Special Topics The Kalman Filter 1 Of 55 What Is A Kalman Filter

Special Topics The Kalman Filter 1 Of 55 What Is A Kalman Filter Visit ilectureonline for more math and science lectures!in this video i will explain what is kalman filter and how is it used.next video in this s. Visit ilectureonline for more math and science lectures!in this video i will explain what is the variance covariance matrix.next video in this ser.

Kalman Filter Part 1 Youtube Kalman filter explained simply. Kalman filter kalman filter. 1.1 course description while the kalman filter has been around for about 30 years, it (and related optimal estimators) have recently started popping up in a wide variety of computer graphics. The kalman filter is an iterative process that estimates the state of a dynamic system from a series of incomplete and noisy measurements. it is recursive, meaning that it can run in real time using only the current input measurements and the previously calculated state and its uncertainty matrix; no additional past information is required.
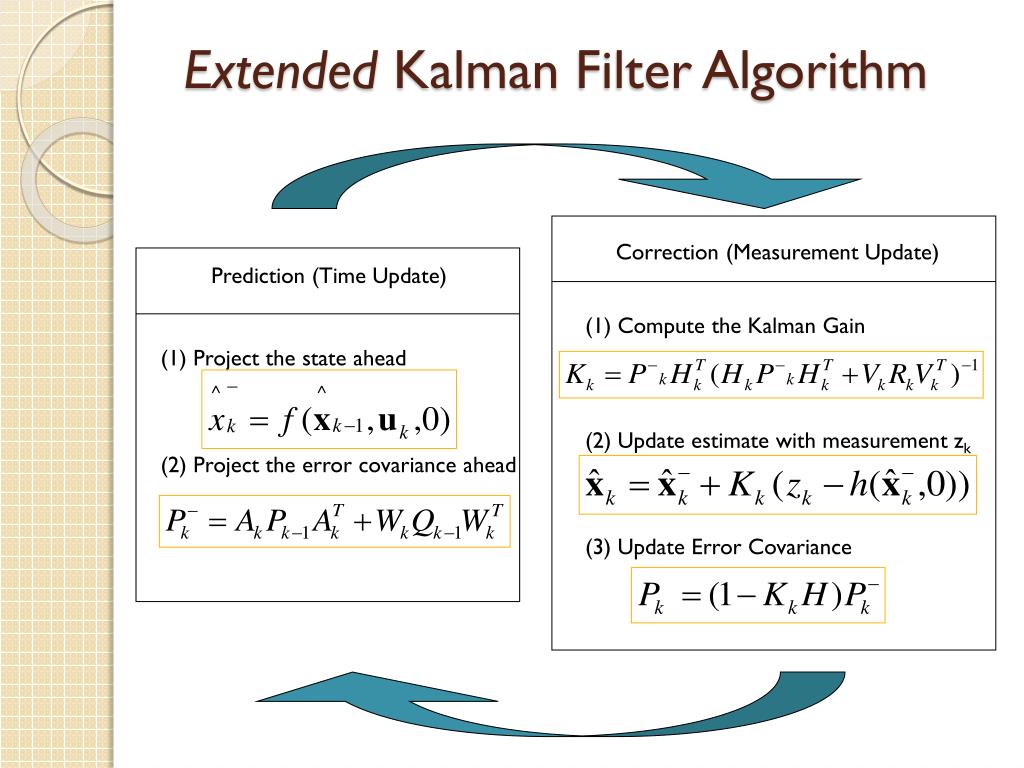
Ppt An Introduction To The Kalman Filter Powerpoint Presentation 1.1 course description while the kalman filter has been around for about 30 years, it (and related optimal estimators) have recently started popping up in a wide variety of computer graphics. The kalman filter is an iterative process that estimates the state of a dynamic system from a series of incomplete and noisy measurements. it is recursive, meaning that it can run in real time using only the current input measurements and the previously calculated state and its uncertainty matrix; no additional past information is required. Consider special case Σxu(t) = 0, i.e., x and u are uncorrelated, so we have lyapunov iteration Σx(t 1) = aΣx(t)at bΣu(t)bt, which is stable if and only if a is stable if a is stable and Σu(t) is constant, Σx(t) converges to Σx, called the. U = f t. t . m. the relationship between the force applied via the brake or throttle during the time period ∆t (the time elapsed between time epochs t position and velocity of 1 and t) and the. the train is given by the following equations: 2. t = x t ( x o t ( t t ) 1 t 1 # t t ) 2 m.
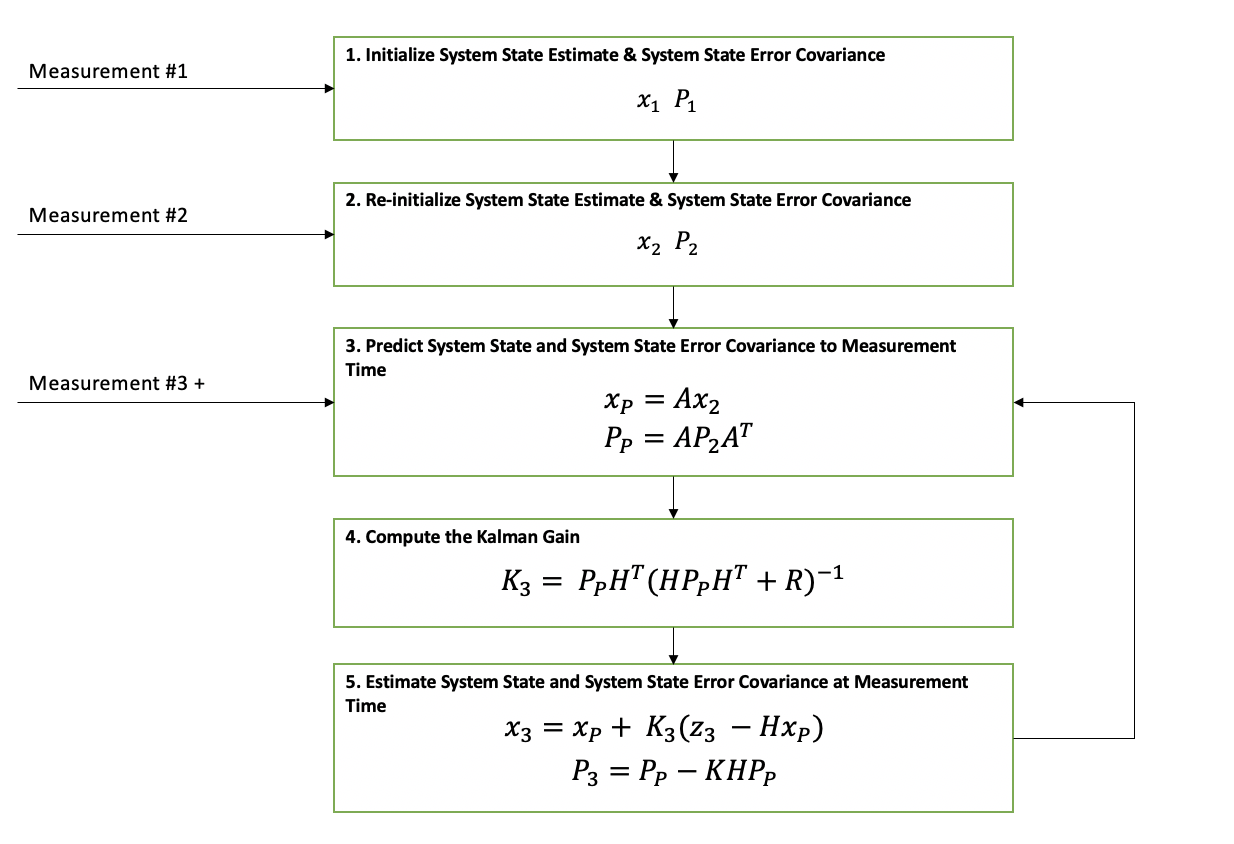
Kalman Filter Explained Simply The Kalman Filter Consider special case Σxu(t) = 0, i.e., x and u are uncorrelated, so we have lyapunov iteration Σx(t 1) = aΣx(t)at bΣu(t)bt, which is stable if and only if a is stable if a is stable and Σu(t) is constant, Σx(t) converges to Σx, called the. U = f t. t . m. the relationship between the force applied via the brake or throttle during the time period ∆t (the time elapsed between time epochs t position and velocity of 1 and t) and the. the train is given by the following equations: 2. t = x t ( x o t ( t t ) 1 t 1 # t t ) 2 m.

Comments are closed.