Skin Labeled Skin Model Dermis Epidermis
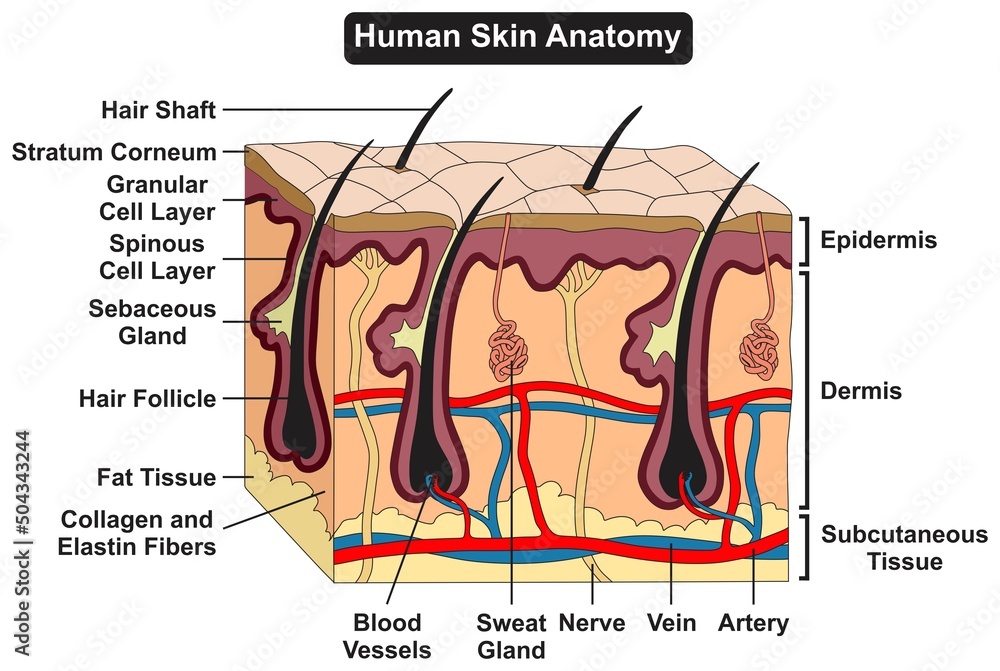
Human Skin Anatomy Structure And Parts Infographic Diagram Epidermis Dermal papillae increase the strength of the connection between the epidermis and dermis; the greater the folding, the stronger the connections made (figure 5.1.4). figure 5.1.4 – layers of the epidermis: the epidermis of thick skin has five layers: stratum basale, stratum spinosum, stratum granulosum, stratum lucidum, and stratum corneum. The skin is by far the largest organ of the human body, weighing about 10 pounds (4.5 kg) and measuring about 20 square feet (2 square meters) in surface area. it forms the outer covering for the entire body and protects the internal tissues from the external environment. the skin consists of two distinct layers: the epidermis and the dermis.

Anatomy Of Human Skin The Most Superficial Layer Of The Skin Is The Figure 5.2 layers of skin the skin is composed of two main layers: the epidermis, made of closely packed epithelial cells, and the dermis, made of dense, irregular connective tissue that houses blood vessels, hair follicles, sweat glands, and other structures. beneath the dermis lies the hypodermis, which is composed mainly of loose connective. The layers of your skin. your skin includes three layers known as epidermis, dermis, and fat. some health issues, such as dermatitis and infections, can affect how these different layers work to. Download 3d model. triangles: 299.5k. vertices: 151.2k. more model information. this model depicts the anatomy of the skin. it is part of a dermatology e learning module for medical students of the university of groningen. license:. The skin is the largest organ in the body, covering its entire external surface. the skin has 3 layers—the epidermis, dermis, and hypodermis, which have different anatomical structures and functions (see image. cross section, layers of the skin). the skin's structure comprises an intricate network that serves as the body's initial barrier against pathogens, ultraviolet (uv) light, chemicals.

Comments are closed.