Selective Repeat Arq Protocol

Selective Repeat Arq Protocol Youtube Learn how selective repeat protocol (srp) works to improve efficiency and reduce bandwidth waste in unreliable links. srp allows the receiver to accept and buffer packets out of order and retransmit only lost or damaged ones. Learn what selective repeat arq is, how it works, and its advantages and disadvantages. see an example of selective repeat arq protocol and compare it with other arq techniques.

5 Selective Repeat Arq Protocol Download Scientific Diagram Learn about the selective repeat arq, a sliding window protocol that ensures reliable in order delivery of data packets. see how it works, its requirements, advantages and disadvantages, and an example of data transmission. Learn about the automatic repeat request (arq) protocol that manages sequence numbers and retransmissions in reliable communications. see how it works with sliding windows, selective acknowledgements, and subdivided messages. Learn how srp ensures reliable data delivery in networks by dividing data into packets, sending acknowledgments, and retransmitting lost packets. see an example of packet transmission using srp and its advantages and disadvantages. Learn about the three common schemes of automatic repeat request (arq) systems: stop & wait, go back n, and selective repeat. compare their efficiency, correctness, and features with examples and diagrams.
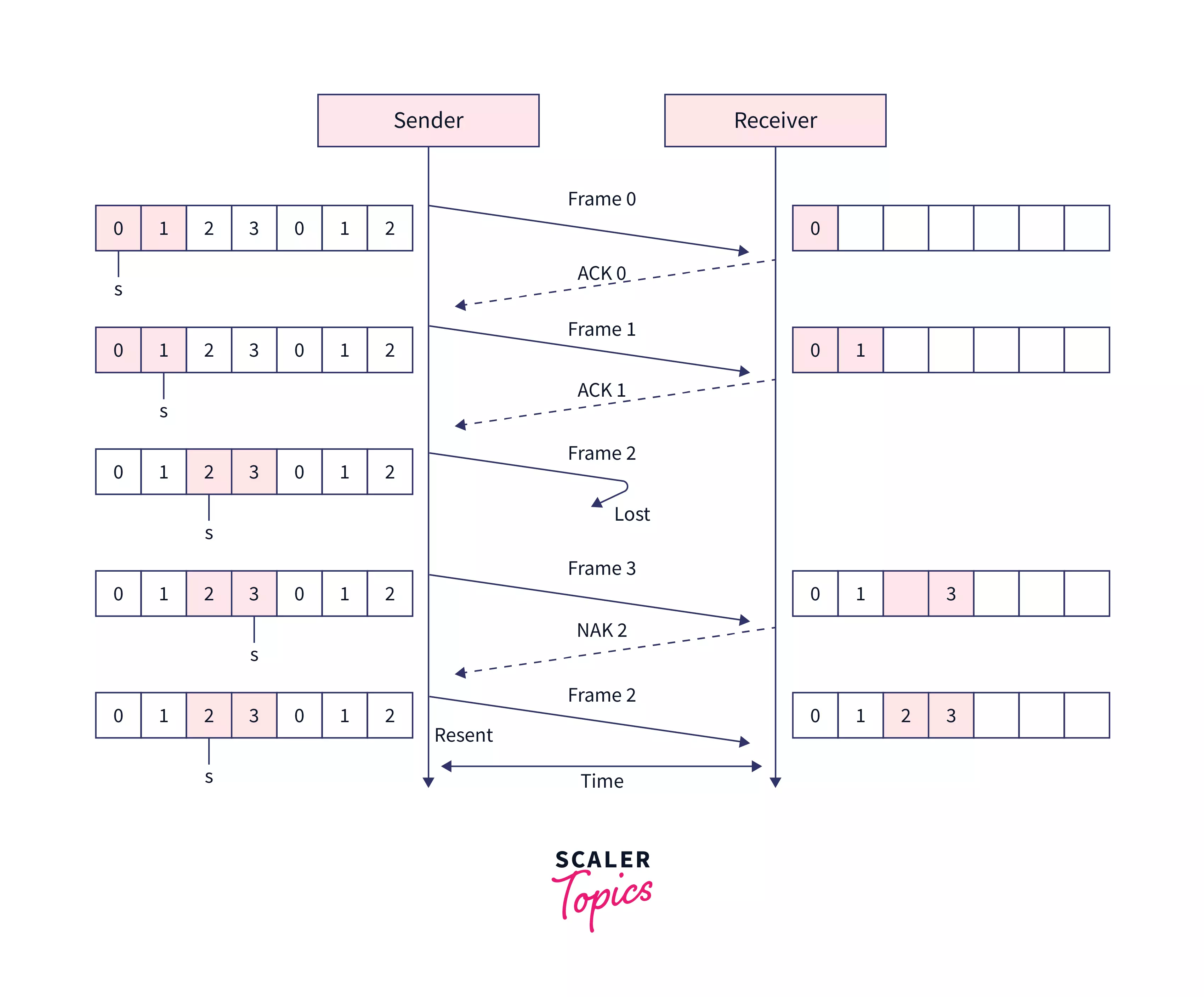
Selective Repeat Arq Protocol Scaler Topics Learn how srp ensures reliable data delivery in networks by dividing data into packets, sending acknowledgments, and retransmitting lost packets. see an example of packet transmission using srp and its advantages and disadvantages. Learn about the three common schemes of automatic repeat request (arq) systems: stop & wait, go back n, and selective repeat. compare their efficiency, correctness, and features with examples and diagrams. Selective repeat protocol (srp) • selective repeat attempts to retransmit only those packets that are actually lost (due to errors) – receiver must be able to accept packets out of order – since receiver must release packets to higher layer in order, the receiver must be able to buffer some packets • retransmission requests – implicit. • nack’sare used in some versions of the go back n and selective repeat protocols to reduce delays, and, in rmp the reliable multicast protocol we will showhow nack’scan reduce the number of control messages. —importance of numbering • unnumbered messages —round trip delay > the time between retransmissions.

Flow Control Selective Repeat Protocol Studytonight Selective repeat protocol (srp) • selective repeat attempts to retransmit only those packets that are actually lost (due to errors) – receiver must be able to accept packets out of order – since receiver must release packets to higher layer in order, the receiver must be able to buffer some packets • retransmission requests – implicit. • nack’sare used in some versions of the go back n and selective repeat protocols to reduce delays, and, in rmp the reliable multicast protocol we will showhow nack’scan reduce the number of control messages. —importance of numbering • unnumbered messages —round trip delay > the time between retransmissions.

Comments are closed.