Sliding Muscle Filament Theory
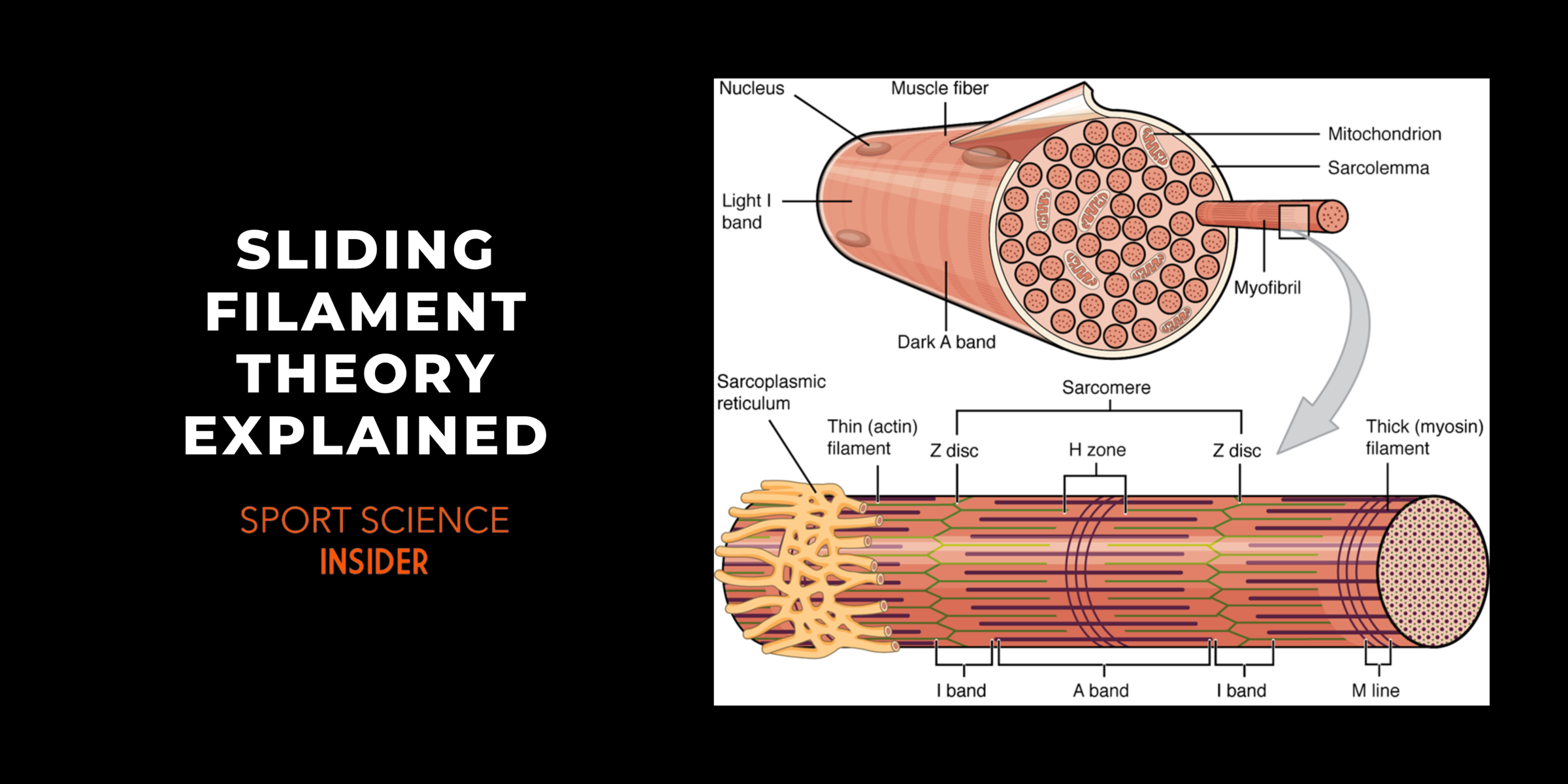
Sliding Filament Theory Steps Explained вђ Sport Science Insider Learn how actin and myosin filaments slide past each other to produce muscle tension and shorten the sarcomere. see diagrams, analogies, and examples of the sliding filament theory and its molecular mechanisms. The sliding filament theory explains the mechanism of muscle contraction based on muscle proteins that slide past each other to generate movement. [1] according to the sliding filament theory, the myosin (thick filaments) of muscle fibers slide past the actin (thin filaments) during muscle contraction, while the two groups of filaments remain.
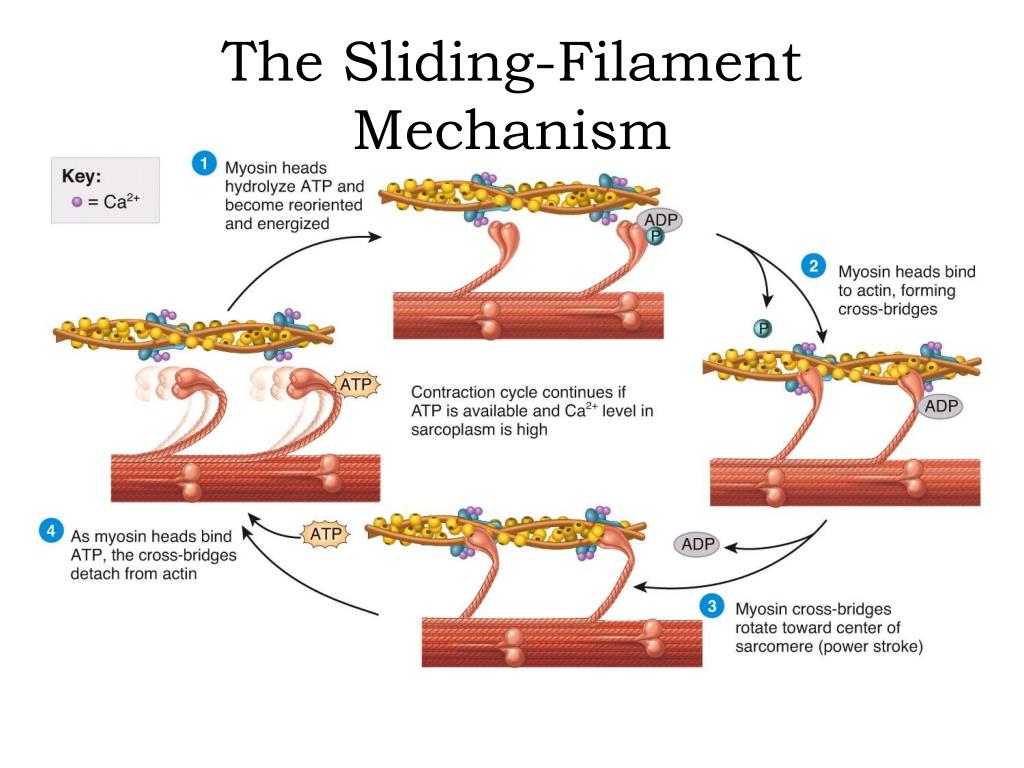
Sliding Filament Theory Example Learn how muscle contractions work at cellular level with proteins sliding against each other causing cross bridges. see a practical example of a bicep curl and an analogy of a bookcase to understand the sliding filament theory. These two 1954 papers really defined the sliding filament model of muscle contraction, but it was not immediately accepted by everyone in the muscle field. three later papers, two by hugh huxley and jean hanson and one by hugh huxley alone, all in 1957, helped to establish sliding filaments beyond reasonable doubt. Sliding filament theory of muscle contraction. once the muscle fiber is stimulated by the motor neuron, actin, and myosin protein filaments within the skeletal muscle fiber slide past each other to produce a contraction. the sliding filament theory is the most widely accepted explanation for how this occurs. according to this theory, muscle. Learn how thick and thin filaments slide past each other in sarcomeres to cause muscle contraction. see the changes in the named bands on the sarcomere and the cross bridges formed by myosin and actin.

Comments are closed.