Retrospective Cohort Vs Case Control Study
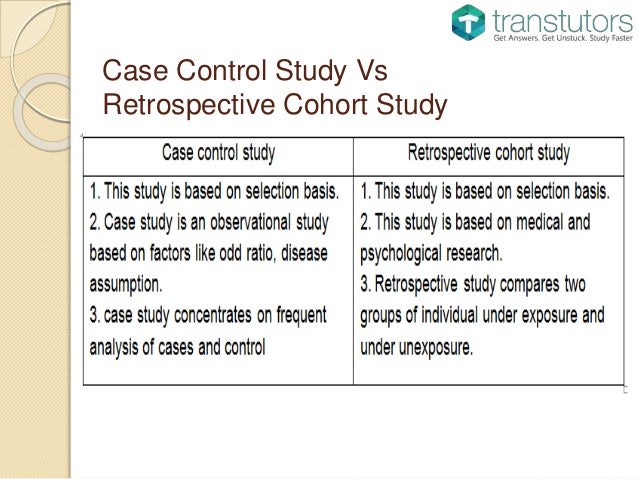
Case Study Control Statistics Introduction. case control and cohort studies are observational studies that lie near the middle of the hierarchy of evidence. these types of studies, along with randomised controlled trials, constitute analytical studies, whereas case reports and case series define descriptive studies (1). although these studies are not ranked as highly as. This study is labeled as 'case control', but it is actually a retrospective cohort study. case control studies have a different design, where researchers select cases and controls based on the presence or absence of the outcome, respectively, and look back in time for disproportionate exposures (2).

Difference Between Retrospective Cohort Study And Case Contro Cohort studies and case control studies are two primary types of observational studies that aid in evaluating associations between diseases and exposures. in this review article, we describe these study designs, methodological issues, and provide examples from the plastic surgery literature. keywords: observational studies, case control study. A retrospective cohort study is a type of observational study that focuses on individuals who have an exposure to a disease or risk factor in common. retrospective cohort studies analyze the health outcomes over a period of time to form connections and assess the risk of a given outcome associated with a given exposure. note. Cohort and case control study designs are not “opposites” as are prospective vs. retrospective, or cross sectional vs. longitudinal, or controlled vs. uncontrolled research designs. rather, like the randomized controlled and quasi controlled designs, these designs are special kinds of research design in the controlled vs. uncontrolled. In a case–control study, a number of cases and noncases (controls) are identified, and the occurrence of one or more prior exposures is compared between groups to evaluate drug–outcome associations ( figure 1 ). a case–control study runs in reverse relative to a cohort study. 21 as such, study inception occurs when a patient experiences.

Comments are closed.