Satellites Spectral Information And Soil Organic Carbon Encyclopedia Mdpi
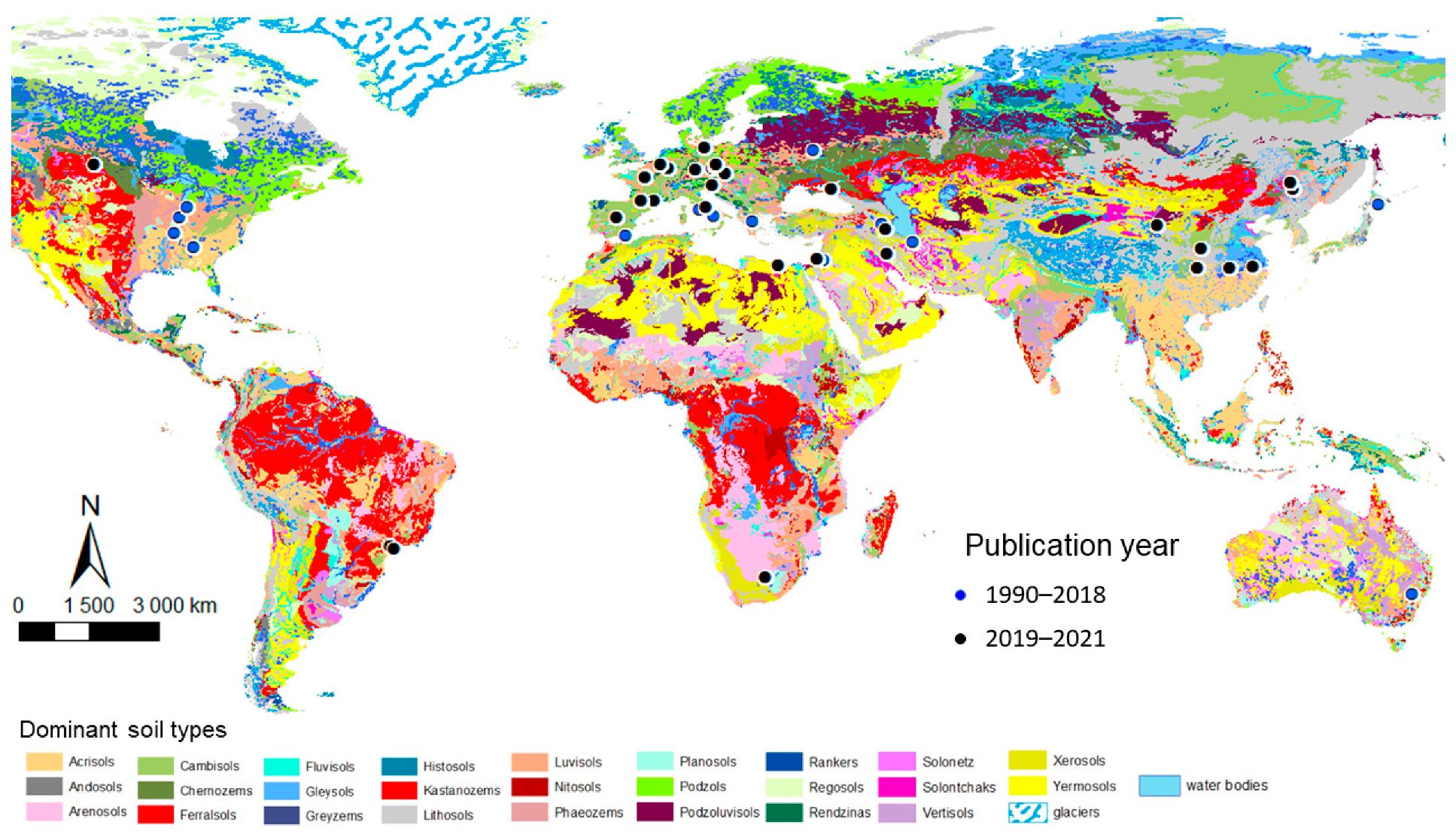
Satellites Spectral Information And Soil Organic Carbon Encyclopedia Mdpi Mapping soil organic carbon (soc) accurately is essential for sustainable soil resource management. hyperspectral data, a vital tool for soc mapping, is obtained through both laboratory and satellite based sources. while laboratory data is limited to sample point monitoring, satellite hyperspectral imagery covers entire regions, albeit susceptible to external environmental interference. this. There is a need to update soil maps and monitor soil organic carbon (soc) in the upper horizons or plough layer for enabling decision support and land management, while complying with several policies, especially those favoring soil carbon storage. this review paper is dedicated to the satellite based spectral approaches for soc assessment that have been achieved from several satellite sensors.
Satellites Spectral Information And Soil Organic Carbon Encyclopedia Mdpi Soil organic carbon (soc) constitutes a crucial component of the global carbon cycle [1,2], playing a pivotal role in climate change mitigation [3,4,5].moreover, soc substantially contributes to soil quality by enhancing soil structure, moisture retention, and overall soil fertility, impacting the well being of ecosystems [6,7], including strengthening their structural stability and functional. Satellite remote sensing has the advantages of fast monitoring, wide coverage and low cost [9]. in particular, hyperspectral satellite data have rich spectral information, making it possible to predict the spatial distribution of somc on a large scale and with high accuracy [10]. the zy1 02d satellite, launched in september 2019, carries an. Soil organic carbon (soc) plays a crucial role for soil health. however, large datasets needed to accurately assess soc at high resolution across scales are labor intensive, time consuming, and expensive. ancillary geodata, including remote sensing spectral indices (rs sis) and topographic indicators (tis), have been proposed as spatial covariates. There is a need to update soil maps and monitor soil organic carbon (soc) in the upper horizons or plough layer for enabling decision support and land management, while complying with several policies, especially those favoring soil carbon storage. a number of satellite based spectral approaches for soc assessment have been achieved from several satellite sensors, study scales and geographical.
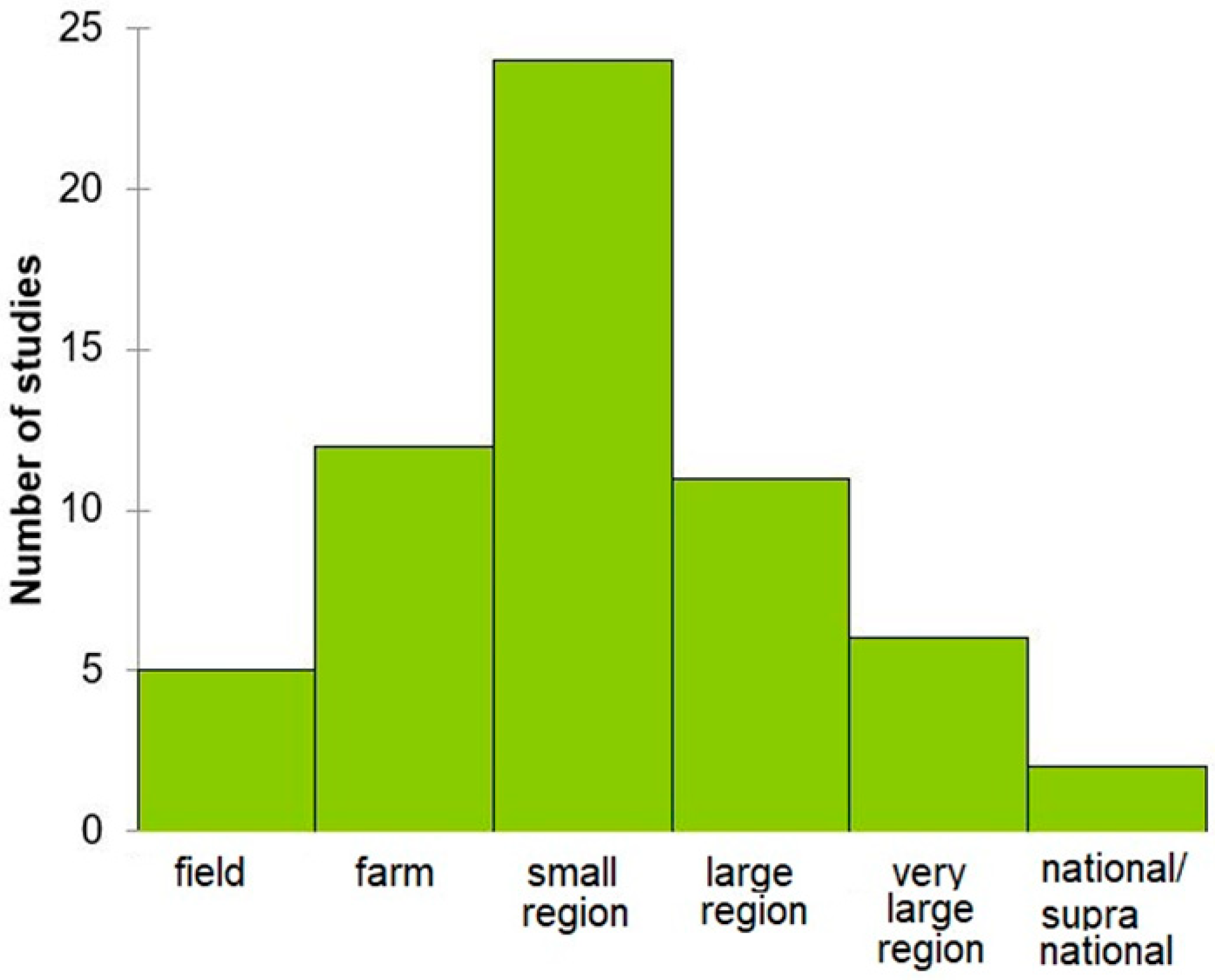
Satellites Spectral Information And Soil Organic Carbon Encyclopedia Mdpi Soil organic carbon (soc) plays a crucial role for soil health. however, large datasets needed to accurately assess soc at high resolution across scales are labor intensive, time consuming, and expensive. ancillary geodata, including remote sensing spectral indices (rs sis) and topographic indicators (tis), have been proposed as spatial covariates. There is a need to update soil maps and monitor soil organic carbon (soc) in the upper horizons or plough layer for enabling decision support and land management, while complying with several policies, especially those favoring soil carbon storage. a number of satellite based spectral approaches for soc assessment have been achieved from several satellite sensors, study scales and geographical. Knowledge of the soil organic carbon (soc) content is critical for environmental sustainability and carbon neutrality. with the development of remote sensing data and prediction models, the comprehensive utilization of multisource remote sensing data based on a fusion approach and testing its effectiveness in soc content prediction is an interesting and challenging topic. Inorganic carbon is distributed in the deep soil layers with a longer cycling period, while organic carbon is distributed in the top soil layers (within 1 m of the soil surface) where carbon cycles directly among soil, air, and plants [4]. due to the huge reserves of soil organic carbon (soc), small variations of soc in the soil by.
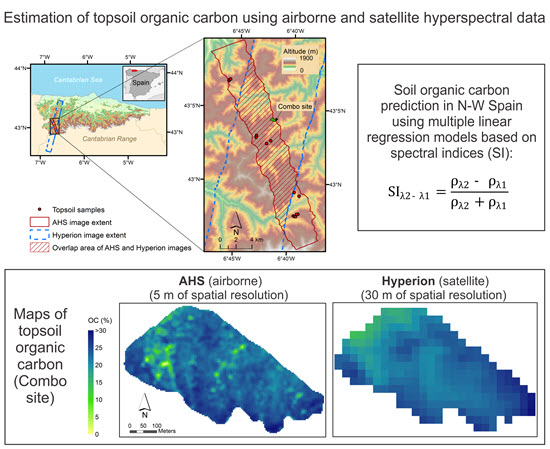
Remote Sensing Free Full Text Prediction Of Topsoil Organic Carbon Knowledge of the soil organic carbon (soc) content is critical for environmental sustainability and carbon neutrality. with the development of remote sensing data and prediction models, the comprehensive utilization of multisource remote sensing data based on a fusion approach and testing its effectiveness in soc content prediction is an interesting and challenging topic. Inorganic carbon is distributed in the deep soil layers with a longer cycling period, while organic carbon is distributed in the top soil layers (within 1 m of the soil surface) where carbon cycles directly among soil, air, and plants [4]. due to the huge reserves of soil organic carbon (soc), small variations of soc in the soil by.

Remote Sensing Free Full Text Soil Organic Carbon Mapping Using

Comments are closed.