Step 2 Measure Important Intervals

Step 2 Measure Important Intervals Pr Interval Medical Mnemonics Step 2: measure important intervals. the measurement of important electrocardiographic intervals usually includes the pr interval, the qrs interval and the qt interval. at a standard paper speed of 25 mm second, the width of each small square (1mm) represents 0.04 seconds. one large square (5mm) represents 0.2 seconds. A systematic approach to ecg interpretation: an efficient and safe method. the ecg must always be interpreted systematically. failure to perform a systematic interpretation of the ecg may be detrimental. the interpretation algorithm presented below is easy to follow and it can be carried out by anyone. the reader will gradually notice that ecg.

Freemusiclessons4u Intervals Ecg tutorial: basic principles of ecg analysis uptodate. The next step is to measure the pr interval. to do this, count the number of small boxes in between the beginning of the p wave and the peak of the qrs complex. then, multiply that number by 0.04 seconds. normal interval length should be between 0.12 – 0.20 seconds. Step 3a: calculate the electrical axis. the mean qrs axis refers to the average orientation of the heart's electrical activity. in most cases, an approximation of the axis will be sufficient for the ecg interpretation. there are many different approaches to axis determination, but this discussion will be limited to a simple technique which uses. Plainly stated, this measurement is from the beginning of the p wave to the beginning of the qrs complex. the normal range for pr interval is: 0.12 – 0.20 seconds (3 to 5 small boxes) it is important that you measure each pr interval on the rhythm strip. some tracings do not have the same pri measurement from one cardiac complex to the next.

Types Of Interval In Mathematics Maths For Kids Step 3a: calculate the electrical axis. the mean qrs axis refers to the average orientation of the heart's electrical activity. in most cases, an approximation of the axis will be sufficient for the ecg interpretation. there are many different approaches to axis determination, but this discussion will be limited to a simple technique which uses. Plainly stated, this measurement is from the beginning of the p wave to the beginning of the qrs complex. the normal range for pr interval is: 0.12 – 0.20 seconds (3 to 5 small boxes) it is important that you measure each pr interval on the rhythm strip. some tracings do not have the same pri measurement from one cardiac complex to the next. Step 3b: calculate the electrical axis. the mean qrs axis is oriented towards the lead with the greatest net qrs deflection. to calculate the net qrs deflection, add up the number of small squares that correspond to the height of the r wave (positive deflection), and subtract the number of small squares that correspond to the height of the q. Amboss is a medical knowledge platform offering ecg learning resources for doctors and students.
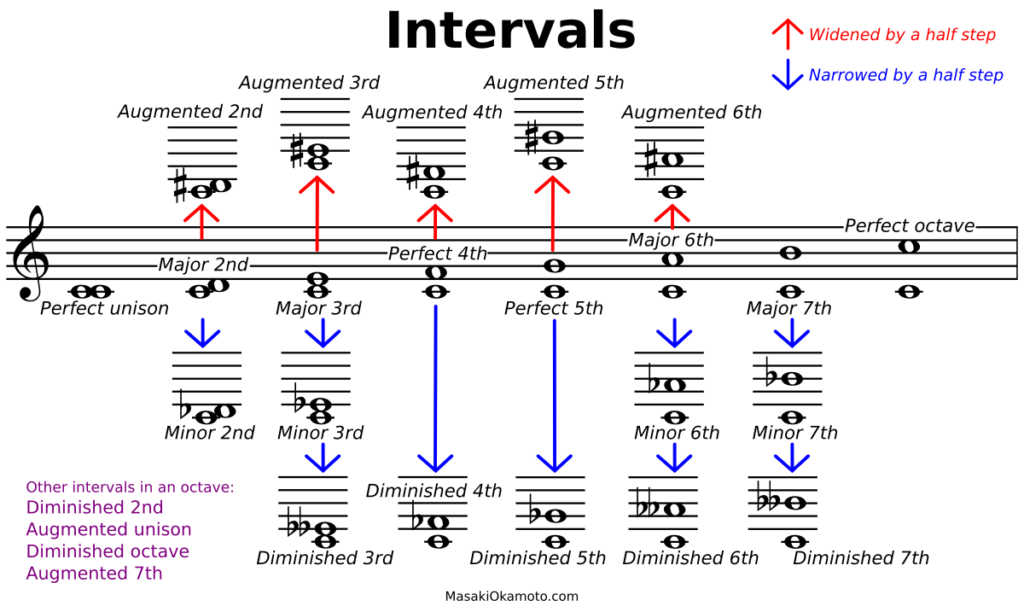
Music Theory Basics Insanely Easy Guide All Musicians Should Learn Step 3b: calculate the electrical axis. the mean qrs axis is oriented towards the lead with the greatest net qrs deflection. to calculate the net qrs deflection, add up the number of small squares that correspond to the height of the r wave (positive deflection), and subtract the number of small squares that correspond to the height of the q. Amboss is a medical knowledge platform offering ecg learning resources for doctors and students.

Musical Intervals 2 Major And Perfect Teaching Resources

Comments are closed.