Sliding Filament Model Of Muscle Contraction
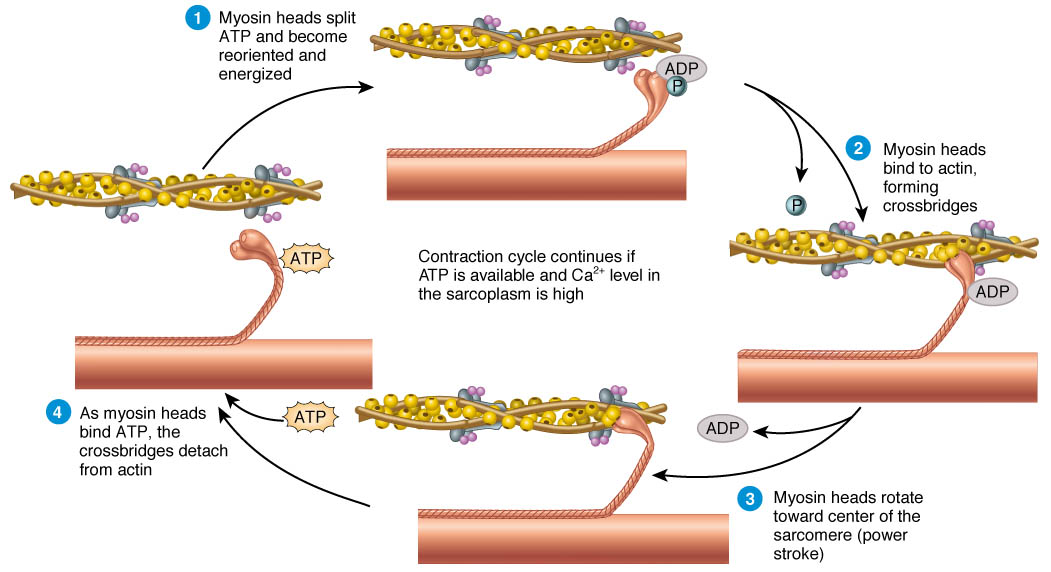
Sliding Filament Model Of Muscle Contraction Learn how actin and myosin filaments slide past each other to produce muscle tension and shorten the sarcomere. see diagrams, analogies, and examples of the sliding filament theory and its molecular mechanisms. Learn how thick and thin filaments slide past each other in sarcomeres to cause muscle contraction. see diagrams, definitions, and examples of the sliding filament theory and its mechanisms.
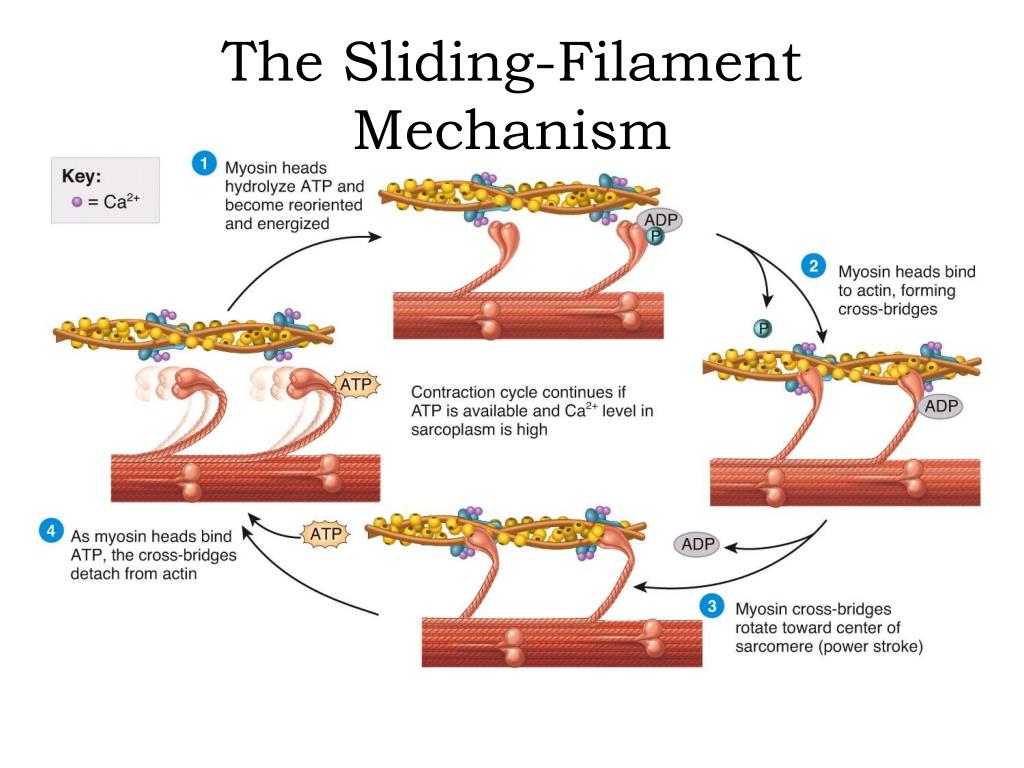
Ppt The Sliding Filament Mechanism Powerpoint Presentation Free The sliding filament theory explains the mechanism of muscle contraction based on muscle proteins that slide past each other to generate movement. [1] according to the sliding filament theory, the myosin ( thick filaments ) of muscle fibers slide past the actin ( thin filaments ) during muscle contraction, while the two groups of filaments remain at relatively constant length. At the level of the sliding filament model, expansion and contraction only occurs within the i and h bands. the myofilaments themselves do not contract or expand and so the a band remains constant. figure \(\pageindex{1}\): the sarcomere and the sliding filament model of contraction: during contraction myosin ratchets along actin myofilaments compressing the i and h bands. Some of the key observations in the studies which outlined the sliding filament model of contraction (huxley & hanson, 1954[alp]; huxley & niedergerke, 1954[alp]) were actually rather simple (but technically innovative) observations. firstly, it was found that, as the sarcomere length changed, for example by stretching a relaxed muscle, the length of the a band remained virtually constant. Learn how actin and myosin myofilaments slide over each other, shortening the sarcomere and generating tension in the muscle. understand the structure and function of the sarcomere, the cross bridge cycle and the key regions involved in contraction.

Actin And Myosin Biology Dictionary Some of the key observations in the studies which outlined the sliding filament model of contraction (huxley & hanson, 1954[alp]; huxley & niedergerke, 1954[alp]) were actually rather simple (but technically innovative) observations. firstly, it was found that, as the sarcomere length changed, for example by stretching a relaxed muscle, the length of the a band remained virtually constant. Learn how actin and myosin myofilaments slide over each other, shortening the sarcomere and generating tension in the muscle. understand the structure and function of the sarcomere, the cross bridge cycle and the key regions involved in contraction. The sliding filament model of muscle contraction describes how muscles generate force and produce movement. muscle contraction occurs as a result of the sliding of thin filaments (actin) over thick filaments (myosin) within muscle fibers. the process of contraction starts when an action potential reaches the muscle fiber and triggers the. The sliding filament model. this review will describe the investigation of the mechanism of muscle contraction and cell motility from 1972 to the present. the preceding article in this issue by andrew szent gyorgyi covers the period up to 1972. in 1972 the field of actomyosin interactions was summarized in a conference at cold spring harbor.

9 3 Muscle Fiber Contraction And Relaxation вђ Biomechanics Of Human The sliding filament model of muscle contraction describes how muscles generate force and produce movement. muscle contraction occurs as a result of the sliding of thin filaments (actin) over thick filaments (myosin) within muscle fibers. the process of contraction starts when an action potential reaches the muscle fiber and triggers the. The sliding filament model. this review will describe the investigation of the mechanism of muscle contraction and cell motility from 1972 to the present. the preceding article in this issue by andrew szent gyorgyi covers the period up to 1972. in 1972 the field of actomyosin interactions was summarized in a conference at cold spring harbor.

38 16 Muscle Contraction And Locomotion Sliding Filament Model Of

Comments are closed.