Simple Ira Vs Sep Ira Overview Differences Pros Cons

Sep Ira Vs Simple Ira How They Differ Which Plan To Choose Both types of iras have their own distinct features and benefits. a simple ira allows employers to make contributions on behalf of their employees. on the other hand, a sep ira only allows employers to make contributions themselves. additionally, a simple ira has an annual contribution limit of $15,500 per employee (as of 2023), while a sep ira. The pros of a sep ira include: • a sep ira is an easy way for a small business owner or self employed individual to set up a retirement plan. • the contribution limit is higher than that for a simple ira. in 2024, the contribution limit is $69,000 to a sep ira.
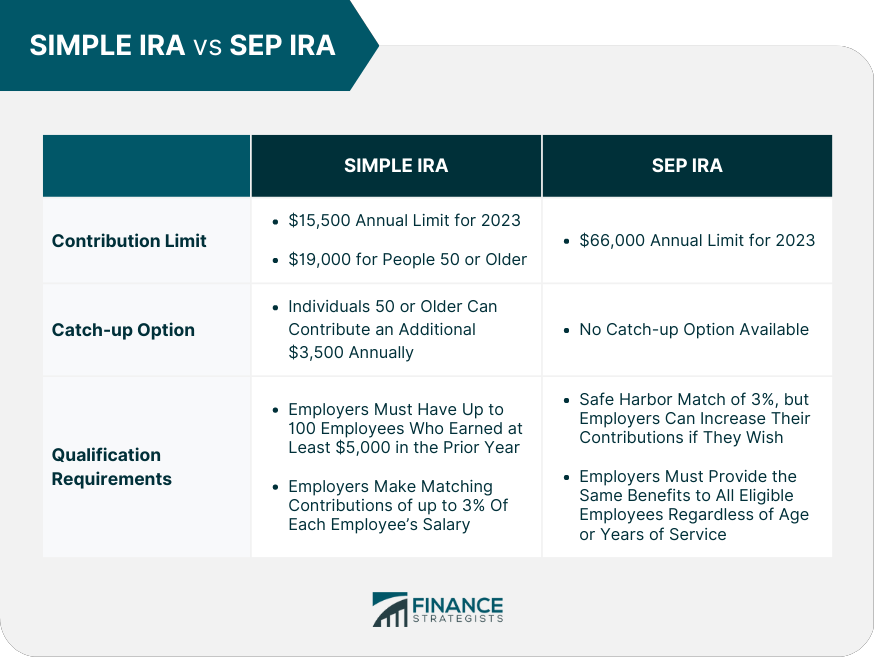
Simple Ira Vs Sep Ira Overview Differences Pros Cons A simple ira allows both the employee and the small business owner or sole proprietor to make contributions. a sep ira, meanwhile, only allows business owners to make contributions for both themselves and their employees. the contribution limits of a simple ira vs. sep ira are different too. the sep ira limit in 2023 is 25% of an employee’s. A sep ira allows employers to contribute up to $66,000 (in 2023), or up to 25 percent of an employee’s salary, whichever is less. in contrast, a simple ira allows employees to contribute up to. Key differences. a sep ira allows significantly higher contributions, $69,000 in 2024, compared to the smaller contributions for a simple ira which are $16,000 in 2024. lastly, simple iras are. Sep iras are available to employers of any size, while simple iras are limited to employers with 100 or fewer employees. income requirements for sep iras are slightly less complex than they are for simple iras. sep iras come with higher annual contribution limits than simple iras do. only an employer can make contributions to an sep ira, but a.
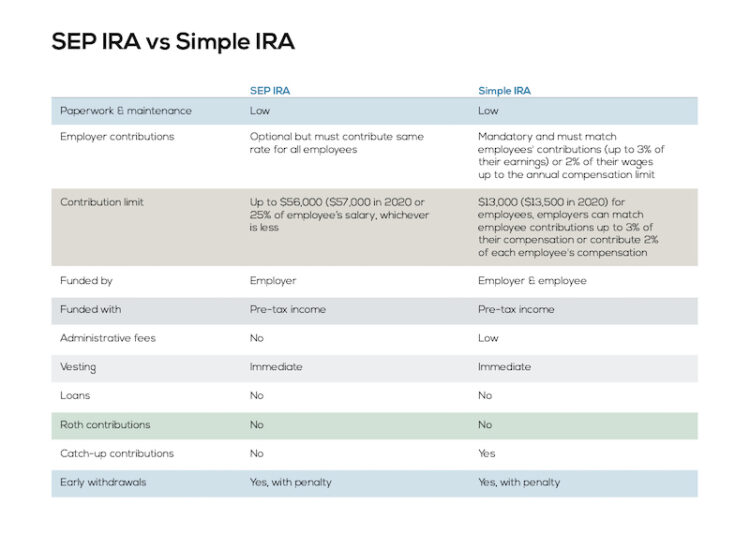
Sep Ira Definition Rules Limits Investinganswers Key differences. a sep ira allows significantly higher contributions, $69,000 in 2024, compared to the smaller contributions for a simple ira which are $16,000 in 2024. lastly, simple iras are. Sep iras are available to employers of any size, while simple iras are limited to employers with 100 or fewer employees. income requirements for sep iras are slightly less complex than they are for simple iras. sep iras come with higher annual contribution limits than simple iras do. only an employer can make contributions to an sep ira, but a. One of the most important differences when it comes to an sep ira vs. simple ira is the contribution limits. an sep ira allows contributions of up to 25% of compensation or a maximum of $66,000 for 2023 ($69,000 for 2024). contribution limits are adjusted annually for inflation. annual contributions are not mandatory, so employers can skip them. Sep iras offer flexible contribution limits, making them an attractive option for small business owners. as an employer, you can contribute up to 25% of your eligible employees’ compensation, up to a maximum of $58,000 for 2021.

The Small Business Guide To Employee Benefits Momentum Wealth One of the most important differences when it comes to an sep ira vs. simple ira is the contribution limits. an sep ira allows contributions of up to 25% of compensation or a maximum of $66,000 for 2023 ($69,000 for 2024). contribution limits are adjusted annually for inflation. annual contributions are not mandatory, so employers can skip them. Sep iras offer flexible contribution limits, making them an attractive option for small business owners. as an employer, you can contribute up to 25% of your eligible employees’ compensation, up to a maximum of $58,000 for 2021.

Comments are closed.