Slope And Deflection Bartleby
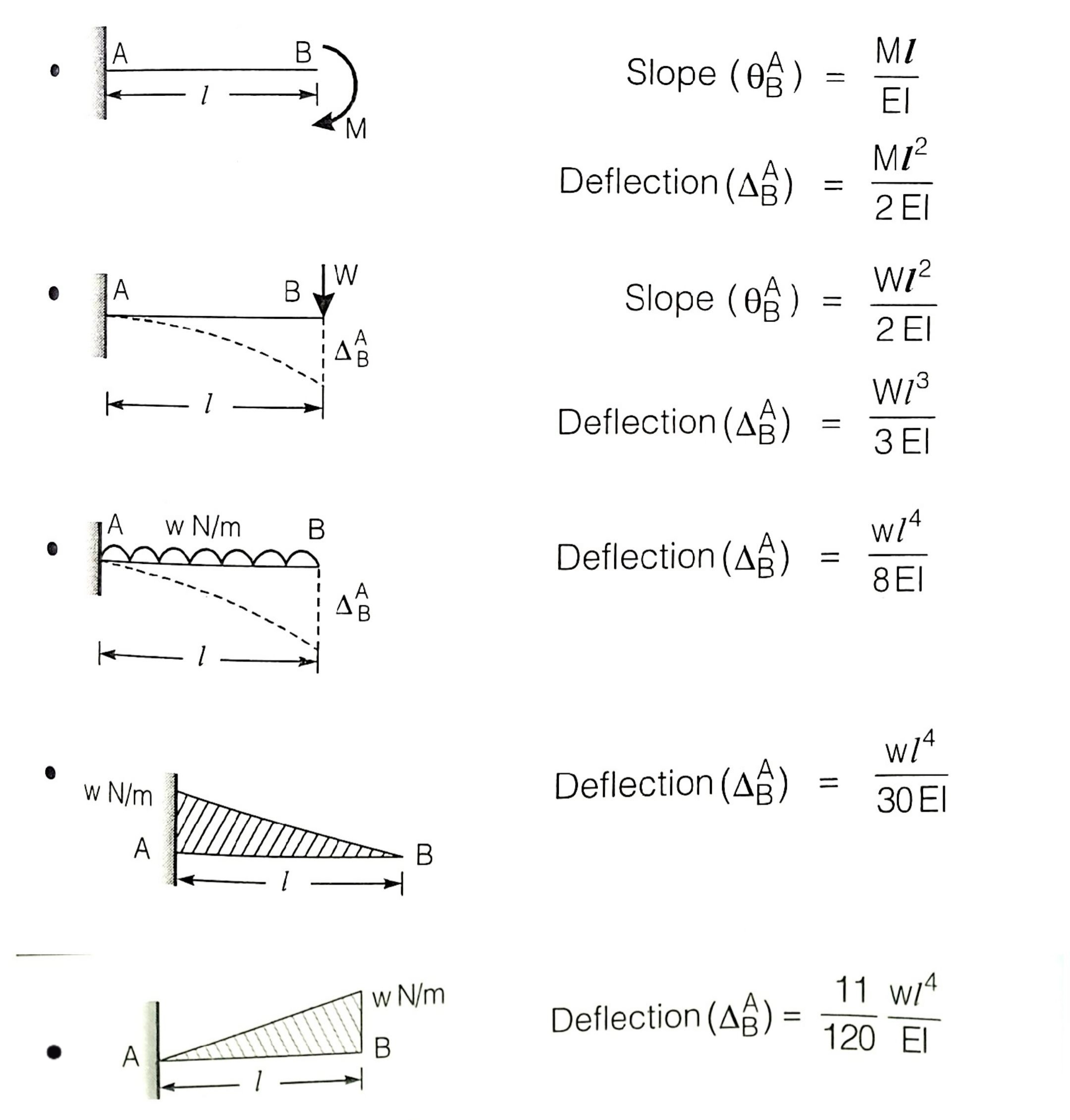
Cantilever Beam Large Deflection Equation Design Talk Methods for determining slope and deflection at a section by double integration method. we already know that, m = e i × d 2 y d x 2. where m is the bending moment of the beam, e i is the flexural rigidity of the beam, e is the young's modulus, i is the moment of inertia. integrating the above equation, d 2 y d x 2 = m e i d y d x = ∫ m e i d. Determine the slope & deflection at the free end of the cantilever beam shown in figure, by conjugate beam or moment area method, take ei is constant throughout. 60 kn 100 kn m a b 5m 4m determine the value of the deflection at c in mm. answer in 2 decimals d. 20kn 30kn c d e 200,000 mpa i = 9 x 107 mm4 b 3m 2m 2m.

Slope And Deflection Bartleby Author: kassimali, aslam. publisher: kassimali, aslam. transcribed image text: problem 1 solve the slope and deflection at points b and c using the double integration method. point b is at 2m from a. point c is at the mid span. 25kn m 10kn m a b e = 200gpa c 8m i = 7.5 x 10 6 mª 10kn m d. this is a popular solution!. A beam carries a distributed load that varies from zero at support a to 50 kn m at its overhanging end, as shown in figure 7.4a.write the equation of the elastic curve for segment ab of the beam, determine the slope at support a, and determine the deflection at a point of the beam located 3 m from support a. θa,rel θb,rel = θa,rel1 θa,rel2 θa,rel3 = θb,rel1 θb,rel2 θb,rel3 (6) (7) figure 9.4: using the moment area method to construct the slope deflection equation. to determine each relative rotation component using the moment area theorem, all of the required curvature diagrams are shown in figure 9.4 along with the appropriate. Mbc = 2ei 6 (2θb − 0.01500) 75. the last slope deflection equation is for the moment at the end of member bc at point c, where c is the near side and b is the far side, so: mcb = 2ei l (2θc θb − 3ψbc) femcb mcb = 2ei 6 (2θc θb − 3(0.00500)) − 75. again, node c is fixed, so θc = 0:.

Answered Slope Deflection Method Is Used Forвђ Bartleby θa,rel θb,rel = θa,rel1 θa,rel2 θa,rel3 = θb,rel1 θb,rel2 θb,rel3 (6) (7) figure 9.4: using the moment area method to construct the slope deflection equation. to determine each relative rotation component using the moment area theorem, all of the required curvature diagrams are shown in figure 9.4 along with the appropriate. Mbc = 2ei 6 (2θb − 0.01500) 75. the last slope deflection equation is for the moment at the end of member bc at point c, where c is the near side and b is the far side, so: mcb = 2ei l (2θc θb − 3ψbc) femcb mcb = 2ei 6 (2θc θb − 3(0.00500)) − 75. again, node c is fixed, so θc = 0:. Deflection limits (serviceability) various guidelines have been derived, based on usage, to determine maximum allowable deflection limits. typically, a floor system with a ll deflection in excess of l 360 will feel bouncy or crack plaster. flat roofs require a minimum slope of 1⁄4” ft to avoid ponding. “ponding” refers to the. Slope deflection equations for mnd moments: modified slope deflection equation when far end is supported by a roller or pin: practice problems. 11.1 using the slope deflection method, compute the end moment of members of the beams shown in figure p11.1 through figure p11.5 and draw the bending moment and shear force diagrams. ei = constant. fig.
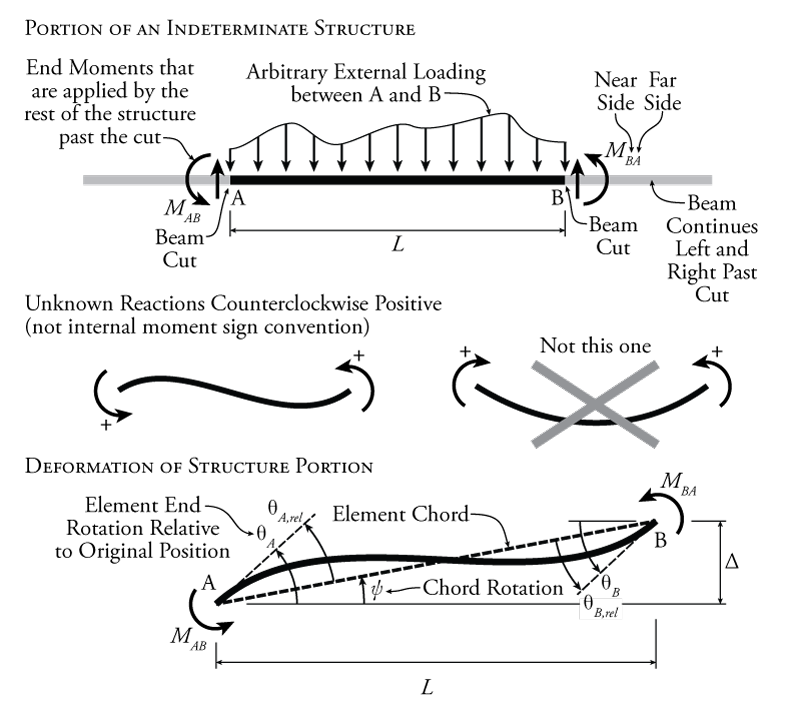
Beam Slope Deflection Equations The Best Picture Of Beam Deflection limits (serviceability) various guidelines have been derived, based on usage, to determine maximum allowable deflection limits. typically, a floor system with a ll deflection in excess of l 360 will feel bouncy or crack plaster. flat roofs require a minimum slope of 1⁄4” ft to avoid ponding. “ponding” refers to the. Slope deflection equations for mnd moments: modified slope deflection equation when far end is supported by a roller or pin: practice problems. 11.1 using the slope deflection method, compute the end moment of members of the beams shown in figure p11.1 through figure p11.5 and draw the bending moment and shear force diagrams. ei = constant. fig.

Comments are closed.