Solved 01 Ethylbenzene Is Converted To Styrene In The Chegg

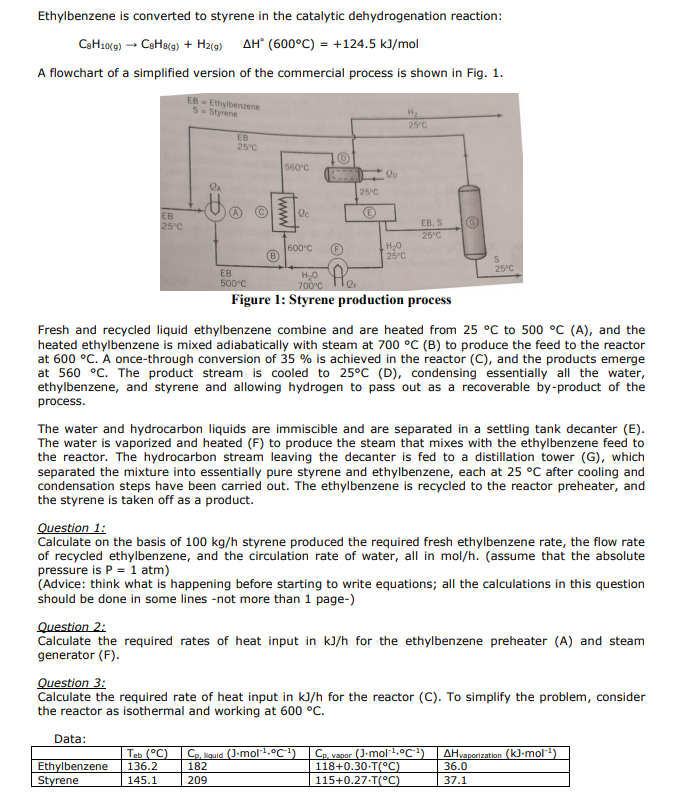
Solved 01 Ethylbenzene Is Converted To Styrene In The Chegg Here’s the best way to solve it. 01: ethylbenzene is converted to styrene in the catalytic dehydrogenation reaction: ch10 (g) c3hz (9) h2: aĦ (600°c) = 124.5 kj mol fresh and recycled liquid ethylbenzene combine and are heated from 25 °c to 500°c (a), and the heated ethylbenzene is mixed adiabatically with steam at 700 c and 1 atm (b. See answer. question: ethylbenzene is converted to styrene in the catalytic dehydrogenation reaction csh₁0 (g) → cshs (g) h₂: aa (600°c) = 124.5 kj mol a flowchart of a simplified version of the commercial process is shown here. eb 25 c eb = ethylbenzene s = styrene qa eb 25°c a eb 500°c Ⓡ 560°c qc 600°c h₂o 700°c 10 po 25.

Solved 01 Ethylbenzene Is Converted To Styrene In The Chegg A once through conversion of $35 \%$ is achieved in the reactor $\left(\mathrm{c}\right.$, and the products emerge at $560^{\circ} \mathrm{c}$. the product stream is cooled to $25^{\circ} \mathrm{c}$ (d), condensing essentially all of the water, ethylbenzene, and styrene and allowing hydrogen to pass out as a recoverable by product of the process. 2. styrene production from ethylbenzene the following text in this section is taken from [2] (shortened) and is permitted for personal use only ! 2.1 data of styrene and ethylbenzene styrene, also known as phenylethylene, vinylbenzene, styrol, or cinnamene, c6h5–ch=ch2, is an impor tant industrial unsaturated aromatic monomer. Problem 4. a 2 × 10 4 cm 3 slurry reactor has 1000 porous catalyst particles cm 3 on which the reaction a → b occurs with a surface rate r ′ ′ ( moles cm 2 sec) = 4 × 10 − 8 c a, with c a in moles cm 3. each particle is 0.02 cm diameter and has a surface area of 500 cm 2. (the catalyst occupies negligible volume in the reactor.). The ethylbenzene is recycled to the reactor preheater, and the styrene is taken off as a product. (a) on a basis of $100 \mathrm{kg} \mathrm{h}$ styrene produced, calculate the required fresh ethylbenzene feed rate, the flow rate of recycled ethylbenzene, and the circulation rate of water, all in mol h.
Solved Ethylbenzene Is Converted To Styrene In The Catalytic Chegg Problem 4. a 2 × 10 4 cm 3 slurry reactor has 1000 porous catalyst particles cm 3 on which the reaction a → b occurs with a surface rate r ′ ′ ( moles cm 2 sec) = 4 × 10 − 8 c a, with c a in moles cm 3. each particle is 0.02 cm diameter and has a surface area of 500 cm 2. (the catalyst occupies negligible volume in the reactor.). The ethylbenzene is recycled to the reactor preheater, and the styrene is taken off as a product. (a) on a basis of $100 \mathrm{kg} \mathrm{h}$ styrene produced, calculate the required fresh ethylbenzene feed rate, the flow rate of recycled ethylbenzene, and the circulation rate of water, all in mol h. The majority of the adsorbed ethylbenzene is converted into styrene while only a fraction the adsorbed ethylbeneze have gone for cracking reaction to produce benzene and toluene. the “two type active sites” model assumed that there are two types of sites (x and z) for the adsorption of ethylbenze (x and z). The optimal operating conditions could enhance the yield of styrene within the range of (51 to 99.6%) and conversion of nitrobenzene within range of (35.7 to 79.6%) compared to the previous works.
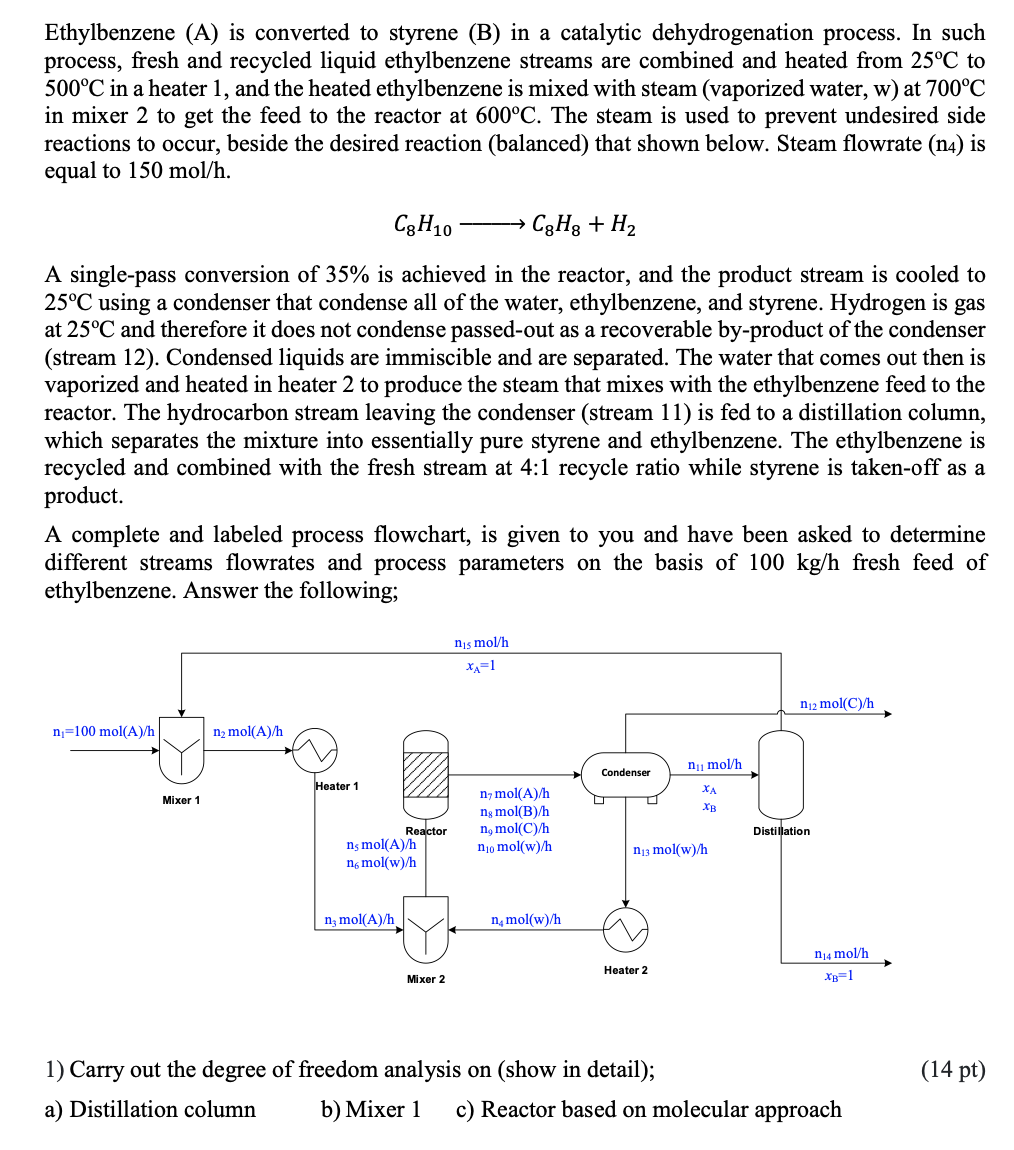
Ethylbenzene A Is Converted To Styrene B In A Chegg The majority of the adsorbed ethylbenzene is converted into styrene while only a fraction the adsorbed ethylbeneze have gone for cracking reaction to produce benzene and toluene. the “two type active sites” model assumed that there are two types of sites (x and z) for the adsorption of ethylbenze (x and z). The optimal operating conditions could enhance the yield of styrene within the range of (51 to 99.6%) and conversion of nitrobenzene within range of (35.7 to 79.6%) compared to the previous works.

Comments are closed.