Proving The Triangle Sum Theorem

Proving The Triangle Sum Theorem Youtube Example 1: one of the acute angles of a right angled triangle is 45°. find the other angle using the triangle sum theorem. identify the type of triangle thus formed. solution: given, ∠1 = 90° (right triangle) and ∠2 = 45°. we know that the sum of the angles of a triangle adds up to 180°. Hypothesis: from the triangle sum theorem, the sum of all three angles equals 180°. again, from the definition of an equilateral triangle, all angles are of equal measure. adding up all the angles, we get, ⇒ x x x = 180°. ⇒ 3x = 180°. ⇒ x = 60°. conclusion: each angle in an equilateral triangle measures 60°. what is the triangle.

Triangle Sum Theorem вђ Definition Proof Examples Practice: triangle angle sum theorem real world: triangle sum theorem this page titled 4.17: triangle angle sum theorem is shared under a ck 12 license and was authored, remixed, and or curated by ck 12 foundation via source content that was edited to the style and standards of the libretexts platform. 1. draw a line parallel to side bc of the triangle that passes through the vertex a. label the line pq. construct this line parallel to the bottom of the triangle. [1] 2. write the equation angle pab angle bac angle caq = 180 degrees. remember, all of the angles that comprise a straight line must be equal to 180°. The angle sum property of a triangle theorem states that the sum of all three internal angles of a triangle is 180 ∘. it is also known as the angle sum theorem or triangle sum theorem. according to the angle sum theorem, in the above abc, m ∠ a m ∠ b m ∠ c = 180 ∘. example: in pqr, ∠ p = 60 ∘, ∠ q = 70 ∘. The sum of the three interior angles in a triangle is always 180°. the triangle sum theorem is also called the triangle angle sum theorem or angle sum theorem. example: find the value of x in the following triangle. solution: x 24° 32° = 180° (sum of angles is 180°) x 56° = 180°. x = 180° – 56° = 124°.
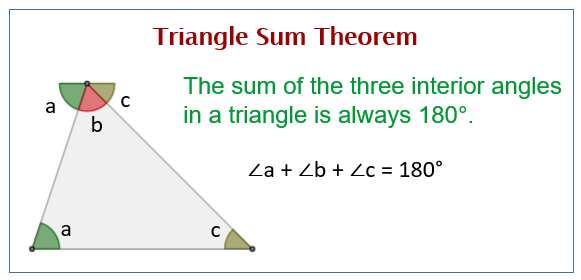
Triangle Sum Theorem Solutions Examples Worksheets Videos The angle sum property of a triangle theorem states that the sum of all three internal angles of a triangle is 180 ∘. it is also known as the angle sum theorem or triangle sum theorem. according to the angle sum theorem, in the above abc, m ∠ a m ∠ b m ∠ c = 180 ∘. example: in pqr, ∠ p = 60 ∘, ∠ q = 70 ∘. The sum of the three interior angles in a triangle is always 180°. the triangle sum theorem is also called the triangle angle sum theorem or angle sum theorem. example: find the value of x in the following triangle. solution: x 24° 32° = 180° (sum of angles is 180°) x 56° = 180°. x = 180° – 56° = 124°. Theorem 1: angle sum property of triangle states that the sum of interior angles of a triangle is 180°. proof: consider a ∆abc, as shown in the figure below. to prove the above property of triangles, draw a line pq parallel to the side bc of the given triangle. since pq is a straight line, it can be concluded that:. Triangle sum theorem. 1. start with Δabc Δ a b c. extend bc¯ ¯¯¯¯ b c ¯ to point d d. line bd b d will be a transversal. 2. draw line ec e c parallel to segment ab a b. draw transversal ac←→ a c ↔. 3. corresponding angles are congruent.
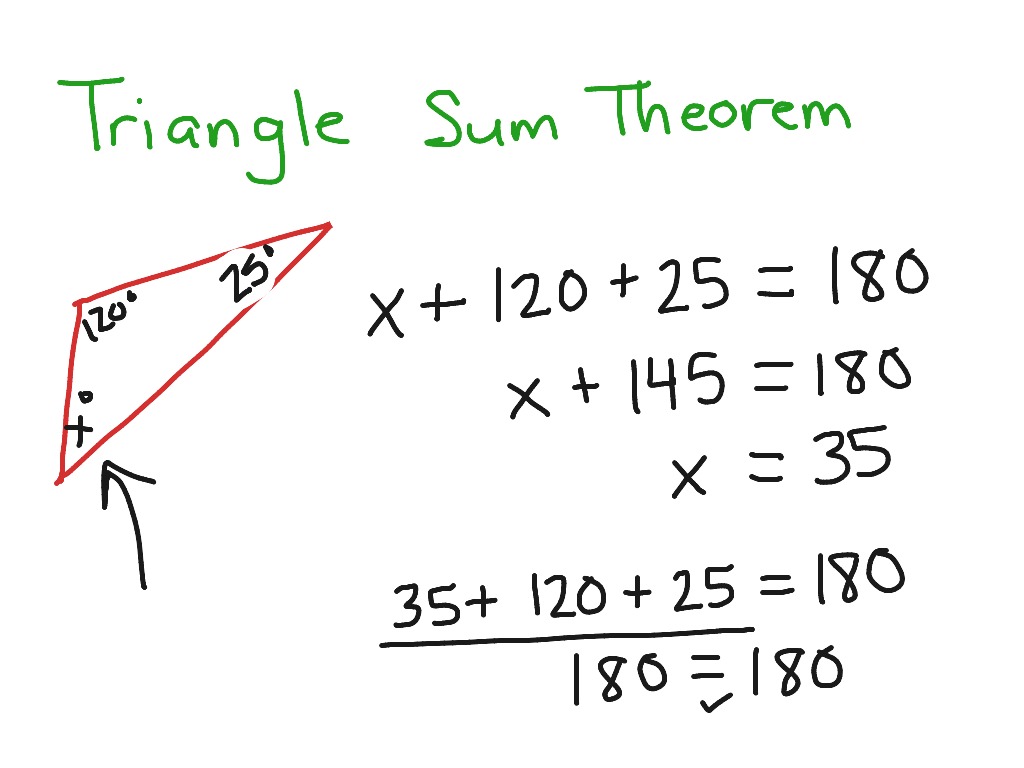
Triangle Sum Theorem Math Geometry Showme Theorem 1: angle sum property of triangle states that the sum of interior angles of a triangle is 180°. proof: consider a ∆abc, as shown in the figure below. to prove the above property of triangles, draw a line pq parallel to the side bc of the given triangle. since pq is a straight line, it can be concluded that:. Triangle sum theorem. 1. start with Δabc Δ a b c. extend bc¯ ¯¯¯¯ b c ¯ to point d d. line bd b d will be a transversal. 2. draw line ec e c parallel to segment ab a b. draw transversal ac←→ a c ↔. 3. corresponding angles are congruent.

Comments are closed.