Spina Bifida Myelomeningocele Meningocele Occulta Causes Symptoms Treatment

Myelomeningocele Definition Symptoms And Treatment Spina bifida occurs in different types: spina bifida occulta, myelomeningocele (my uh lo muh ning go seel) or the very rare type, meningocele (muh ning go seel). spina bifida occulta. occulta means hidden. spina bifida occulta is the mildest and most common type. this type of spina bifida results in a small separation or gap in one or more of. Myelomeningocele is the most serious type of spina bifida and causes moderate to severe disabilities, such as muscle weakness, loss of bladder or bowel control, and or paralysis. babies with myelomeningoceles lower in their spine typically have less severe symptoms than babies with myelomeningoceles higher in their spine. advertisement.
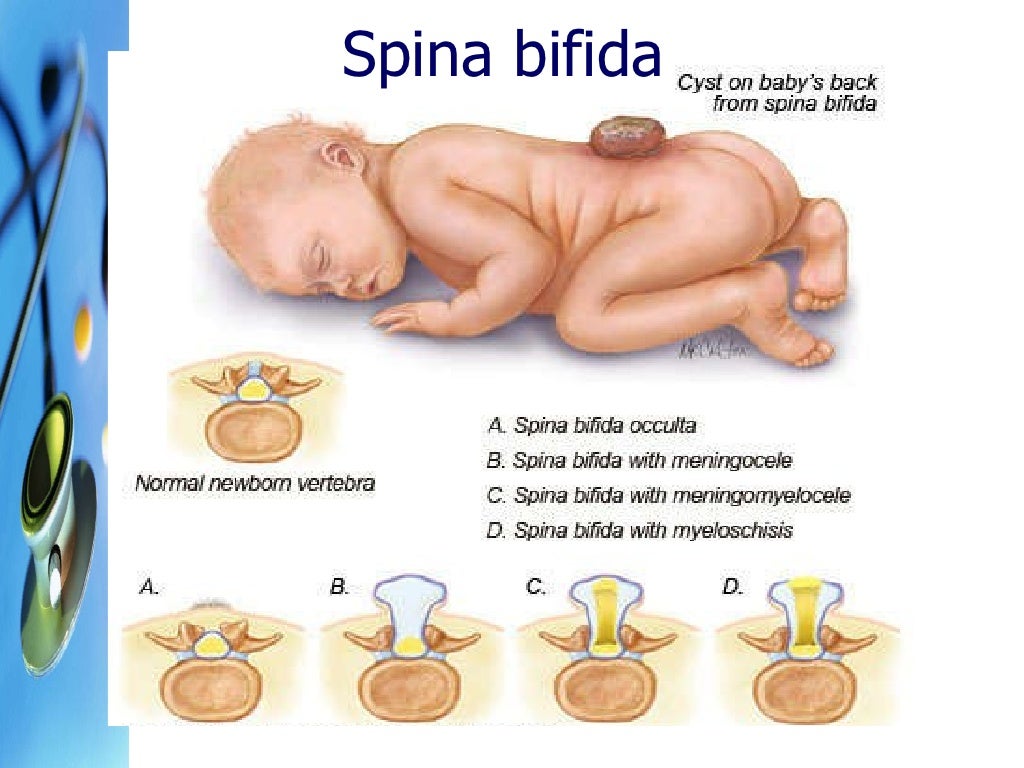
Meningomyelocoele Spina bifida occulta, or hidden spina bifida, is a mild form of spina bifida caused by a gap forming between the vertebrae in your spinal cord. this gap happens during fetal development in the uterus. spina bifida occulta rarely causes symptoms, and most people diagnosed with the condition don’t know they have it. Spina bifida occulta. meningocele. myelomeningocele. spina bifida occulta. spina bifida occulta is the mildest and most common form of this disorder. it usually only involves a minimal portion of the spine; it usually shows no symptoms, and it does not require treatment. when an infant is born with spina bifida occulta, the skin covers the. Spina bifida symptoms. the myelomeningocele lesion can occur at any level on the developing spine, but most are found in the lumbo sacral region. depending on the lesion’s location, myelomeningocele may cause: bladder and bowel problems (incontinence) sexual dysfunction. weakness and loss of sensation below the defect. Spina bifida can be screened with blood tests during pregnancy, but typically the diagnosis is made with an ultrasound exam. maternal serum alpha fetoprotein (msafp) test. for the msafp test, a sample of blood is drawn and tested for alpha fetoprotein (afp). this is a protein produced by the baby.
Infant With Spina Bifida Note The Protruding Meningocele Reproduced Spina bifida symptoms. the myelomeningocele lesion can occur at any level on the developing spine, but most are found in the lumbo sacral region. depending on the lesion’s location, myelomeningocele may cause: bladder and bowel problems (incontinence) sexual dysfunction. weakness and loss of sensation below the defect. Spina bifida can be screened with blood tests during pregnancy, but typically the diagnosis is made with an ultrasound exam. maternal serum alpha fetoprotein (msafp) test. for the msafp test, a sample of blood is drawn and tested for alpha fetoprotein (afp). this is a protein produced by the baby. There are four types of spina bifida: occulta, closed neural tube defects, meningocele, and myelomeningocele. the symptoms of spina bifida vary from person to person, depending on the type and level of involvement. most cases are mild and do not require special treatment. the more serious cases involve nerve damage. Spina bifida occulta. symptoms of spina bifida occulta include: a gap in between vertebrae. no visible opening outside. no fluid filled sack outside the body. small birthmark or dimple on the back.

Diagnosis Focus Spina Bifida Shield Healthcare There are four types of spina bifida: occulta, closed neural tube defects, meningocele, and myelomeningocele. the symptoms of spina bifida vary from person to person, depending on the type and level of involvement. most cases are mild and do not require special treatment. the more serious cases involve nerve damage. Spina bifida occulta. symptoms of spina bifida occulta include: a gap in between vertebrae. no visible opening outside. no fluid filled sack outside the body. small birthmark or dimple on the back.

Comments are closed.