Skeletal Muscle Fiber Diagram Vrogue Co
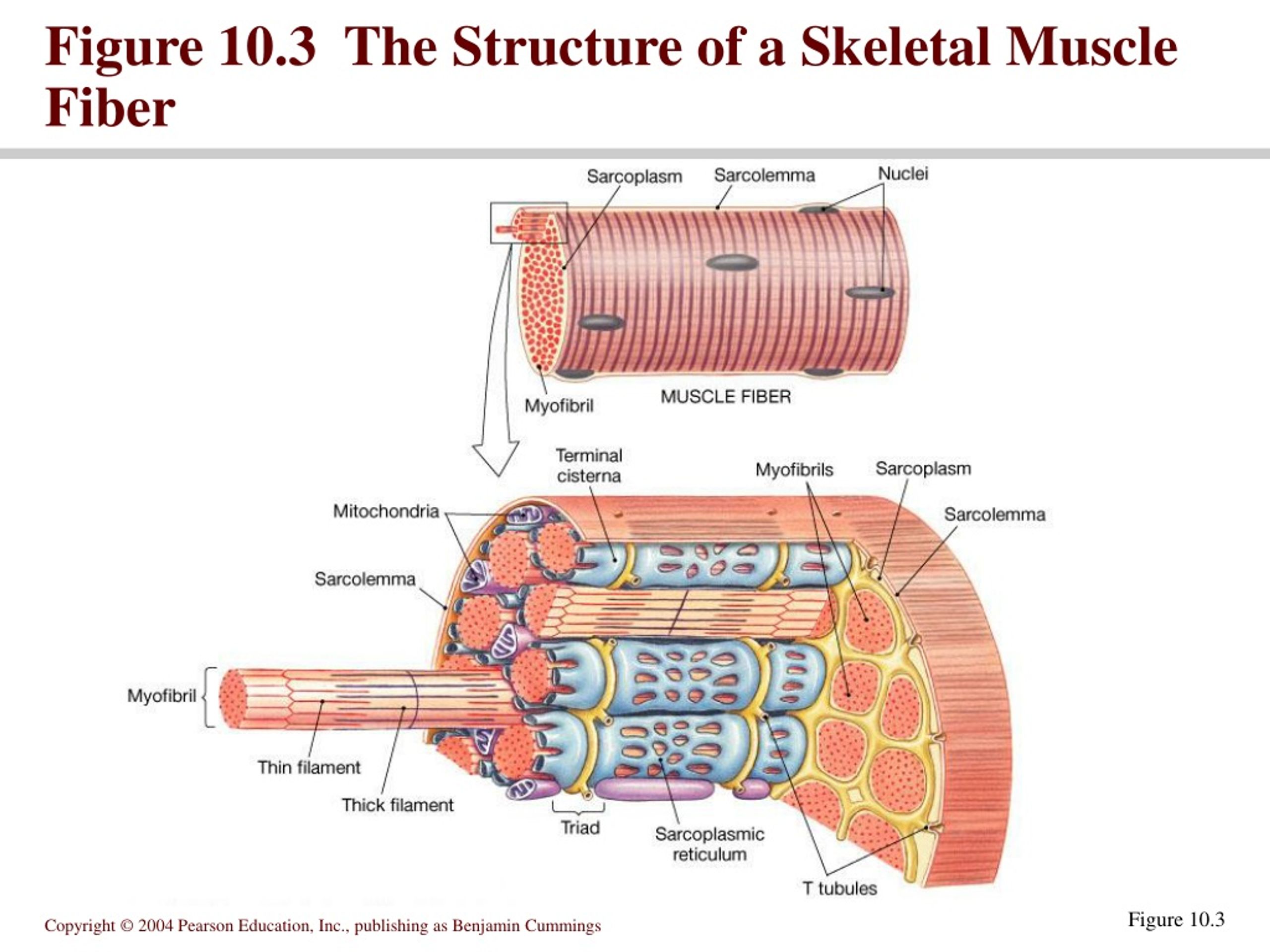
Figure 10 3 The Structure Of A Skeletal Muscle Fiber Vrogue Co Muscles attach to bones directly or through tendons or aponeuroses. skeletal muscles maintain posture, stabilize bones and joints, control internal movement, and generate heat. skeletal muscle fibers are long, multinucleated cells. the membrane of the cell is the sarcolemma; the cytoplasm of the cell is the sarcoplasm. Skeletal muscle fibers. because skeletal muscle cells are long and cylindrical, they are commonly referred to as muscle fibers. skeletal muscle fibers can be quite large for human cells, with diameters up to 100 μm and lengths up to 30 cm (11.8 in) in the sartorius of the upper leg. during early development, embryonic myoblasts, each with its.

Structure Of A Skeletal Muscle Fiber Diagram Quizlet Vrogue Co Skeletal muscle is an excitable, contractile tissue responsible for maintaining posture and moving the orbits, together with the appendicular and axial skeletons. it attaches to bones and the orbits through tendons. excitable tissue responds to stimuli through electrical signals. contractile tissue is able to generate tension of force. These myoblasts asre located to the periphery of the myocyte and flattened so as not to impact myocyte contraction. myocyte: skeletal muscle cell: a skeletal muscle cell is surrounded by a plasma membrane called the sarcolemma with a cytoplasm called the sarcoplasm. a muscle fiber is composed of many myofibrils, packaged into orderly units. Skeletal muscle is one of the three types of muscle tissue, alongside cardiac and smooth muscle. it is classified as a striated muscle tissue, which functions to contract and permit movements under voluntary control. this article will discuss the structure of skeletal muscle tissue, it’s mode of contraction and relevant clinical conditions. Muscles and muscle tissue. this type of tissue is found in skeletal muscles and is responsible for the voluntary movements of bones. muscle is defined as a tissue primarily composed of specialized cells fibers which are capable of contracting in order to effect movement. this can relate to movement of the body or body parts with our external.

Comments are closed.