Pythagoras Theorem Finding An Unknown Side In A Right Angled
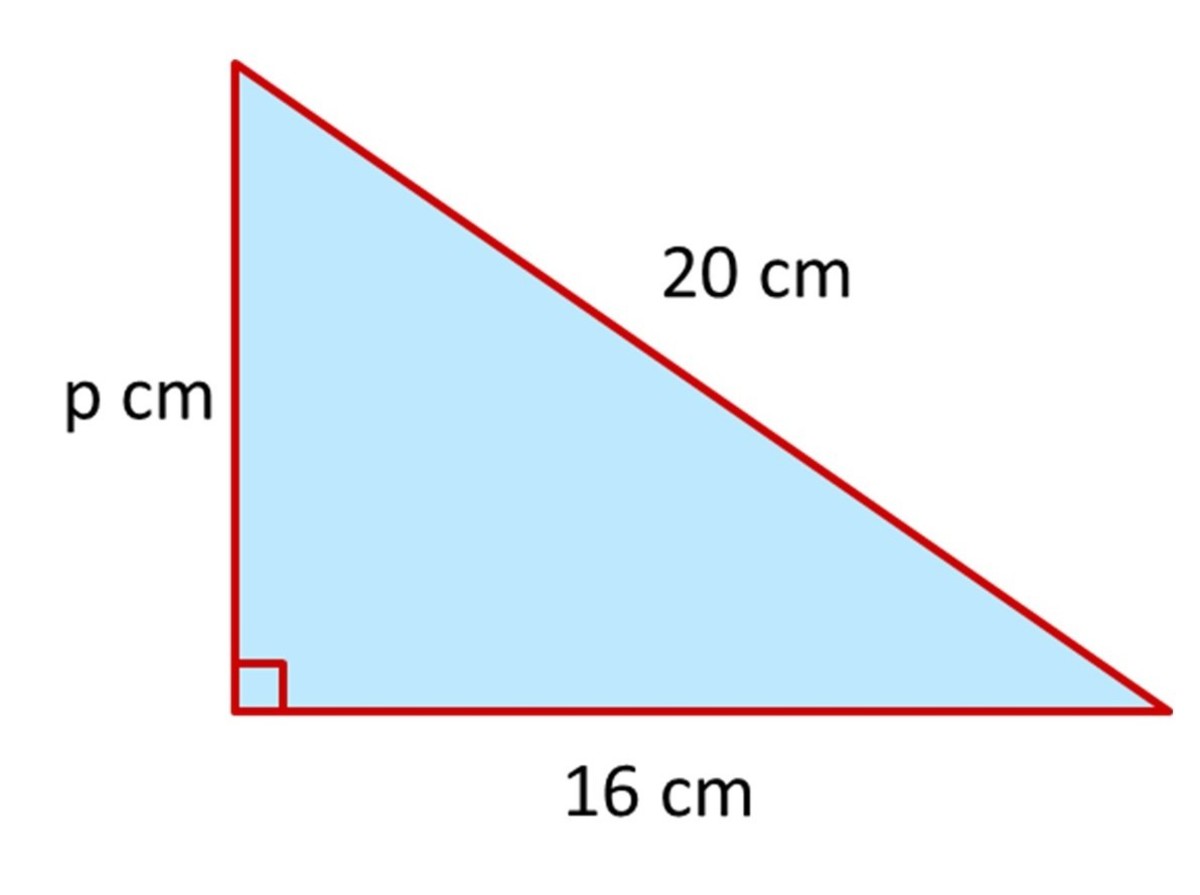
How To Use Pythagoras Theorem To Find Missing Sides On Right Angled Pythagoras' theorem, or the pythagorean theorem, can be used to find unknown sides in right angled triangles. in this video we learn how to do that. the theo. Pythagoras' theorem states that for any right angled triangle, the square on the hypotenuse (the longest of the three sides) is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides. put more simply, if we square the lengths of the two shorter sides and add the answers together, our final answer will equal the length of the hypotenuse squared.
How To Use Pythagoras Theorem To Find Missing Sides On Right Angled Pythagoras theorem formula, proof, examples. Pythagoras theorem formula, proof, examples byju's. Pythagoras theorem. The pythagorean theorem states that the square of the longest side of a right triangle (called the hypotenuse) is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides. pythagorean theorem formula shown with triangle abc is: a^2 b^2=c^2 . side c is known as the hypotenuse. the hypotenuse is the longest side of a right triangle. side a and side.
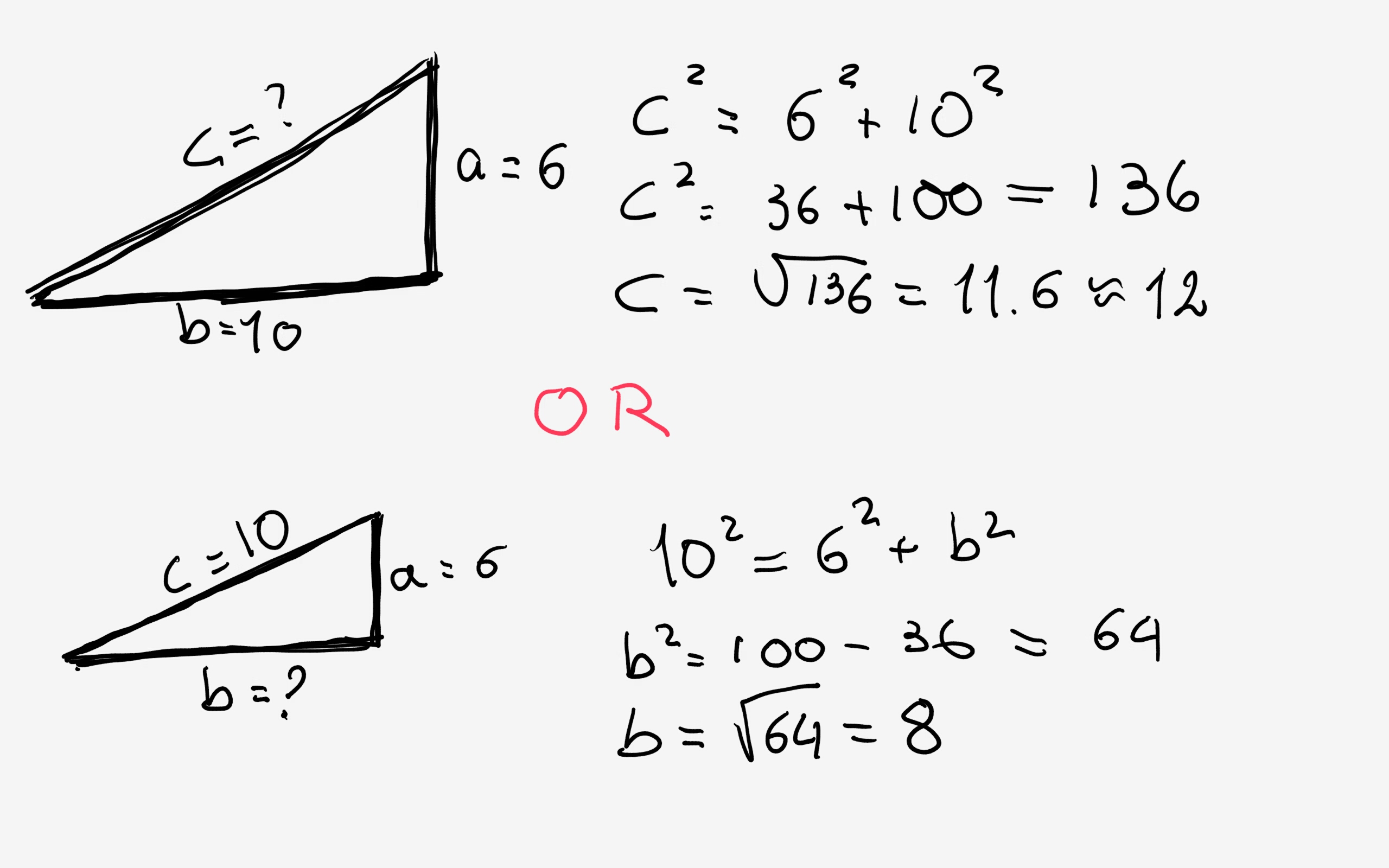
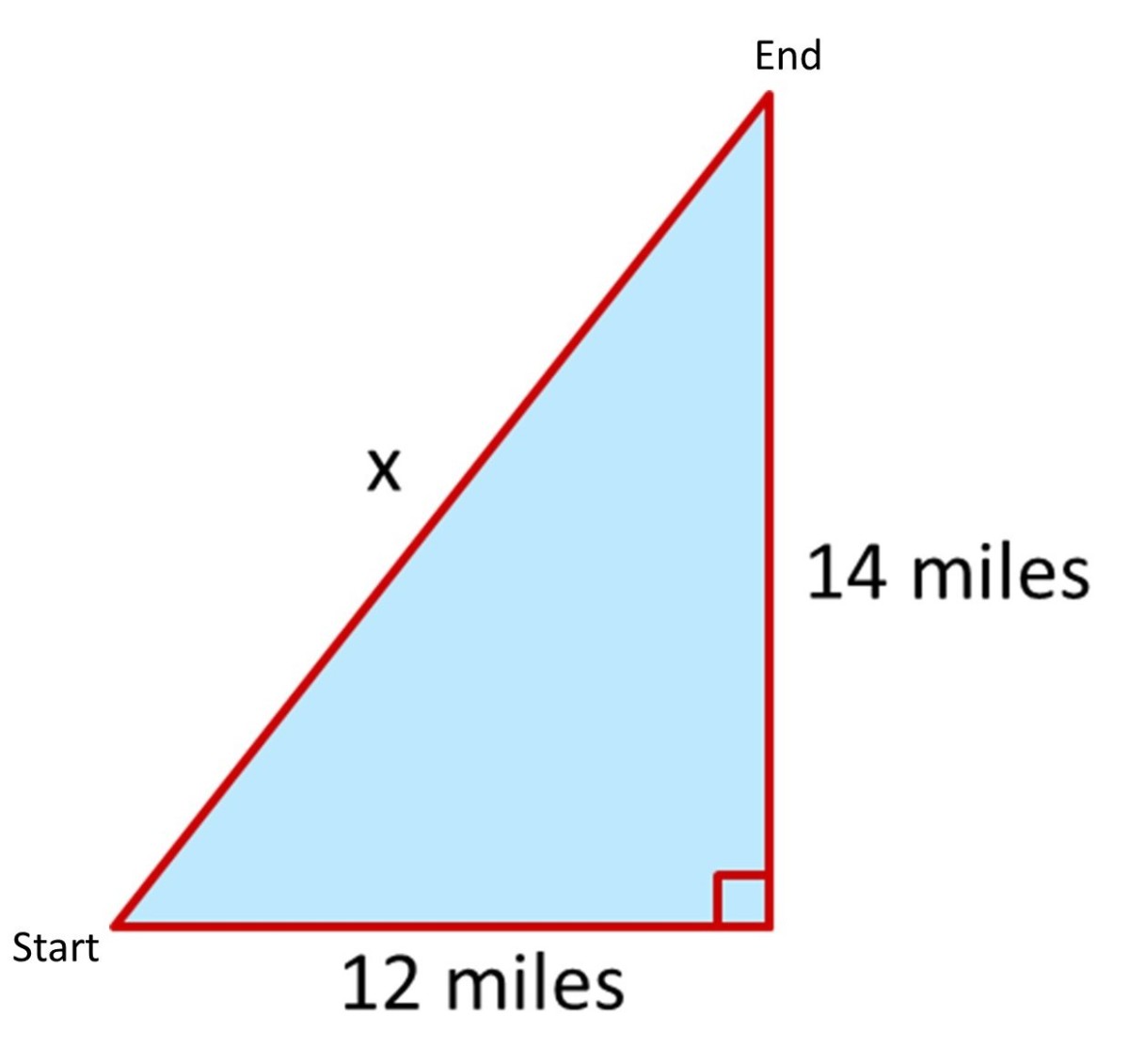
Finding Side Lengths Of A Right Triangle Using The Pythagorean Theorem Pythagoras theorem. The pythagorean theorem states that the square of the longest side of a right triangle (called the hypotenuse) is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides. pythagorean theorem formula shown with triangle abc is: a^2 b^2=c^2 . side c is known as the hypotenuse. the hypotenuse is the longest side of a right triangle. side a and side. Example 2 (solving for a leg) use the pythagorean theorem to determine the length of x. step 1. identify the legs and the hypotenuse of the right triangle. the legs have length 24 and x x are the legs. the hypotenuse is 26. step 2. substitute values into the formula (remember 'c' is the hypotenuse). a2 b2 = c2 x2 242 = 262 a 2 b 2 = c 2 x. Solution. since this is a right angle triangle, we can use pythagoras' theorem to find the unknown side length. using the formula for the theorem: c2 = a2 b2 c 2 = a 2 b 2. where c c is the hypotenuse (side length opposite the right angle), we replace a a by 8 8, b b by 6 6 and c c by x x, which leads to: x2 = 82 62 x 2 = 8 2 6 2.

Pythagoras Theorem Finding An Unknown Side In A Right Angled Example 2 (solving for a leg) use the pythagorean theorem to determine the length of x. step 1. identify the legs and the hypotenuse of the right triangle. the legs have length 24 and x x are the legs. the hypotenuse is 26. step 2. substitute values into the formula (remember 'c' is the hypotenuse). a2 b2 = c2 x2 242 = 262 a 2 b 2 = c 2 x. Solution. since this is a right angle triangle, we can use pythagoras' theorem to find the unknown side length. using the formula for the theorem: c2 = a2 b2 c 2 = a 2 b 2. where c c is the hypotenuse (side length opposite the right angle), we replace a a by 8 8, b b by 6 6 and c c by x x, which leads to: x2 = 82 62 x 2 = 8 2 6 2.

How To Find A Missing Side In A Right Angled Triangle Pythagoras

Comments are closed.