Rotator Cuff Tear Orthopaedicprinciplescom
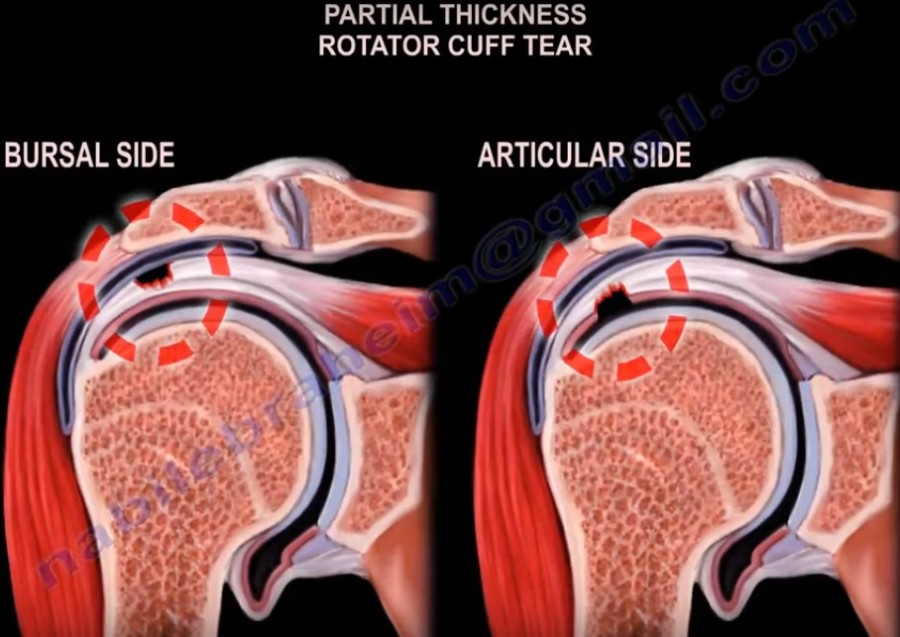
Rotator Cuff Tear Classification вђ Orthopaedicprinciples This explains why certain rotator cuff tears (termed functional rotator cuff tears), despite being massive in size, may demonstrate “normal” kinematic patterns maybe acute or chronic, partial or full thickness, and traumatic or degenerative. ellman’s staging of partial thickness tears may help in guiding management:. Rotator cuff tear classification. courtesy: prof nabil ebraheim, university of toledo, ohio, usa. massive rotator cuff tears. rotator cuff tear classification.

Rotator Cuff Tears And Impingement Orthopaedicprinciplescom Summary. rotator cuff tears are a very common source of shoulder pain and decreased motion that can occur due to both traumatic injuries in young patients as well as degenerative disease in the elderly patient. diagnosis can be suspected clinically with provocative tests of the supraspinatous, infraspinatous, teres minor and subscapularis, but. Neer initially described three different stages of cuff lesions : •. stage 1: reversible edema and hemorrhage are present in a patient younger than 25 years. •. stage 2: fibrosis and tendinitis affect the rotator cuff of a patient typically in the 25 to 40 year old age group. pain often recurs with activity. Certain doctors specialize in rotator cuff tear arthropathy (arthritis of the shoulder associated with a massive cuff tear). such individuals may be found in the shoulder services of major schools of medicine. you can also call 206 598 0312 to make an appointment. Rotator cuff arthropathy is a specific pattern of shoulder degenerative joint disease that results from a rotator cuff tear leading to abnormal glenohumeral wear and subsequent superior migration of the humeral head. diagnosis can be made primarily with shoulder radiographs showing glenohumeral arthritis with a decreased acromiohumeral interval.

Comments are closed.