Secant Method For Solution To Nonlinear Equations
Fortran Program For Secant Method Numerical Fameintensive Suppose that a function f(x) has a root x, and that an iterative solution method produces a sequence x i to this root. de ne e i to be the corresponding sequence of errors, e i = jx i xj the method is said to have a convergence rate rif it is the case that lim i!1 e i (e i 1)r = c for some nite nonzero constant c. for the bisection method, we. The velocity of a body is given by v(t) =5e−t 6 v ( t) = 5 e − t 6, where v v is in m s and t t is in seconds. a) use secant method to find when the velocity will be 7.0 7.0 m s. use only two iterations and take t = 2 t = 2 and t = 3.5 t = 3.5 seconds as the initial guesses.

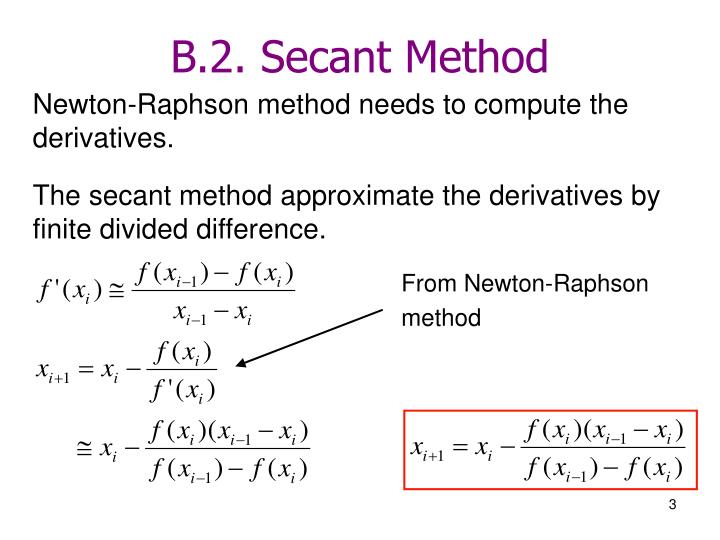
Secant Method Definition Formula Steps And Examples Secant method solved example. example: compute two iterations for the function f(x) = x 3 – 5x 1 = 0 using the secant method, in which the real roots of the equation f(x) lies in the interval (0, 1). solution: using the given data, we have, x 0 = 0, x 1 = 1, and. f(x 0) = 1, f(x 1) = 3. using the secant method formula, we can write. Newton’s method is the only viable general purpose method to solve systems of nonlinear equations. but, as a general purpose algorithm for nding zeros of functions, it has 3 serious drawbacks. 1.the function f(x) must be smooth. 2.the derivative f0(x) must be computed. 3.the starting guess must be \su ciently accurate". The secant method requires two initial guesses ( = 0 and = −1) near the root. secant is a function that implements the secant method. the input to this function is ) ( , (from the equation )= r. example. apply the secant method to solve (for the root of )= − 1 3− t= r inside [ s v]. Or, simplifying, equation c.4.1 secant method. xn 1 = xn − 1f(xn) − xnf(xn − 1) f(xn) − f(xn − 1) of course, to get started with n = 1, we need two initial guesses, x0 and x1, for the root. example c.4.2 approximating √2, again. in this example we compute, approximately, the square root of two by applying the secant method to the.

Comments are closed.