Pythagorean Theorem Using A Trapezoid Youtube

Question Video Applying The Pythagorean Theorem To Solve More Complex Let's prove the pythagorean theorem using the area of a trapezoid together!~ music ~chromonicci warmth. chll.to b10d5131. This is a short, animated visual proof of the pythagorean theorem (the right triangle theorem) using the trapezoid that is now attributed to president james.
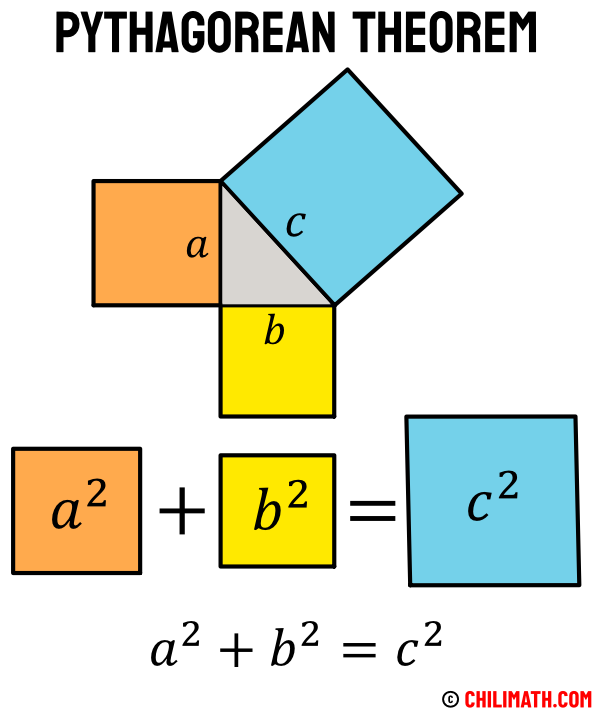
Pythagorean Theorem Definition Formula Examples Chilimath Find the base of a trapezoid if it is an isoseceles trapezoid and one base is 10 with the sides being 10.and a height of 8. Transcript. former u.s. president james garfield wrote a proof of the pythagorean theorem. he used a trapezoid made of two identical right triangles and half of a square to show that the sum of the squares of the two shorter sides equals the square of the longest side of a right triangle. created by sal khan. The pythagorean theorem applies to right triangles only. it is true that some problems involving non right triangles can be solved using the pythagorean theorem indirectly, but only by creating right triangles. for example, given the sides of an isosceles triangle, one can find the altitude to the unequal side by drawing this altitude, and then using the pythagorean theorem on one of the tw. Instead of a square, it uses a trapezoid, which can be constructed from the square in the second of the above proofs by bisecting along a diagonal of the inner square, to give the trapezoid as shown in the diagram. the area of the trapezoid can be calculated to be half the area of the square, that is, \[{\frac {1}{2}}(b a)^{2}.\].

Proving The Pythagorean Theorem Using A Trapezoid Youtube The pythagorean theorem applies to right triangles only. it is true that some problems involving non right triangles can be solved using the pythagorean theorem indirectly, but only by creating right triangles. for example, given the sides of an isosceles triangle, one can find the altitude to the unequal side by drawing this altitude, and then using the pythagorean theorem on one of the tw. Instead of a square, it uses a trapezoid, which can be constructed from the square in the second of the above proofs by bisecting along a diagonal of the inner square, to give the trapezoid as shown in the diagram. the area of the trapezoid can be calculated to be half the area of the square, that is, \[{\frac {1}{2}}(b a)^{2}.\]. Aboutabout this video. transcript. the pythagorean theorem is a cornerstone of math that helps us find the missing side length of a right triangle. in a right triangle with sides a, b, and hypotenuse c, the theorem states that a² b² = c². the hypotenuse is the longest side, opposite the right angle. created by sal khan. Find the area of the trapezoid using the trapezoid area formula: a = 1 2 (b 1 b 2) h; find the sum of the areas of the three right triangles in the diagram. the areas found in the previous two problems should be the same value. set the expressions equal to each other and simplify to get the pythagorean theorem. review (answers).

Pythagorean Theorem Iv Visual Proof Garfield S Trapezoid Youtube Aboutabout this video. transcript. the pythagorean theorem is a cornerstone of math that helps us find the missing side length of a right triangle. in a right triangle with sides a, b, and hypotenuse c, the theorem states that a² b² = c². the hypotenuse is the longest side, opposite the right angle. created by sal khan. Find the area of the trapezoid using the trapezoid area formula: a = 1 2 (b 1 b 2) h; find the sum of the areas of the three right triangles in the diagram. the areas found in the previous two problems should be the same value. set the expressions equal to each other and simplify to get the pythagorean theorem. review (answers).

Question Video Applying The Pythagorean Theorem To Find The Area Of A

Comments are closed.