Recent And Emerging Crohns Disease Therapies
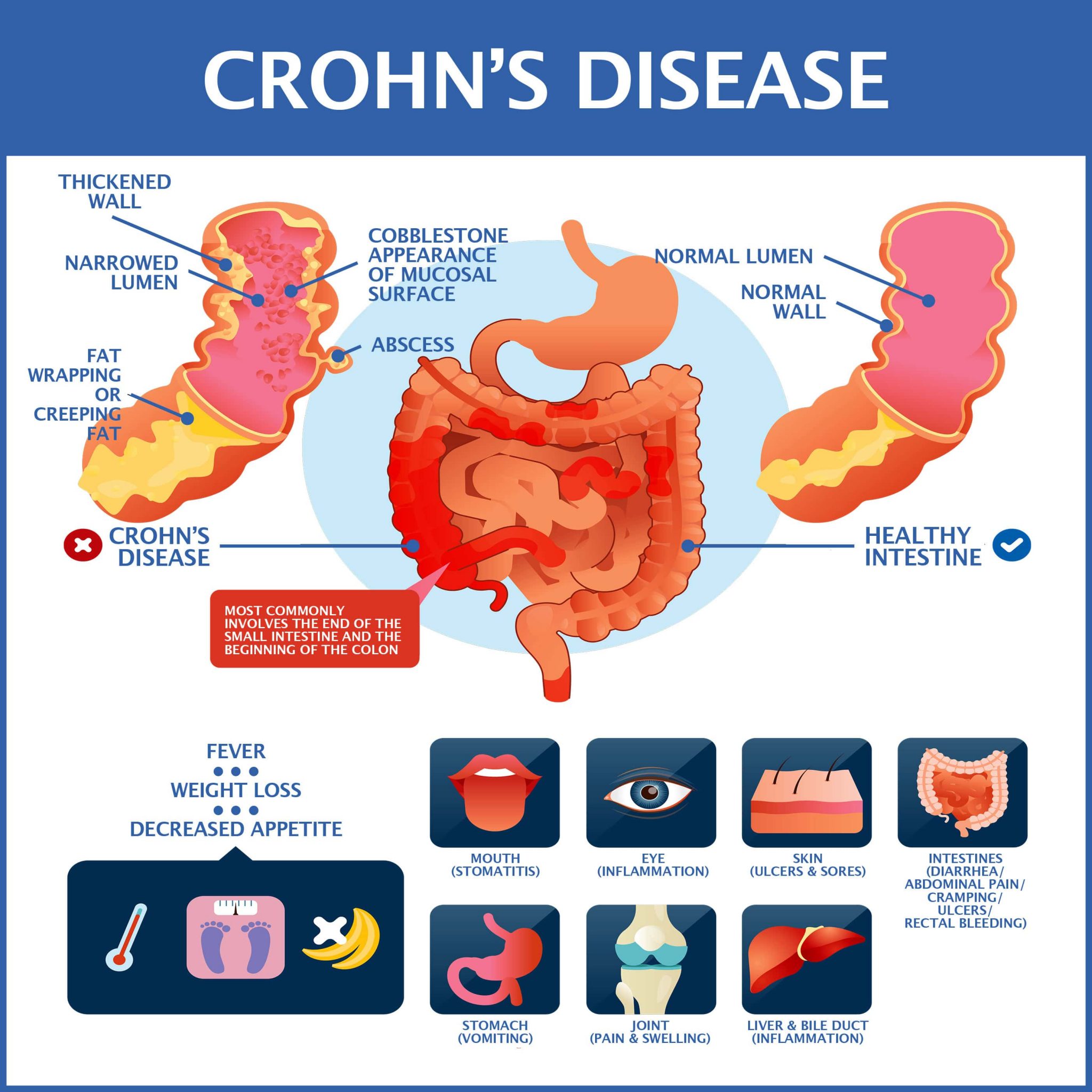
Been Diagnosed With Crohnтащs юааdiseaseюаб Gastroenterology Of Greater Orlando Inflammatory bowel disease (ibd), which includes crohn's disease (cd) and ulcerative colitis (uc), is a condition that involves inflammation of the digestive tract. in recent years, treatment options for ibd have rapidly expanded. the goal of these newer treatments is to improve control of inflammation in the gut, which can greatly improve. Patients with moderate to severe crohn’s disease now have a new treatment option to suppress their intestinal inflammation and painful symptoms, and help them maintain their relief. data from a phase 3 trial published today in the new england journal of medicine show that upadacitinib—a breakthrough, once daily oral medication—helps.

Crohn S Disease Update On Recent And Emerging Therapies Youtube During the past decade, the armamentarium of therapeutic agents for crohn’s disease has expanded, with new data regularly emerging on safety and efficacy of agents new and old. aga has just released new clinical practice guidelines evaluating therapies for luminal and fistulizing crohn’s disease. the guidelines assessed the overall benefit. In a span of less than 12 months, 3 agents were approved for moderate to severe ulcerative colitis (uc) worldwide—first, ozanimod, an s1p receptor modulator in may 2021; then filgotinib, a jak1 inhibitor in november 2021 in europe, and finally upadacitinib (upa) in march 2022. 1 these approvals came after a several year dearth of newly approved medications in the field, and after the same. Introduction. despite the development of multiple biological therapies for crohn’s disease (cd), remission rates at 1 year from individual agents are still only 30–50%. . this decreases as second line therapies are required and 80% of patients eventually require surgery in their lifetime. 1 early pharmacotherapies (such as anti tnf) have a broad mechanism of action and are relatively. This comprehensive narrative review provides an overview of recent developments in cd treatment, summarizing phase 2 and phase 3 clinical trial data. we delve into the clinical efficacy and safety profiles of emerging therapies, encompassing jak inhibitors, il 23 inhibitors, anti adhesion molecules, s1p1 receptor modulators, and combined.

Crohn S Disease Recent And Emerging Therapies Youtube Introduction. despite the development of multiple biological therapies for crohn’s disease (cd), remission rates at 1 year from individual agents are still only 30–50%. . this decreases as second line therapies are required and 80% of patients eventually require surgery in their lifetime. 1 early pharmacotherapies (such as anti tnf) have a broad mechanism of action and are relatively. This comprehensive narrative review provides an overview of recent developments in cd treatment, summarizing phase 2 and phase 3 clinical trial data. we delve into the clinical efficacy and safety profiles of emerging therapies, encompassing jak inhibitors, il 23 inhibitors, anti adhesion molecules, s1p1 receptor modulators, and combined. Introduction: crohn's disease (cd) is a chronic inflammatory bowel disease characterized by unpredictable flare ups and periods of remission. while several therapeutic options, such as anti tumor necrosis factor (tnf), anti integrin, and interleukin (il) 12 23 inhibitors, as well as il 23 and janus kinase (jak) inhibitors, have been approved for cd treatment, a substantial number of patients. Vedolizumab, a monoclonal antibody against α 4 β 7 integrin (figure 3 and table s1), was approved for the treatment of crohn’s disease on the basis of its ability to induce clinical remission.

Comments are closed.