman pasien covid 19 yang mengalami sesak nafas dan mengalami penurunan saturasi oksigen bisa diatasi dengan teknik proning (tengkurap). hanya saja teknik ini merupakan pertolongan pertama atau sementara sebelum mendapatkan dukungan oksigen dan perawatan di rumah sakit. “posisi prone (tengkurap) bisa membantu menaikan saturasi oksigen. During the coronavirus disease 2019 (covid 19) pandemic, the use of prone position has been exponential. a rate of use of prone as high as 70% or more has been reported in large prospective cohorts [1 , 2 , 3 ], to be compared with less than 20% before the pandemic [4, 5]. this finding was observed even though the level of evidence and the. Results. pp was applied in 21 patients who were breathing spontaneously. the application of pp was associated with a significant increase in oxygen saturation measured by pulse oximetry (spo 2) from 82%±12% to 96%±3% (p<0.001) 1 hour later. moreover, pp was associated with a significant reduction in respiratory rate from 31±10 to 21±4.

Comments are closed.