Pythagorean Theorem For A Right Triangle Formula And Problems
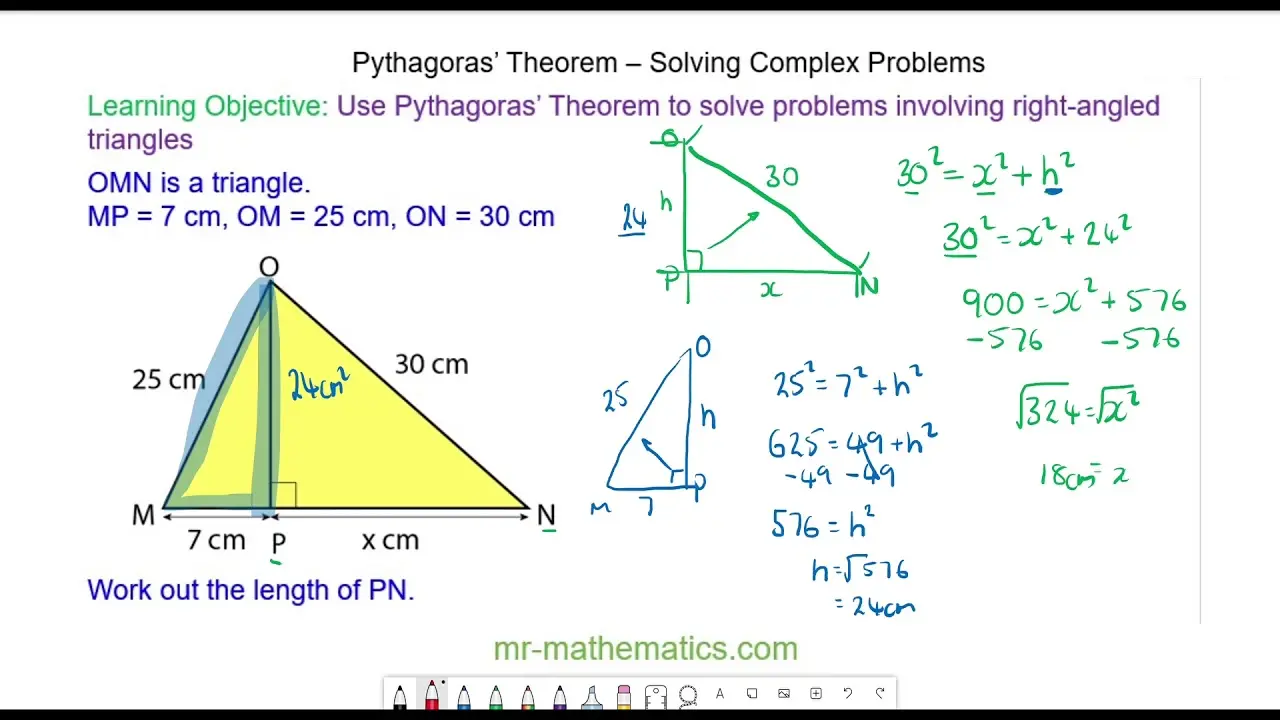
Pythagorean Theorem For A Right Triangle Formula And Problems Here are eight (8) pythagorean theorem problems for you to solve. you might need to find either the leg or the hypotenuse of the right triangle. these problems vary in type and difficulty, providing you an opportunity to level up your skills. Example 2 (solving for a leg) use the pythagorean theorem to determine the length of x. step 1. identify the legs and the hypotenuse of the right triangle. the legs have length 24 and x x are the legs. the hypotenuse is 26. step 2. substitute values into the formula (remember 'c' is the hypotenuse). a2 b2 = c2 x2 242 = 262 a 2 b 2 = c 2 x.
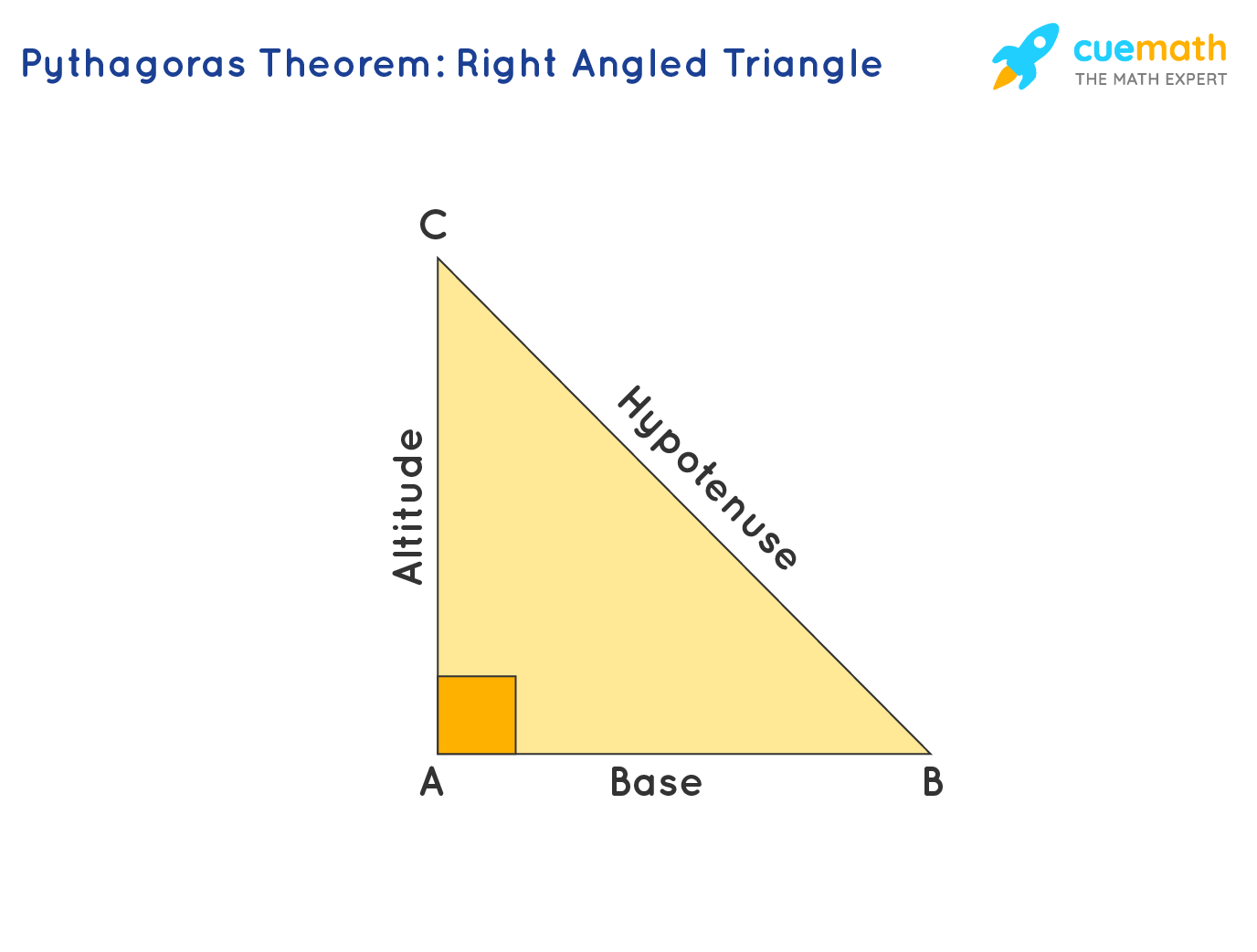
Pythagoras Theorem Problems Examples Formula Pythagorean theorem definition, formula & examples. Pythagorean theorem formula shown with triangle abc is: a^2 b^2=c^2 . side c is known as the hypotenuse. the hypotenuse is the longest side of a right triangle. side a and side b are known as the adjacent sides. they are adjacent, or next to, the right angle. you can only use the pythagorean theorem with right triangles. for example,. A right triangle's hypotenuse. the hypotenuse is the largest side in a right triangle and is always opposite the right angle. (only right triangles have a hypotenuse). the other two sides of the triangle, ac and cb are referred to as the 'legs'. in the triangle above, the hypotenuse is the side ab which is opposite the right angle, ∠c ∠ c. Pythagoras theorem.

Comments are closed.