Scientific Method Definition And Examples
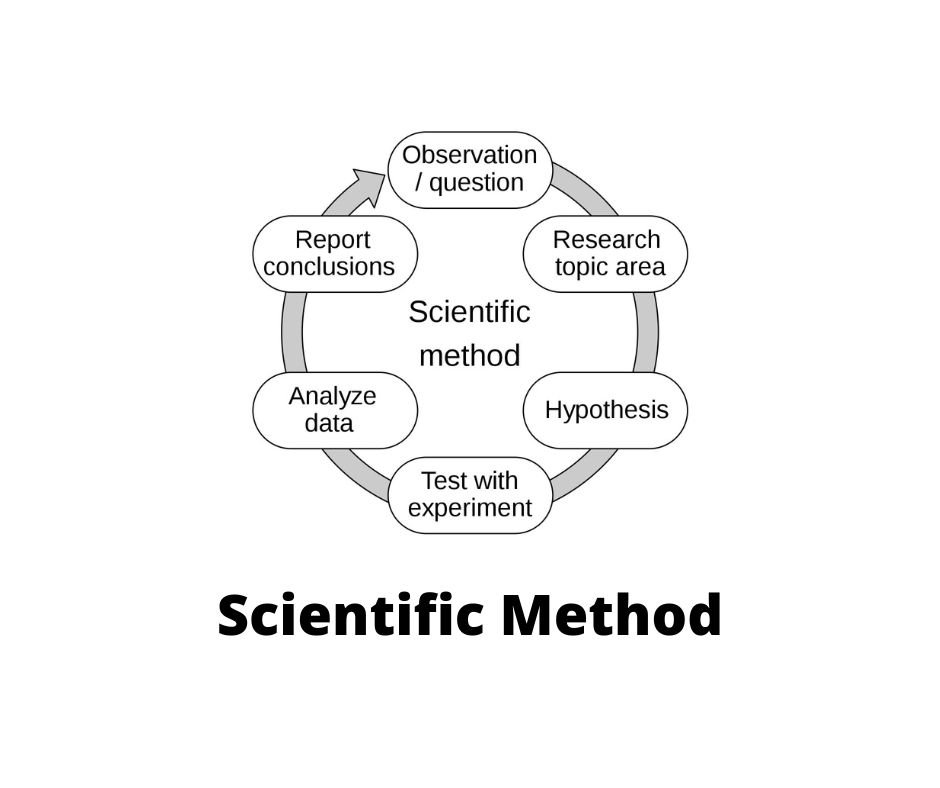
Scientific Method Characteristics Steps B Ed Notes The scientific method is a series of steps that scientific investigators follow to answer specific questions about the natural world. scientists use the scientific method to make observations, formulate hypotheses, and conduct scientific experiments . a scientific inquiry starts with an observation. Scientific method, mathematical and experimental technique employed in the sciences. more specifically, it is the technique used in the construction and testing of a scientific hypothesis. the process of observing, asking questions, and seeking answers through tests and experiments is not unique to any one field of science.
Functionalism In Psychology Definition Examples Criticism 2024 The scientific method is a powerful analytical or problem solving method of learning more about the natural world. the scientific method is a combined method, which consists of theoretical knowledge and practical experimentation by using scientific instruments, analysis and comparisons of results, and then peer reviews. The scientific method. at the core of biology and other sciences lies a problem solving approach called the scientific method. the scientific method has five basic steps, plus one feedback step: make an observation. ask a question. form a hypothesis, or testable explanation. make a prediction based on the hypothesis. Science is a systematic and logical approach to discovering how things in the universe work. scientists use the scientific method to make observations, form hypotheses and gather evidence in an. The six steps of the scientific method include: 1) asking a question about something you observe, 2) doing background research to learn what is already known about the topic, 3) constructing a hypothesis, 4) experimenting to test the hypothesis, 5) analyzing the data from the experiment and drawing conclusions, and 6) communicating the results.

Comments are closed.