Sine And Cosine Of Complements Example Basic Trigonometry

Sine And Cosine Of Complements Example Basic Trigonometry Practice this lesson yourself on khanacademy.org right now: khanacademy.org math trigonometry basic trigonometry cc trig ratios similarity e trig. This shows us something important: the sine of an angle is equal to the cosine of its complementary angle. so, in this case: for example, to find the sine of 25 degrees, you can use the cosine of its complement: in summary, understanding how sine and cosine relate through complementary angles is a powerful trick in trigonometry.

Trigonometry Solution: the sine of an angle and the cosine of its complement are equal. 15º and 75º are complementary. sin (75º) = cos (15º) = 0.97. cos (75º) = sin (15º) = 0.26. in right Δ abc, m ∠ c = 90º, sin a = x 0.1 and cos b = 2 x 0.4. find x. solution: if a and b are the acute angles of a right triangle, sin a = cos b. Example: if a, b and c are the interior angles of a right angle triangle, right angled at b then find the value of a, given that tan 2a = cot (a – 30°) and 2a is an acute angle. solution: using the trigonometric ratio of complementary angles, cot (90° a) = tan a. from this ratio, we can write the above expression as: ⇒ tan 2a = cot (90. In #1 you saw that sina = cosb and sinb = cosa. this means that the sine and cosine of complementary angles are equal. 3. find 80 ∘ and cos10 ∘. explain the result. sin80 ∘ ≈ 0.985 and cos10 ∘ ≈ 0.985. sin80 ∘ = cos10 ∘ because 80 ∘ and 10 ∘ are complementary angle measures. sin80 ∘ and cos10 ∘ are the ratios of the same. In #1 you saw that sina = cosb and sinb = cosa. this means that the sine and cosine of complementary angles are equal. 3. find 80 ∘ and cos10 ∘. explain the result. sin80 ∘ ≈ 0.985 and cos10 ∘ ≈ 0.985. sin80 ∘ = cos10 ∘ because 80 ∘ and 10 ∘ are complementary angle measures. sin80 ∘ and cos10 ∘ are the ratios of the same.

Mastering Trigonometry A Beginner S Guide To Understanding Sine In #1 you saw that sina = cosb and sinb = cosa. this means that the sine and cosine of complementary angles are equal. 3. find 80 ∘ and cos10 ∘. explain the result. sin80 ∘ ≈ 0.985 and cos10 ∘ ≈ 0.985. sin80 ∘ = cos10 ∘ because 80 ∘ and 10 ∘ are complementary angle measures. sin80 ∘ and cos10 ∘ are the ratios of the same. In #1 you saw that sina = cosb and sinb = cosa. this means that the sine and cosine of complementary angles are equal. 3. find 80 ∘ and cos10 ∘. explain the result. sin80 ∘ ≈ 0.985 and cos10 ∘ ≈ 0.985. sin80 ∘ = cos10 ∘ because 80 ∘ and 10 ∘ are complementary angle measures. sin80 ∘ and cos10 ∘ are the ratios of the same. The cosine of an angle and the sine of its complement are also equal. if a b = 90°, then cos (a)=sin (b) and cos (b)=sin (a). for example: if sin (30°)=0.5, then cos (60°)=0.5 because 30° 60° = 90°. this property is particularly useful in trigonometric calculations, especially when dealing with complementary angles in the context of. Trigonometric co function identities are relationships between the basic trigonometric functions (sine and cosine) based on complementary angles. they also show that the graphs of sine and cosine are identical, but shifted by a constant of \frac {\pi} {2} 2π. the identities are extremely useful when dealing with sums of trigonometric functions.
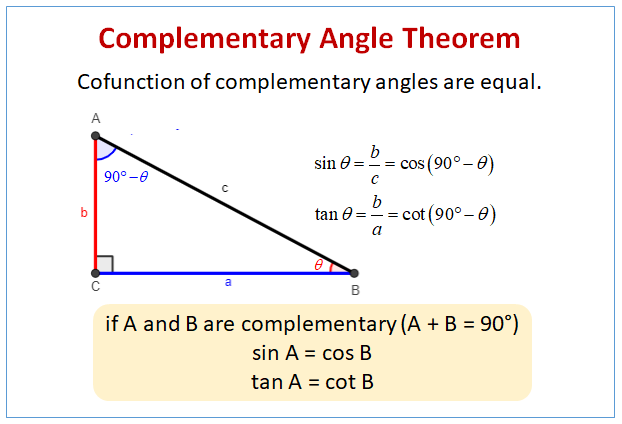
Sin And Cos Of Complementary Angles Examples Solutions Videos The cosine of an angle and the sine of its complement are also equal. if a b = 90°, then cos (a)=sin (b) and cos (b)=sin (a). for example: if sin (30°)=0.5, then cos (60°)=0.5 because 30° 60° = 90°. this property is particularly useful in trigonometric calculations, especially when dealing with complementary angles in the context of. Trigonometric co function identities are relationships between the basic trigonometric functions (sine and cosine) based on complementary angles. they also show that the graphs of sine and cosine are identical, but shifted by a constant of \frac {\pi} {2} 2π. the identities are extremely useful when dealing with sums of trigonometric functions.

Basic Trigonometry вђ A Quick Recap Finding Value Of Trignometric Fun

Comments are closed.