Spread Plate And Pour Plate Method Microbiology

Spread Plate And Pour Plate Method Microbiology Pinterest Plates Spread plate method is one of the widely used culture techniques in microbiology laboratories due to its ease and simplicity. this method is suitable for aerobic and facultative aerobic microorganisms. it is an easy, simple, and economical method; however, it requires the sample to be in liquid or suspension. Achieve this type of distribution are: spread, pour, thin layer, layered, and membrane filter (2). principles using the spread method a small volume of a bacterial suspension is distributed evenly over the surface of an agar plate using a smooth sterilized spreader (2). in the case of track plates, gravity is used to.
Solved 1 What Do You Think Is Most Important The Number Of Ethanol is used to sterilize the glass spreader. flame the glass spreader over a bunsen burner. spread the sample evenly over the surface of the agar using a cool alcohol flamed glass rod spreader, carefully rotating the petri dish underneath at an angle of 45 o at the same time. incubate the plate at 37°c for 24 48 hours. The pour plate method technique was established in the laboratory of robert koch and is still being used widely since his period. this method is suitable for facultative, microaerophilic, and anaerobic microorganisms. it is simple, less resource consuming, easy, and economical; however, it requires the sample to be in liquid or suspension. Using this method, a small volume (0.1 1.0 ml) of liquid containing an unknown number of bacteria is spread over the surface of an agar plate, creating a "spread plate." the spread plates are incubated for 24 36 hours. during that time, each individual viable bacterial cell multiplies to form a readily visible colony. Pour plate method: procedure, uses, (dis) advantages. written by acharya tankeshwar in general microbiology. pour plate method is usually the method of choice for counting the number of colony forming bacteria present in a liquid specimen. because the sample is mixed with the molten agar medium, a larger volume can be used than the spread plate.
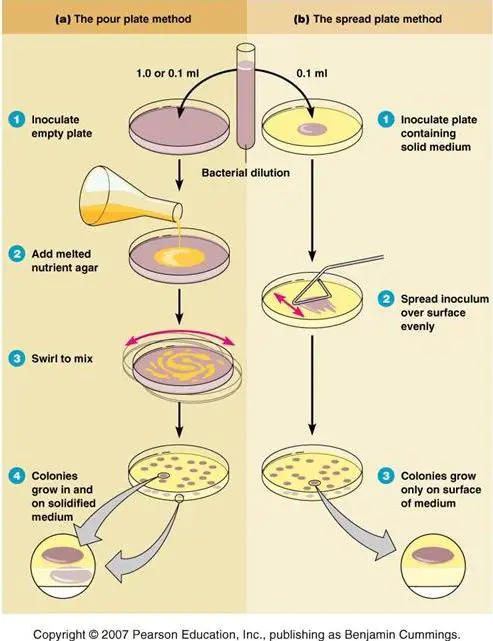
Pour Plate Method Procedure Uses Dis Advantages вђ Microbe Online Using this method, a small volume (0.1 1.0 ml) of liquid containing an unknown number of bacteria is spread over the surface of an agar plate, creating a "spread plate." the spread plates are incubated for 24 36 hours. during that time, each individual viable bacterial cell multiplies to form a readily visible colony. Pour plate method: procedure, uses, (dis) advantages. written by acharya tankeshwar in general microbiology. pour plate method is usually the method of choice for counting the number of colony forming bacteria present in a liquid specimen. because the sample is mixed with the molten agar medium, a larger volume can be used than the spread plate. The dilution of microbes is very important to get to microbes diluted enough to count on a spread plate (described later). figure: streak plate: four streak plates. successful streaks lead to individual colonies of microbes. in microbiology, streaking is a technique used to isolate a pure strain from a single species of microorganism, often. Procedure of spread plate technique. make a dilution series from a sample. pipette out 0.1 ml from the appropriate desired dilution series onto the center of the surface of an agar plate. dip the l shaped glass spreader into alcohol. flame the glass spreader (hockey stick) over a bunsen burner. spread the sample evenly over the surface of agar.

Comments are closed.