Skeletal Muscle Tissue Under Microscope Art Floppy Vrogue Co

Skeletal Muscle Tissue Under Microscope Art Floppy Vrogue Co Skeletal muscle histology. this type of tissue is found in skeletal muscles and is responsible for the voluntary movements of bones. skeletal muscle is an excitable, contractile tissue responsible for maintaining posture and moving the orbits, together with the appendicular and axial skeletons. it attaches to bones and the orbits through tendons. Finally, i will share the main differentiating points of the skeletal muscle microscope slide from smooth and cardiac muscles. so, if you want to learn the basic microscopic features of the skeletal muscle histology slide and differentiate it from smooth and cardiac muscles, let’s continue this article till the end.
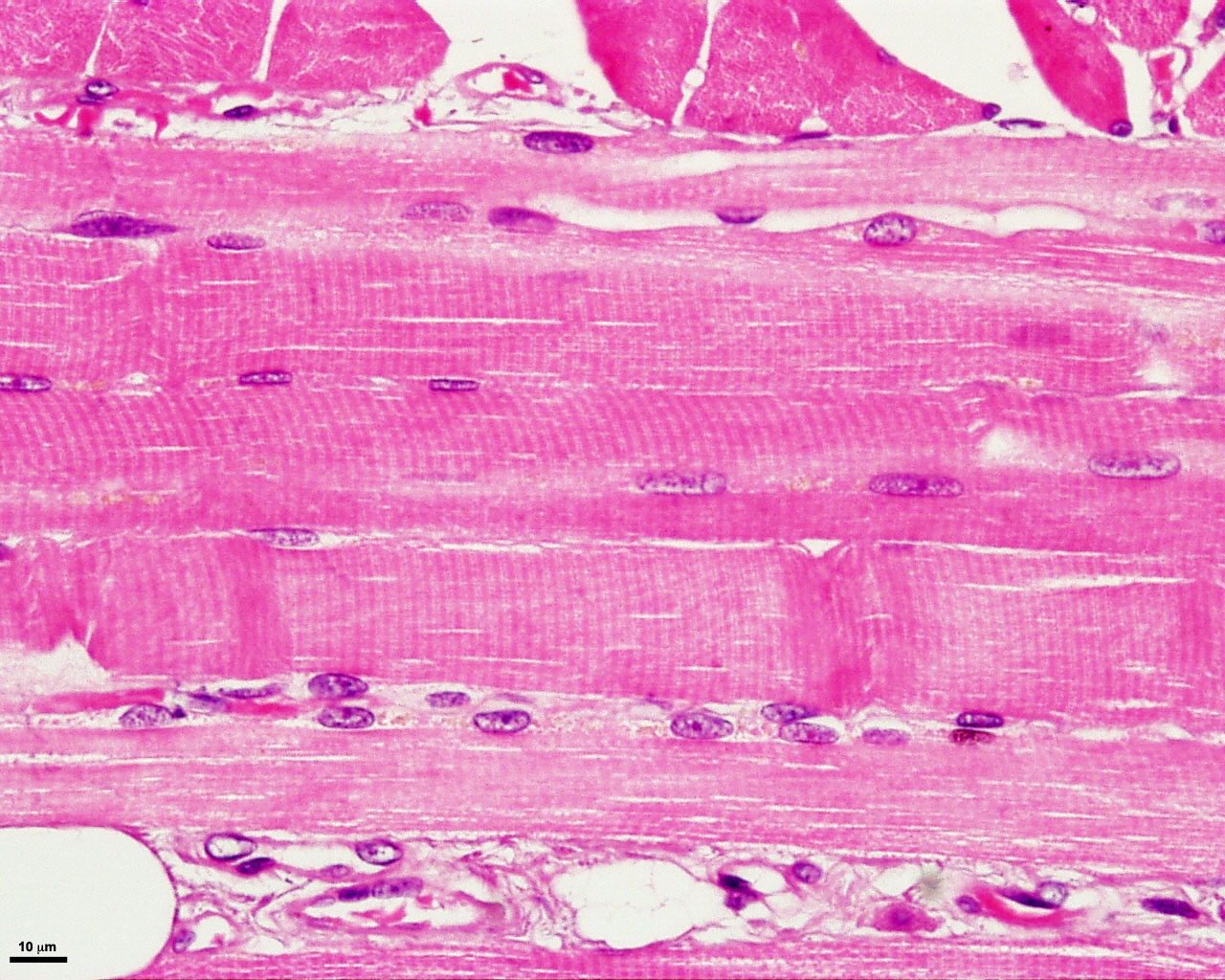
Skeletal Muscle Tissue Under Microscope Art Floppy Vrogue Co Microscopic anatomy of skeletal muscles. skeletal muscle is found attached to bones. it consists of long multinucleate fibers. the fibers run the entire length of the muscle they come from and so are usually too long to have their ends visible when viewed under the microscope. the fibers are relatively wide and very long, but unbranched. fibers. Looking closer at skeletal muscle. all skeletal muscle fibres are not the same. they differ in structure and function, for example, in the speed they can contract. skeletal muscle fibres contract at different speeds depending on: their ability to split atp (an energy releasing chemical) the way they produce atp. how quickly they get tired. Muscles attach to bones directly or through tendons or aponeuroses. skeletal muscles maintain posture, stabilize bones and joints, control internal movement, and generate heat. skeletal muscle fibers are long, multinucleated cells. the membrane of the cell is the sarcolemma; the cytoplasm of the cell is the sarcoplasm. Choose a name for the bookmark and select the folder in which you want it saved. skeletal muscle fibers are elongated cylindrical shaped cells with multiple, peripherally located nuclei and a cytoplasm filled with contractile filaments. have polygonal cross sections (50 to 100 µm in diameter) with nuclei at the periphery.

Skeletal Muscle Tissue Under Microscope Art Floppy Vrogue Co Muscles attach to bones directly or through tendons or aponeuroses. skeletal muscles maintain posture, stabilize bones and joints, control internal movement, and generate heat. skeletal muscle fibers are long, multinucleated cells. the membrane of the cell is the sarcolemma; the cytoplasm of the cell is the sarcoplasm. Choose a name for the bookmark and select the folder in which you want it saved. skeletal muscle fibers are elongated cylindrical shaped cells with multiple, peripherally located nuclei and a cytoplasm filled with contractile filaments. have polygonal cross sections (50 to 100 µm in diameter) with nuclei at the periphery. Muscle tissue is composed of cells specialized for contraction. muscle is classified into three types according to their structure and function: skeletal and cardiac muscle cells are called striated because they show an alternating series of bands. the repeating arrangement of their basic contractile unit, the sarcomere, produces these striations. Fascicle. perimysium. width of skeletal muscle fiber. nucleus (of skeletal muscle) striation (in skeletal muscle) mitochondria (of muscle fiber) myofibrils. nucleus (in muscle fiber) study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like endomysium (skeletal muscle fiber), skeletal muscle fiber (in cross section), fascicle and more.

Comments are closed.