Quick Special Right Triangles Review
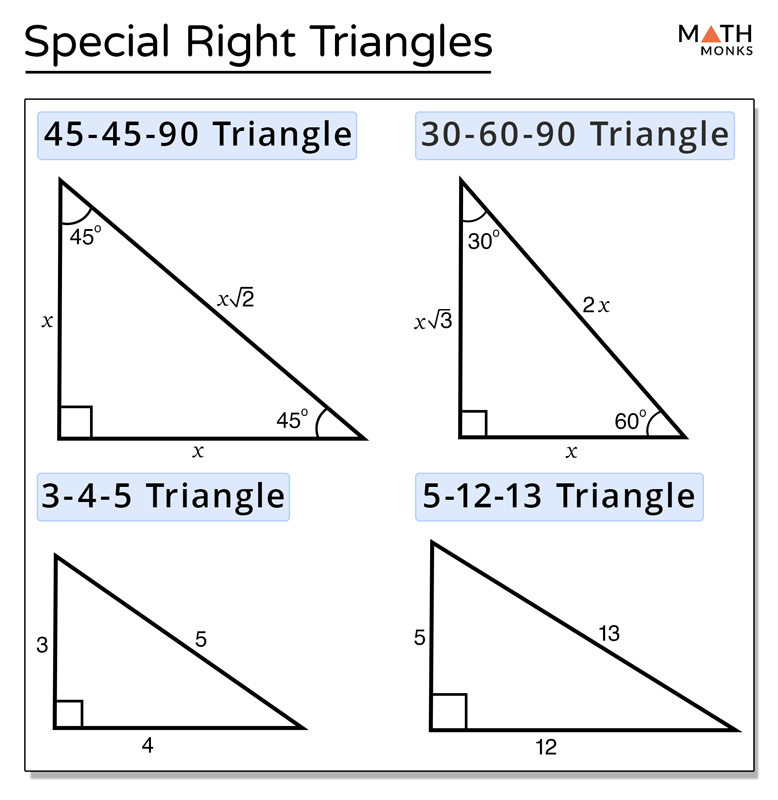
Special Right Triangles вђ Definition Formula Examples 45 45 90 triangles. 45 45 90 triangles are right triangles whose acute angles are both 45 ∘ . this makes them isosceles triangles, and their sides have special proportions: k k 2 ⋅ k 45 ∘ 45 ∘. how can we find these ratios using the pythagorean theorem? 45 ° 45 ° 90 °. 1. a 2 b 2 = c 2 1 2 1 2 = c 2 2 = c 2 2 = c. In this video we are going to explore how to find the missing measures of a right triangle using special right triangles⭐️ quick pythagorean triple review.

Special Right Triangles Sss Aaa Examples Included Right triangle review notes: pythagorean theorem opposite legs trigonometry relations adjacent hypotenuse note: sm e cos e esc e sec e cot e utilizing the pythagorean theorem or trig identities can determine angle and side measurements of any light triangle. however, "special right triangles" have features that make calculations easy! ! 13 25 17. Given: isosceles right triangle xyz (45° 45° 90° triangle) prove: in a 45° 45° 90° triangle, the hypotenuse is times the length of each leg. because triangle xyz is a right triangle, the side lengths must satisfy the pythagorean theorem, a2 b2 = c2, which in this isosceles triangle becomes a2 a2 = c2. by combining like terms, 2a2 = c2. Aboutabout this video. transcript. a 45 45 90 triangle is a special type of right triangle, where the ratio of the lengths of the sides of a 45 45 90 triangle is always 1:1:√2, meaning that if one leg is x units long, then the other leg is also x units long, and the hypotenuse is x√2 units long. created by sal khan. questions. One of the two special right triangles is called a 30 60 90 triangle, after its three angles. 30 60 90 theorem: if a triangle has angle measures 30∘, 60∘ and 90∘, then the sides are in the ratio x: x 3–√: 2x. the shorter leg is always x, the longer leg is always x 3–√, and the hypotenuse is always 2x. if you ever forget these.

Comments are closed.