Sedation In Icu Sedation In The Intensive Care Unit

Sedation In Icu Sedation In The Intensive Care Unit Youtube Published january 30, 2014. n engl j med 2014;370: 444 454. doi: 10.1056 nejmra1208705. vol. 370 no. 5. patients in intensive care units (icus) are treated with many interventions (most notably. The richmond agitation sedation scale: validity and reliability in adult intensive care unit patients. american journal of respiratory and critical care medicine 2002; 166: 1338–44 in the sedation group, the mean rass score was −2.3 on day 1 increasing to −1.8 by day 7, and in the non sedation group the mean rass score was −1.3 on day 1.

Sedation In The Intensive Care Unit Good And Bad The Lancet Intensive care unit (icu) sedation practices have dramatically changed over the last 20 years [ 1 – 4 ]. historically, patients were often deeply sedated to “let them rest” [ 4 ]. strong evidence indicates these practices are dangerous and associated with poor outcomes [ 5, 6 ]. current practice is to use minimum sedation and wake. Patients admitted to the intensive care unit (icu) routinely experience pain, agitation and anxiety, use of invasive monitoring, and need for invasive procedures or mechanical ventilation. appropriate analgesia and sedation are therefore essential. Critical illness can be a frightening experience for a variety of reasons, and adequate sedation may reduce this. pain is a common problem and may be worsened by invasive and unpleasant procedures. agitation is thought to occur at least once in 71% of patients in a medical surgical icu. April 03, 2020. the state of pharmacological sedation in the icu is ever changing. traditionally, patients who were mechanically ventilated in the icu were kept deeply sedated with continuous depressant infusions to maximize ventilator synchrony and decrease discomfort that may arise during critical illness. "this convention of heavy depressant.
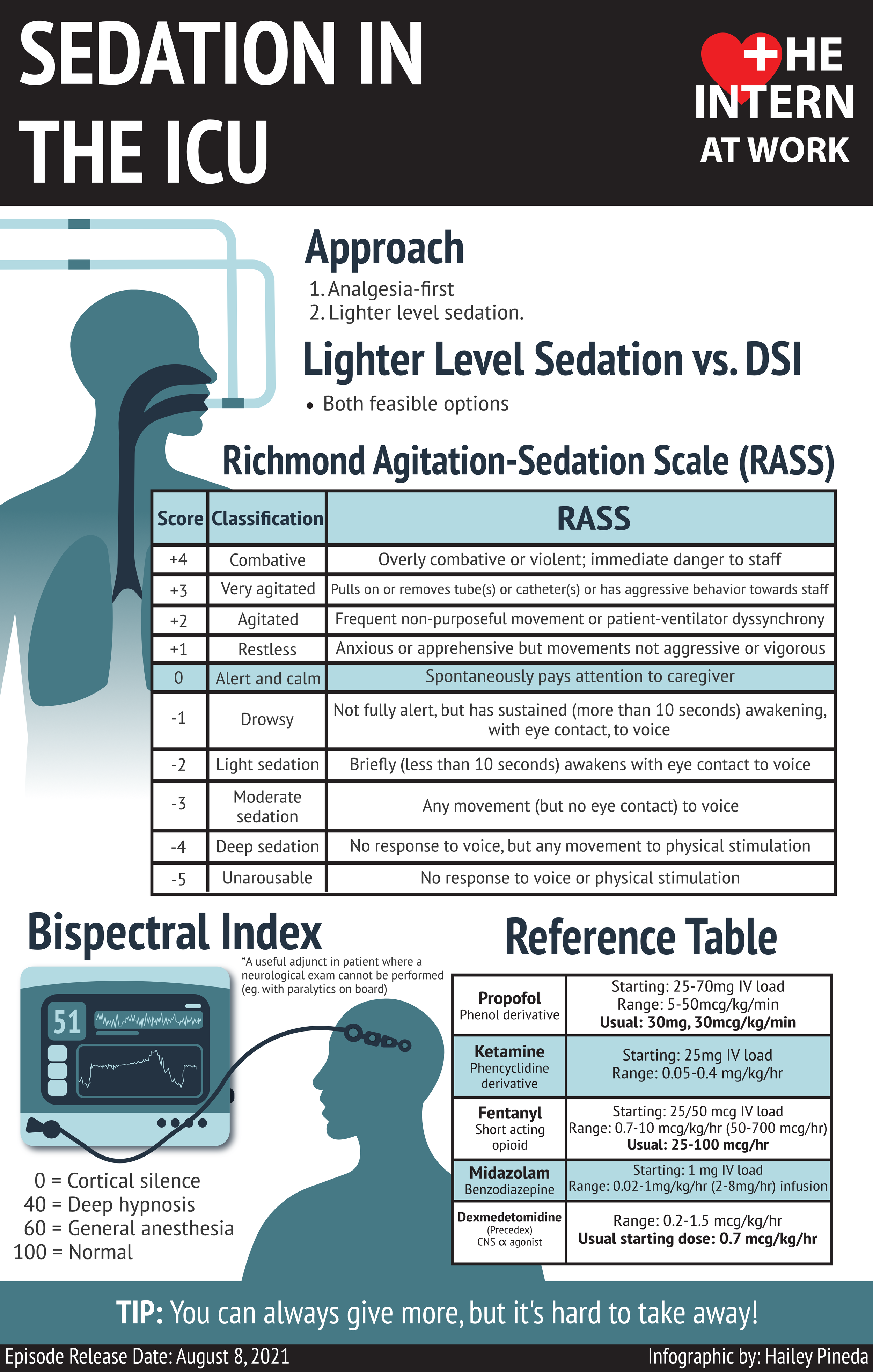
Icu Sedation вђ The Intern At Work Critical illness can be a frightening experience for a variety of reasons, and adequate sedation may reduce this. pain is a common problem and may be worsened by invasive and unpleasant procedures. agitation is thought to occur at least once in 71% of patients in a medical surgical icu. April 03, 2020. the state of pharmacological sedation in the icu is ever changing. traditionally, patients who were mechanically ventilated in the icu were kept deeply sedated with continuous depressant infusions to maximize ventilator synchrony and decrease discomfort that may arise during critical illness. "this convention of heavy depressant. The sedation of criti cally ill adults — part 1: assessment: the first in a two part series focuses on as sessing sedated patients in the icu. am j nurs 2007;107:40 8. 40. van eijk mm, van marum. Abstract. purpose of review: this narrative review illustrates literature over the last 5 years relating to sedation delivery to mechanically ventilated adult patients in intensive care units. recent findings: there has been an increase in dexmedetomidine related publications but although systematic reviews suggest dexmedetomidine reduces.

Intensive Care Sedation Brainstem Biometrics The sedation of criti cally ill adults — part 1: assessment: the first in a two part series focuses on as sessing sedated patients in the icu. am j nurs 2007;107:40 8. 40. van eijk mm, van marum. Abstract. purpose of review: this narrative review illustrates literature over the last 5 years relating to sedation delivery to mechanically ventilated adult patients in intensive care units. recent findings: there has been an increase in dexmedetomidine related publications but although systematic reviews suggest dexmedetomidine reduces.

Comments are closed.