Skeletal Muscle Tissue And Structure Preview Human Histology

File Skeletal Muscle Histology 001 Jpg Embryology Skeletal muscle is an excitable, contractile tissue responsible for maintaining posture and moving the orbits, together with the appendicular and axial skele. Skeletal muscle histology. this type of tissue is found in skeletal muscles and is responsible for the voluntary movements of bones. skeletal muscle is an excitable, contractile tissue responsible for maintaining posture and moving the orbits, together with the appendicular and axial skeletons. it attaches to bones and the orbits through tendons.

Skeletal Muscle Tissue And Structure Preview Human Histology Skeletal muscle is one of the three types of muscle tissue, alongside cardiac and smooth muscle. it is classified as a striated muscle tissue, which functions to contract and permit movements under voluntary control. this article will discuss the structure of skeletal muscle tissue, it’s mode of contraction and relevant clinical conditions. 1. introduction. striated muscle is composed of two major muscle types—skeletal and cardiac. while the cardiac (heart) muscle functionally represents a set of self‐stimulating, non‐fatiguing muscle cells with an intermediate energy requirement, skeletal muscle represents a set of innervated, voluntary muscle cells that exhibit fatigue with high energy requirements (e.g., muscles of the. Summary. skeletal muscles are composed of large, elongated, and cylindrical cells that are also called muscle fibers. each fiber has multiple nuclei in the periphery, and the capillaries that supply the skeletal muscle are typically found at the corners of the muscle fibers. within each muscle fiber, there are myofibrils, which are long, thin. Choose a name for the bookmark and select the folder in which you want it saved. skeletal muscle fibers are elongated cylindrical shaped cells with multiple, peripherally located nuclei and a cytoplasm filled with contractile filaments. have polygonal cross sections (50 to 100 µm in diameter) with nuclei at the periphery.
:watermark(/images/watermark_5000_10percent.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/overview_image/1829/cyleTwutK5OQGBEyIoNMw_skeletal-muscle-tissue_english.jpg)
Skeletal Muscle Tissue Histology Kenhub Summary. skeletal muscles are composed of large, elongated, and cylindrical cells that are also called muscle fibers. each fiber has multiple nuclei in the periphery, and the capillaries that supply the skeletal muscle are typically found at the corners of the muscle fibers. within each muscle fiber, there are myofibrils, which are long, thin. Choose a name for the bookmark and select the folder in which you want it saved. skeletal muscle fibers are elongated cylindrical shaped cells with multiple, peripherally located nuclei and a cytoplasm filled with contractile filaments. have polygonal cross sections (50 to 100 µm in diameter) with nuclei at the periphery. Muscles and muscle tissue. this type of tissue is found in skeletal muscles and is responsible for the voluntary movements of bones. muscle is defined as a tissue primarily composed of specialized cells fibers which are capable of contracting in order to effect movement. this can relate to movement of the body or body parts with our external. Muscle tissue is composed of cells specialized for contraction. muscle is classified into three types according to their structure and function: skeletal and cardiac muscle cells are called striated because they show an alternating series of bands. the repeating arrangement of their basic contractile unit, the sarcomere, produces these striations.
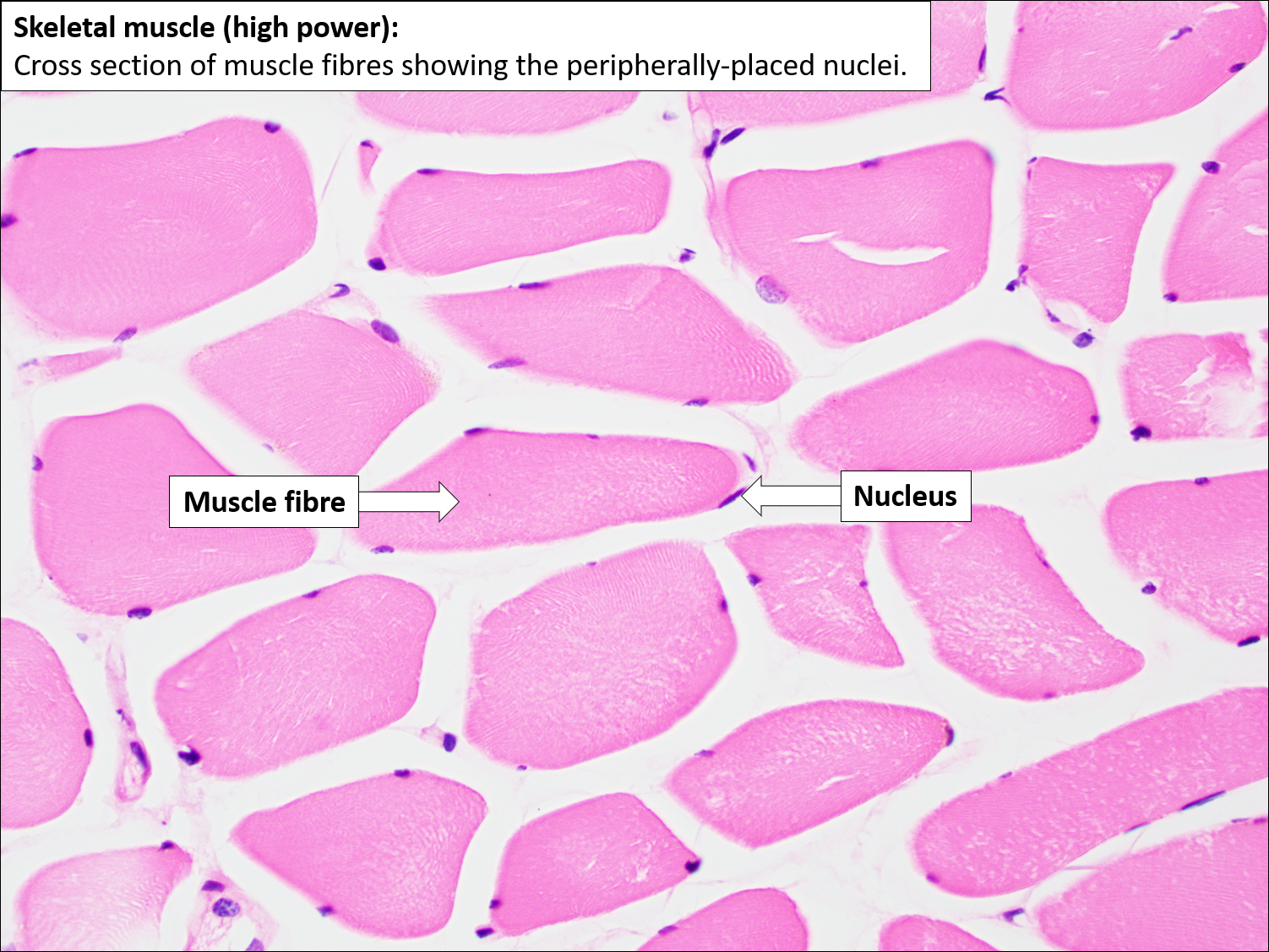
Skeletal Muscle вђ Normal Histology вђ Nus Pathweb Nus Pathweb Muscles and muscle tissue. this type of tissue is found in skeletal muscles and is responsible for the voluntary movements of bones. muscle is defined as a tissue primarily composed of specialized cells fibers which are capable of contracting in order to effect movement. this can relate to movement of the body or body parts with our external. Muscle tissue is composed of cells specialized for contraction. muscle is classified into three types according to their structure and function: skeletal and cardiac muscle cells are called striated because they show an alternating series of bands. the repeating arrangement of their basic contractile unit, the sarcomere, produces these striations.

Comments are closed.