Rectus Femoris Muscle Injury Radiology Case Radiopaedia Org
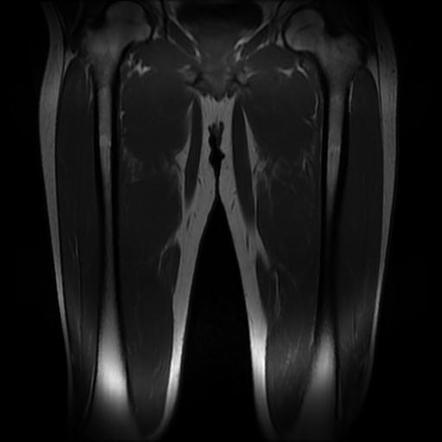
Rectus Femoris Muscle Injury Radiology Case Radiopaedia Org Patient data. there is an irregular fluid cleft involving the right rectus femoris muscle which correlates with the site of pain. it involves proximal mid third of the thigh. it measures 80 x 22 x 5 mm. the rest of the quadriceps muscles shows normal echopattern. direct and indirect heads of the rectus femoris are intact. The rectus femoris muscle crosses two joints, plays an active part in knee extension and hip flexion and features a high proportion of fast twitch (type ii) muscle fibers and is characterized by a complex musculotendinous architecture, which is considered a predisposing factor for strain injury 1. muscle injury patterns include strains.
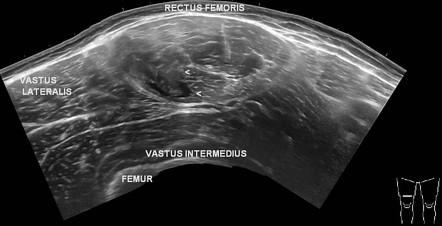
Rectus Femoris Muscle Injury Radiology Case Radiopaedia Org A case of an intramuscular degloving injury of the rectus femoris muscle. the rectus femoris muscle features unique characteristics, including a double tendinous origin and a long intramuscular extension of the indirect tendon resulting in a configuration in which an outer unipennate muscle surrounds an inner bipennate muscle. At the distal thigh, the tendons of these muscles merge to form the quadriceps tendon. the rectus femoris acts to extend the lower leg at the knee and flex the thigh at the hip. it is a direct antagonist to the hamstrings and it is innervated by the posterior division of the femoral nerve (l2, l3, l4). 4a. figure 4:. Schubert r, distal rectus femoris tendon tear. case study, radiopaedia.org (accessed on 09 apr 2024) doi.org 10.53347 rid 15342. —28 year old man with grade iii rectus femoris muscle strain. longitudinal sonogram (c), in same location as a, and diagram (d) were obtained during contraction. dynamic scanning improves lesion definition and confirms that tear is at musculotendinous junction. rf = rectus femoris muscle, h = hematoma, t = tendon.

Comments are closed.